 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Research on Damage Identification of Cable-Stayed Bridges Based on Modal Fingerprint Data Fusion
1 School of Transportation and Geomatics Engineering, Shenyang Jianzhu University, Shenyang, 110168, China
2 College of Civil Engineering, Shenyang Jianzhu University, Shenyang, 110168, China
* Corresponding Author: Xiaowei Zhang. Email:
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring 2024, 18(4), 485-503. https://doi.org/10.32604/sdhm.2024.049698
Received 15 January 2024; Accepted 15 March 2024; Issue published 05 June 2024
Abstract
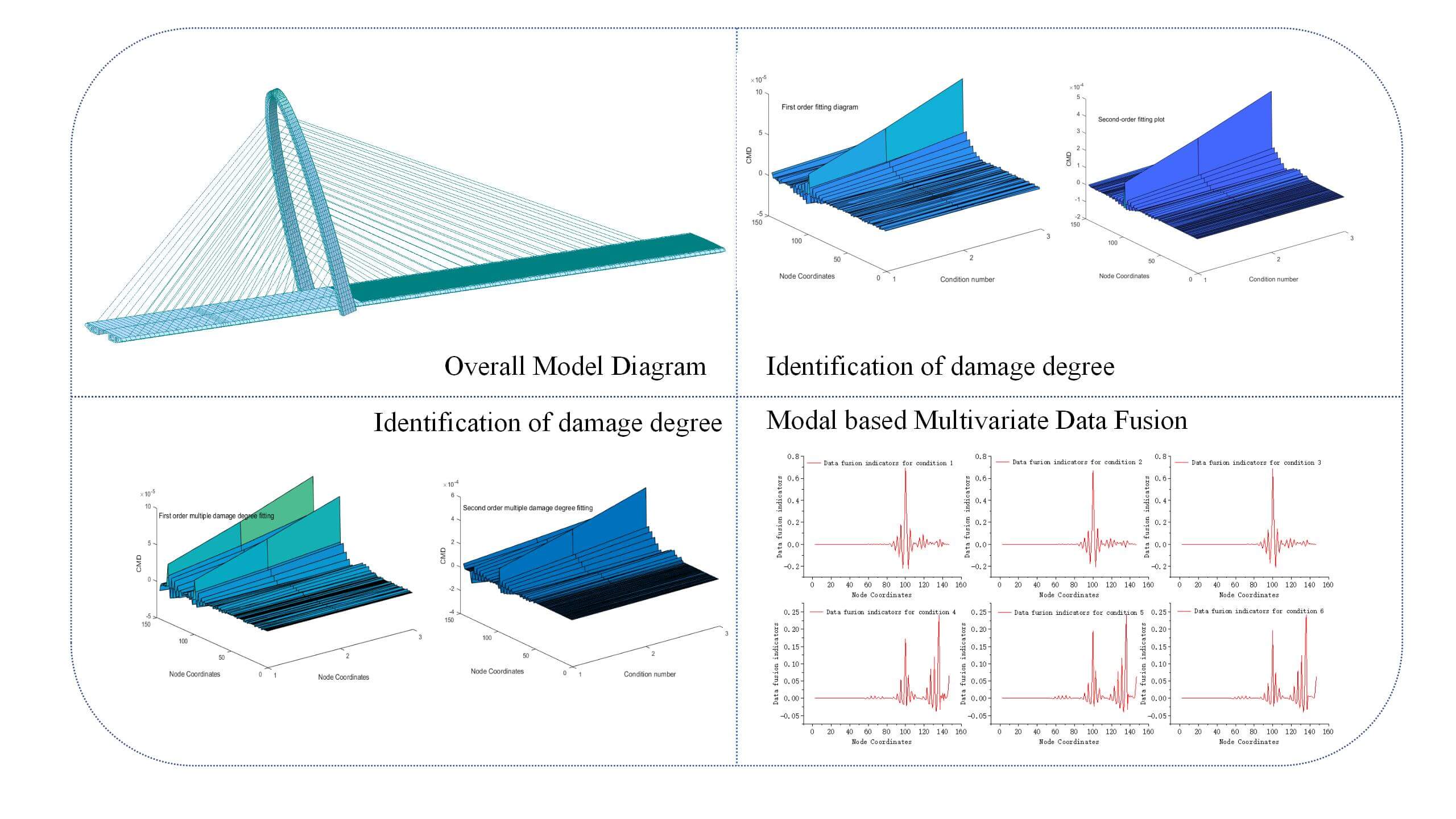
This study addresses the issue of inaccurate single damage fingerprint recognition during the process of bridge damage identification. To improve accuracy, the proposed approach involves fusing displacement mode difference and curvature mode difference data for single damage identification, and curvature mode difference and displacement mode wavelet coefficient difference data for two damage identification. The methodology begins by establishing a finite element model of the cable-stayed bridge and obtaining the original damage fingerprints, displacement modes, curvature modes, and wavelet coefficient differences of displacement modes through modal analysis. A fusion program based on the D-S evidence theory criterion is then developed using Matlab to calculate the displacement mode difference (DMD), curvature mode difference (CMD), and wavelet coefficient difference of displacement mode (WCDM) for data fusion. The recognition effect of a single fingerprint is analyzed using modal data for both single and two damage conditions. Additionally, the fusion of multiple fingerprint initial data is performed, and the recognition effect of the data fusion method is quantitatively analyzed through sub peak to peak comparison. It is observed that when the fusion index is used as the recognition index, the sub peak to peak ratio is smaller compared to using the curvature mode as the damage index. Consequently, the reduction in single damage is more significant, ranging from 12% to 48%, while the reduction in multi damage is approximately 2%. This method demonstrates the ability to accurately identify the location of damage, yielding satisfactory recognition results and showing promising feasibility.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools