 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on Optimized Feature Mode Decomposition and Improved Deep Belief Network
School of Mechanical Engineering, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang, 050018, China
* Corresponding Author: Guangfei Jia. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sensing Data Based Structural Health Monitoring in Engineering)
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring 2024, 18(4), 445-463. https://doi.org/10.32604/sdhm.2024.049298
Received 02 January 2024; Accepted 01 March 2024; Issue published 05 June 2024
Abstract
The vibration signals of rolling bearings exhibit nonlinear and non-stationary characteristics under the influence of noise. In intelligent fault diagnosis, unprocessed signals will lead to weak fault characteristics and low diagnostic accuracy. To solve the above problem, a fault diagnosis method based on parameter optimization feature mode decomposition and improved deep belief networks is proposed. The feature mode decomposition is used to decompose the vibration signals. The parameter adaptation of feature mode decomposition is implemented by improved whale optimization algorithm including Levy flight strategy and adaptive weight. The selection of activation function and parameters is crucial in the application of deep belief networks. The improved deep belief networks are proposed based on Hard swish activation function and the improved whale optimization algorithm. The optimized diagnosis model is applied to weak fault diagnosis of bearings. The experimental results show that this method has faster convergence speed and anti-noise performance under the interference of −5 db noise, and effectively improves the adaptive feature extraction ability of the model and the accuracy of fault diagnosis. Under different conditions, the average accuracy reached 97.8% and 97.6%, with good generalization performance.Graphic Abstract
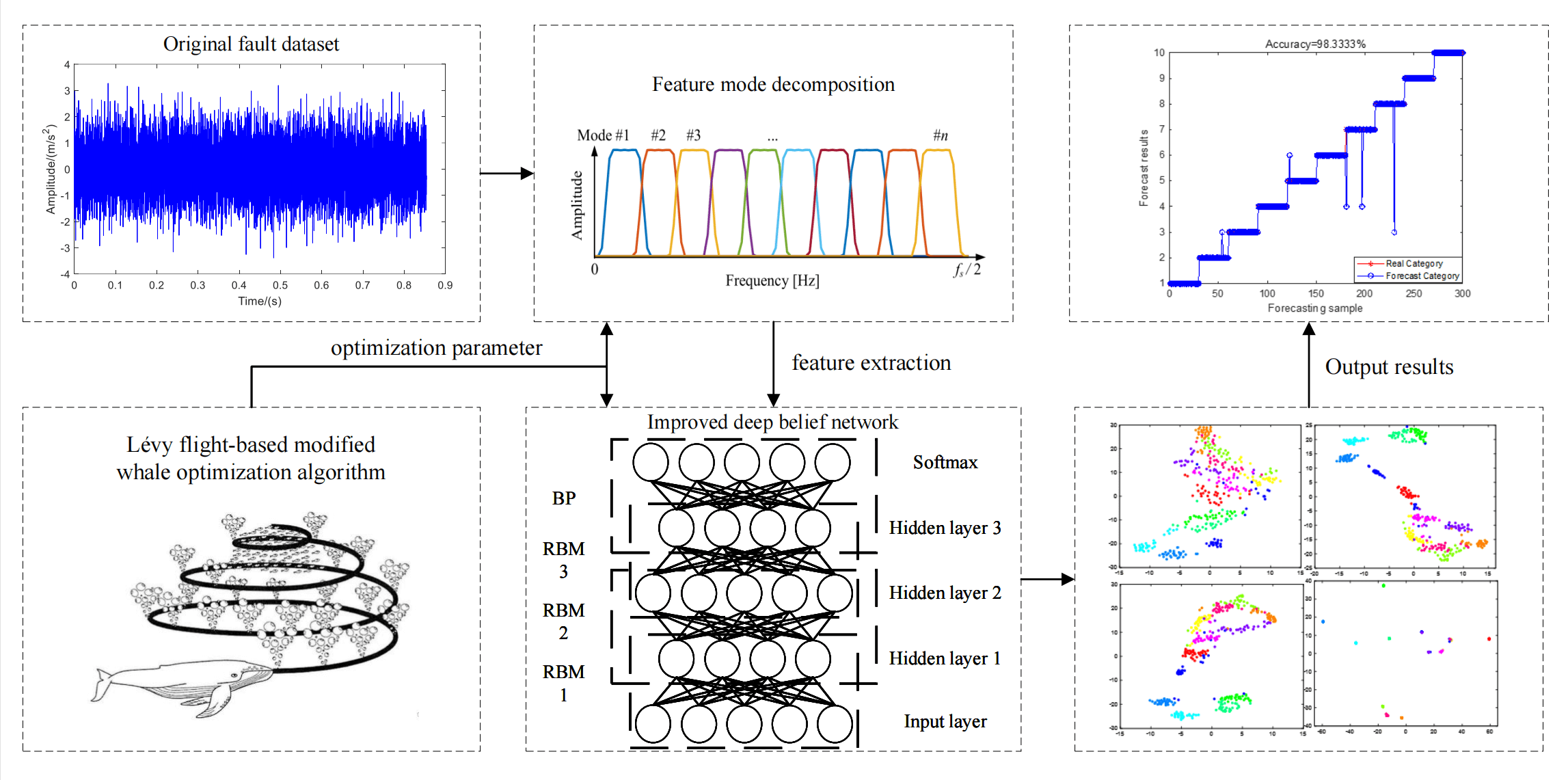
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools