 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Investigation of FRP and SFRC Technologies for Efficient Tunnel Reinforcement Using the Cohesive Zone Model
1 China Communications Construction Investment Development Co., Ltd., Fuzhou, 350000, China
2 Rail Transit Branch of China Communications Construction Co., Ltd., Beijing, 101317, China
3 School of Civil Engineering, Fujian University of Technology, Fuzhou, 350118, China
* Corresponding Author: Wei Zhang. Email:
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring 2024, 18(2), 161-179. https://doi.org/10.32604/sdhm.2023.044580
Received 03 August 2023; Accepted 24 October 2023; Issue published 22 March 2024
Abstract
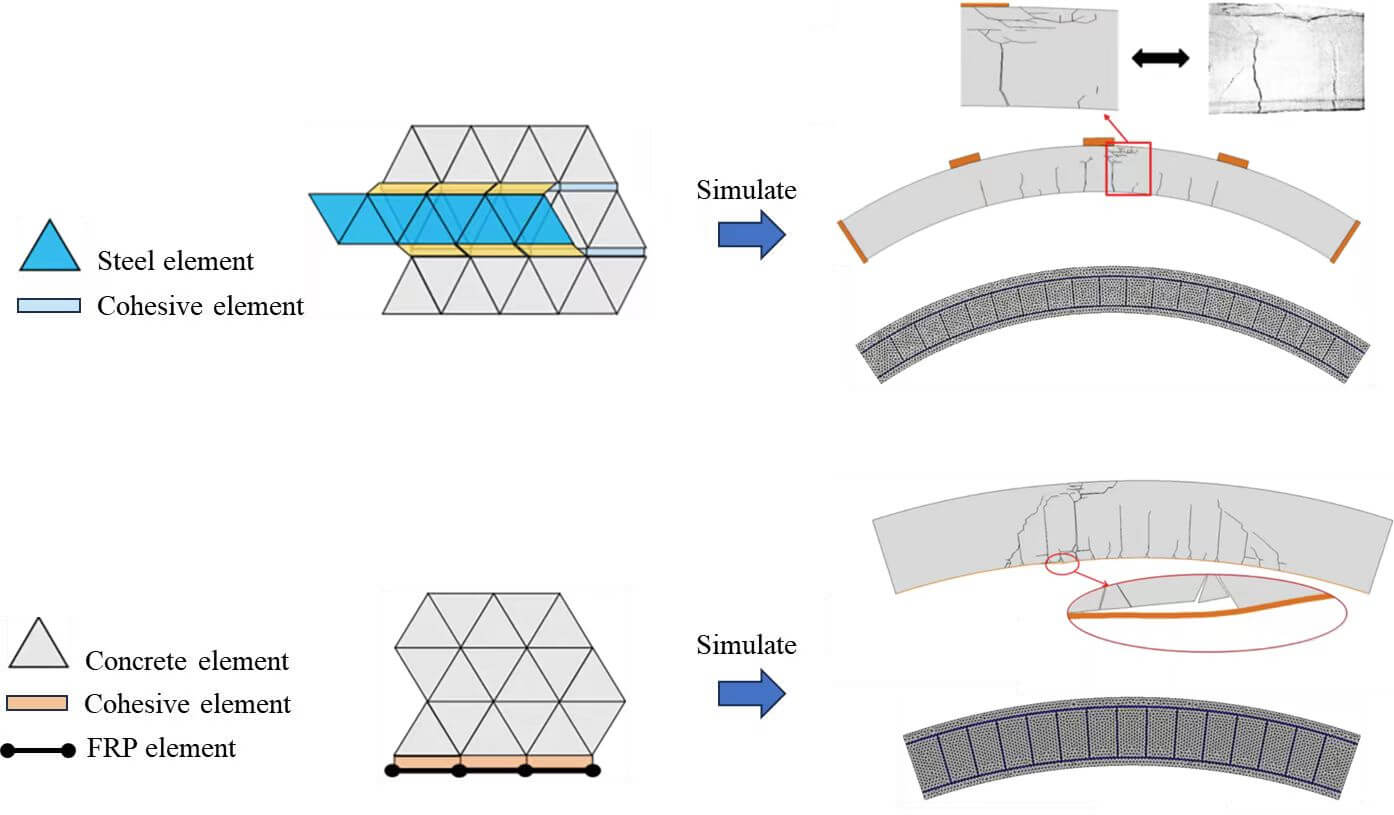
Amid urbanization and the continuous expansion of transportation networks, the necessity for tunnel construction and maintenance has become paramount. Addressing this need requires the investigation of efficient, economical, and robust tunnel reinforcement techniques. This paper explores fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) and steel fiber reinforced concrete (SFRC) technologies, which have emerged as viable solutions for enhancing tunnel structures. FRP is celebrated for its lightweight and high-strength attributes, effectively augmenting load-bearing capacity and seismic resistance, while SFRC’s notable crack resistance and longevity potentially enhance the performance of tunnel segments. Nonetheless, current research predominantly focuses on experimental analysis, lacking comprehensive theoretical models. To bridge this gap, the cohesive zone model (CZM), which utilizes cohesive elements to characterize the potential fracture surfaces of concrete/SFRC, the rebar-concrete interface, and the FRP-concrete interface, was employed. A modeling approach was subsequently proposed to construct a tunnel segment model reinforced with either SFRC or FRP. Moreover, the corresponding mixed-mode constitutive models, considering interfacial friction, were integrated into the proposed model. Experimental validation and numerical simulations corroborated the accuracy of the proposed model. Additionally, this study examined the reinforcement design of tunnel segments. Through a numerical evaluation, the effectiveness of innovative reinforcement schemes, such as substituting concrete with SFRC and externally bonding FRP sheets, was assessed utilizing a case study from the Fuzhou Metro Shield Tunnel Construction Project.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools