 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chenhui Peng1, Jinbiao Tang1, Derun Zhang1,2,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2026.075421
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Big Data and Machine Learning for Health Monitoring and Maintenance of Transportation Infrastructure)
Abstract Rutting is a serious issue in asphalt pavement, which may reduce the pavement driving quality and safety. Accurately predicting rutting depth is a crucial task in pavement engineering, providing crucial decision support for asphalt pavement design and maintenance. However, accurate prediction of pavement rutting still remains a significant challenge for pavement engineers. This research first selects the loading number, temperature, dynamic modulus, asphalt layer thickness, and base layer type and thickness as candidate features. Data preprocessing, including outlier handling and feature selection, is then performed. Finally, based on the stacking algorithm, a multi-model fusion approach… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Niken Chatarina*, Suyadi Suyadi, Noorhidana Vera Agustriana, Chairani Zilia, Mariyanto Mariyanto
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2026.067525
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sustainable and Durable Construction Materials)
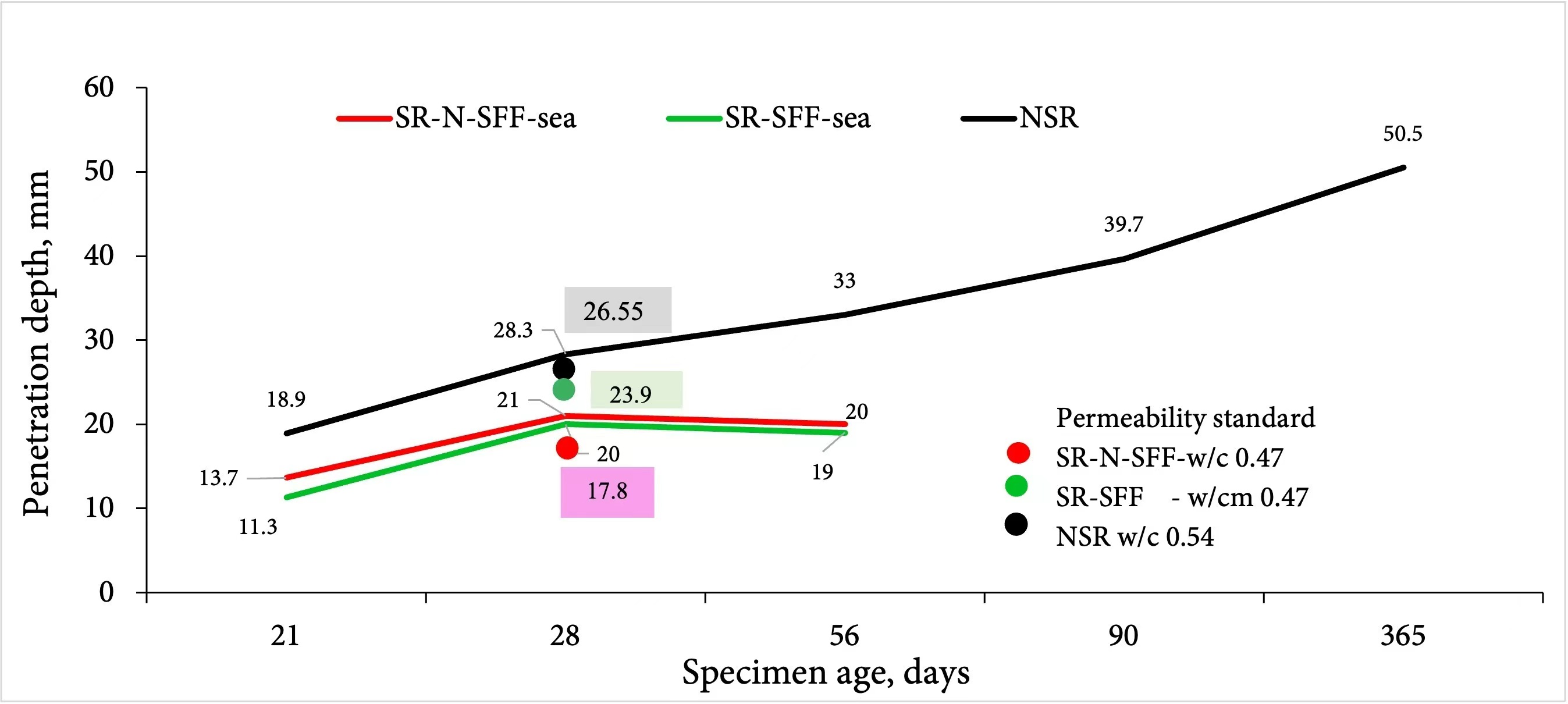
Abstract In strong aggressive areas, Indonesian standards specify a maximum penetration of 30 mm. Concrete utilizes sulfate-resistant Portland Pozzolan Cement (PPC) for a target strength of 30 MPa, with and without silica fume and plastic fiber (SR-SFF-sea and SR-N-SFF). Some samples of SR-N-SFF are immersed in the sea (SR-N-SFF-sea), while others are protected (SR-N-SFF-protected). Additionally, concrete using non-sulfate-resistant cement (NSR-sea) with a strength of 20.75 MPa was also evaluated. All samples were subjected to penetration depth testing according to the DIN EN 12390-8 standard, demonstrating that they met the penetration requirements for intense aggression. The study… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Supriyanto1,*, Chatarina Niken1, Suripto Dwi Yuwono2, Mohd Isneini1, Suyadi Kartorono1
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2026.073449
Abstract This study investigates the impact of Type D additive, Plastiment 83 AM, on the compressive strength and microstructure of Portland Composite Cement (PCC) concrete with a target compressive strength of 18.7 MPa, utilizing a mixing, stirring, and treatment model that simulates batching plant conditions. The study investigated additive dosages of 0%, 0.15%, 0.25%, 0.35%, and 0.40%, with stirring durations of 15 min, 2, 4, 6, and 6.5 h. Compressive strength tests were conducted at the ages of 7, 14, 28, 56, and 90 days on cylindrical specimens, and at 24 h for setting time tests.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
You-Yong Tang1, Yong-Hao Liu2, Dong-Yang Wei1, Xiao-Wei Feng2, Jose Campos e Matos3, David Hui4, Hua-Ping Wang1,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2026.075676
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Smart Sensors and Smart CFRP Components for Structural Health Monitoring of Aerospace, Energy and Transportation Structures)
Abstract Carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) laminates are widely used in aerospace, new energy, and transportation engineering due to their high specific strength and stiffness. However, interlaminar delamination damage can lead to sudden structural failure, and the occurrence and prediction of such hidden defects are difficult to identify and evaluate using conventional inspection methods. To address this, smart CFRP laminates integrated with fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors offer a new approach for real-time structural health monitoring (SHM). Nevertheless, the influence mechanisms of the two integration methods—embedded and surface-bonded FBG sensors—on the static strength and impact resistance… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chao Guo1, Chao Deng2, Xing Bai3, Ziyuan Fan4, Jintao Li2, Yuan Ren2,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.075363
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Applications for Bridge Structures)
Abstract Hangers play a crucial role in transferring loads in suspension bridges, yet their condition often deteriorates faster than expected due to corrosion and fatigue effects. Premature hanger failure poses serious risks to bridge safety and results in significant economic loss due to frequent replacement and traffic interruption. To address these challenges, this study proposes an integrated framework to evaluate the life-cycle safety and operational cost of bridge hangers. Traffic data obtained from Weigh-in-Motion (WIM) systems are used to simulate dynamic hanger responses. A wire-to-hanger deterioration model is then employed to capture the time-dependent interaction between… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zhihua Xiong, Xiaoling Liu*, Yinfeng Wang
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.074619
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Applications for Bridge Structures)
Abstract Autonomous truck platooning, as a novel transportation mode, has attracted significant attention due to its potential to improve transportation efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and lower operational costs. However, this emerging mode poses new challenges to the dynamic performance of long-span bridges. This study aims to investigate the impact of autonomous truck platoons on the dynamic performance of continuous beam bridges. Using finite element software to construct accurate vehicle-bridge interaction models, we simulated the dynamic response between vehicle platoons and bridge structures. The study systematically evaluated the effects of four key factors—vehicle speed, number of formations,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jun Wang1, Qian Fang1,*, Weiguo He2, Yanxin Chen1, Qizhao You1
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.076570
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Durability Assessment of Engineering Structures and Advanced Construction Technologies)
Abstract This study presents a comprehensive investigation into the deformation mechanisms of existing metro stations subjected to the simultaneous construction of adjacent foundation pits and underground tunnels. A refined three-dimensional numerical modeling framework is developed to simulate the entire construction process, capturing the complex interactions between excavation activities and station structures. The modeling encompasses deep excavation, side-crossing, and overcrossing passage construction, and the staged installation of support systems. Six construction schemes, varying in excavation sequence, interlayer thickness (clear distance), and passageway layout, are systematically analyzed. Field monitoring data are incorporated to validate the numerical models, enhancing… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Radha Krishna Mallik1, Gokarna Bahadur Motra1, Krishna Shrestha2,3,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.075535
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Vibration Control, Dampers and Structural Health Monitoring)
Abstract The study proposes a low-cost friction damper designed to enhance the seismic performance of buildings, particularly in regions where existing structures lack adequate seismic resistance and conventional friction dampers are cost-prohibitive or require specialized fabrication. Friction dampers are displacement-controlled devices that dissipate energy through constant slip-force action and relative displacement between attachment points, typically ensuring elastic structural behavior under Design Basis Earthquake (DBE) demands and controlled yielding under Maximum Considered Earthquake (MCE) conditions. To address limitations in current practice, the proposed device integrates the damping mechanism of vehicle leaf-spring suspension systems with rotational plate friction… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yi Wang1,2,*, Yansong Li2, Bingxu Cai2, Yukai Zhu1, Hairong Wu1
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072553
Abstract Prefabricated buildings have developed rapidly due to their advantages in energy efficiency, environmental protection, and high construction efficiency, which have greatly promoted the advancements of connection technology and the mechanical properties of prefabricated hollow panels. This study proposes a new optimization scheme for prefabricated wall structures using transversely arranged prefabricated hollow plates and develops a new joint connection. First, the constitutive relations are experimentally validated to establish an accurate finite element analysis model; Then the equal-size specimens are compared with the control specimens without node connections; Finally, the effects of axial compression ratio, aspect ratio, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Tao Yuan1, Qin Tang2, Zhiwen Zhu2,*, Jin Jiang2, Lin Zhang1, Gangqiao Wang1
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072805
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Resilient and Sustainable Infrastructure: Monitoring, Safety, and Durability)
Abstract Using field monitoring data, this study directly compares the stress responses of fatigue-prone orthotropic steel deck (OSD) details with an epoxy asphalt concrete (EAC) overlay during in-service winter and summer seasons. This study was conducted on the E’dong Yangtze River Bridge in China, a cable-stayed bridge featuring a main span of 936 m and an EAC-paved deck pavement. The findings reveal that across all OSD details, stress levels and loading cycles are generally higher in summer than in winter. The most pronounced increase occurs at the rib-to-deck (RD) detail, particularly on the deck plate side.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Peijun Xie1,2, Shoulong Zhang1,2,3,#,*, Pengfei Huang1,2, Jintuan Zhang4,#,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072958
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Durability Assessment of Engineering Structures and Advanced Construction Technologies)
Abstract To ensure the safety of the integral hoisting of precast pier boxes for sea-crossing bridges, this study focused on the sidewall height of the pier box and the width of the hoisting sling as core variables, established a finite element model using ABAQUS, and conducted a safety analysis of the hoisting process. The results showed that optimal structural safety and cost-effectiveness were achieved by first casting the concrete base plate of the pier box, then constructing the sidewalls to a height of 500 mm, and subsequently using REE-100T eye & eye round slings for hoisting. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yiyan Chen1,2, Yihu Chen1,2,*, Min Zhang3, Xiaogang Ye4, Jindan Zhang1,2
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.073581
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Durability Assessment of Engineering Structures and Advanced Construction Technologies)
Abstract The large thickness of the common composite precast base slab leads to difficulties in construction through reinforcement installation and pipeline laying. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a lightweight ribbed base slab, reducing the base slab thickness to 30 mm compared to the ordinary precast base slab, adding concrete ribs to improve the mechanical properties of the base slab, and analyzing its damage pattern, stiffness change, and deflection deformation through static loading experiments. Based on the experimental conditions, the effect of concrete rib height, rib width, and top chord reinforcement diameter on the short-term… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Giada Faraco*, Andrea Vincenzo De Nunzio, Nicola Ivan Giannoccaro*, Arcangelo Messina
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.075327
Abstract Damage detection and localization analysis have gained increasing importance over the years, due to the growing number of catastrophic events and the associated risks that small, undetected cracks in structures may evolve into severe failures if not identified in time. In this context, vibration-based methods have been extensively investigated for structural damage detection. Among them, one of the most widely used approaches since its introduction is the curvature method. It has been successfully employed in numerous studies, consistently providing reliable results. However, the use of second-order or higher-order derivatives can be challenging when dealing with… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shuigen Hu1,2, Hao Wang3, Qingyang Wei4,*, Maosen Cao2,4, Drahomír Novák5
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.073665
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining Applications in Fault Diagnosis and Damage Identification of Infrastructure)
Abstract As vital hydraulic infrastructures, concrete dams demand uncompromising safety assurance. Seismic effect commonly serves as a potential factor contributing to the damage of concrete dams, making seismic performance analysis crucial for structural integrity. Numerical simulation based on damage mechanics is usually considered as the approach for investigating the seismic damage behavior of concrete dams. To address the limitations of existing studies and extract the key dynamic characteristics of concrete arch dams, a concrete elastoplastic damage mechanics model is adopted, a seismic load input technique involving the viscoelastic boundary along with equivalent nodal forces is generated,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Trinh Thi Nhu Quynh1, Hoa-Cuc. Nguyen2, Bich-Ngoc. Mach2, Thanh Q. Nguyen3,4,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.070202
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Applications for Bridge Structures)
Abstract This study introduces a method for processing various types of random real-world signals from bridges in both experimental models and real-world scenarios using a wireless sensor system. By analyzing and processing signals collected during actual traffic on bridges, the study identifies and provides parameters that meet current quality inspection requirements to ensure the safety of bridge users. The parameters investigated in this study include deformation, natural frequency, amplitude, impact factor, and damping coefficient. Research has determined and highlighted key parameters to assess the quality of bridge spans to meet quality inspection standards. Using actual traffic More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiansong Xie1,*, Xiaoqian Qian2
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.074148
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sustainable and Resilient Civil Infrastructure with Intelligence and Digital Transformation)
Abstract Correlation function of acceleration responses-based damage identification methods has been developed and employed, while they still face the difficulty in identifying local or minor structural damages. To deal with this issue, a robust structural damage identification method is developed, integrating a modified holistic swarm optimization (MHSO) algorithm with a hybrid objective function. The MHSO is developed by combining Hammersley sequence-based population initialization, chaotic search around the worst solution, and Hooke-Jeeves pattern search around the best solution, thereby improving both global exploration and local exploitation capabilities. A hybrid objective function is constructed by merging acceleration correlation… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xianghui Li1,2, Xin Fu3, Libo Pan2, Fancong Zeng1,2,*, Zhijiang Zuo1,2
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.073124
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Non-contact Sensing in Infrastructure Health Monitoring)
Abstract The present study proposes an autonomous visual inspection system based on Wall-Climbing Robot (WCR), with a view to addressing the shortcomings of traditional building crack detection methods, namely their low measurement accuracy, high manual dependence and insufficient environmental adaptability. The system has been developed to construct a crack recognition model with robust illumination adaptation by fusing the improved YOLOv5s target detection algorithm with the Canny edge enhancement algorithm. The system has been realized as a lightweight deployment on an embedded device (MaixCAM). The robot platform employs a design scheme integrating a dual-chamber negative pressure adsorption… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Qi Feng1,2, Dan Wang3,*, Weijie Hu1, Wenhao Zhao2
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072968
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Innovative and Sustainable Materials for Reinforced Concrete Structures)
Abstract Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC) represent an advanced class of fiber-reinforced cement-based materials developed over the past three decades, characterized by remarkable tensile strain-hardening and multiple-cracking behavior. By incorporating hybrid fibers, Hybrid Fiber engineered cementitious composites (HFECC) can be tailored to meet specific engineering demands in terms of strength, deformation, dynamic mechanical performance, and cost-effectiveness. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the critical fiber volume theory, experimental investigations into quasi-static and dynamic mechanical properties, and the structural performance of HFECC. Furthermore, current research gaps and future directions for the development and application of HFECC are More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lishuai Zhu1, Guangcai Zhang1,*, Qun Xie1,*, Zhen Peng2, Li Ai3, Ruijun Liang1, Taochun Yang1
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.074620
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Sustainable and Resilient Civil Infrastructure with Intelligence and Digital Transformation)
Abstract Structural displacement monitoring faces significant challenges under complex environmental conditions due to the loss or degradation of target features, making it difficult for traditional methods to ensure high accuracy and robustness. Therefore, this study proposes a structural displacement identification and quantification method that integrates YOLOv8n with an improved edge-orientation gradient-based template matching algorithm. By combining deep learning techniques with traditional template matching methods, the accuracy and robustness of monitoring are enhanced under adverse conditions such as noise and extremely low illumination. Specifically, in the edge-orientation gradient matching stage, the Canny-Devernay sub-pixel edge detection technique and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Wael A. Altabey*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.073949
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Sensing, Smart Materials and Intelligent Algorithms for Structural Health Monitoring in Various Domains)
Abstract The study of long-term pavement performance is a fundamental topic in the field of highway engineering. Through comprehensive and in-depth research on the pavement system, the previous scattered, one-sided, superficial, and perceptual knowledge and experience are summarized and sublimated into a systematic and complete engineering theory, thereby providing powerful guidance and assistance for the practice of pavement design, construction, maintenance, operation, and management. In this research, the mentoring system deployment technology for automatic monitoring is carried out for long-term pavement performance. By burying a variety of sensors in different parts of the road surface, base,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Qunjie Huang1, Yu Huang2, Yangqing Liu2, Qiaoming Guo3, Zhiyun Liu4,*, Haibin Ding4, Lihua Li5
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.073362
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Health Monitoring of Transportation Infrastructure Structure)
Abstract Based on the theory of wave dynamics, this study systematically derives the steady-state analytical solution for the scattering of plane SV-waves by composite lined tunnels in an infinite space using the wave function expansion method. On this basis, a theoretical calculation model for circular composite linings under blast loading is established. Based on the steady-state analytical solution, the δ(x)-function and the Heaviside step function are introduced to construct the Duhamel integral, transforming the transient wave problem into an integral form. By further incorporating the Fourier integral transform, an analytical solution for the transient response around a… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yu Wang1, Yao Song2, Hongyong Yang1, Yu Zhu2, Jian Xu2, Dehao Ding2, Huahuai Sun3,*, Shunyao Cai4
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.073132
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Intelligent Operation and Maintenance Applications for Bridge Structures)
Abstract Long-span suspension bridges are inherently vulnerable to earthquakes due to their low stiffness and damping. A novel design, the main-cable-looped (MCL) suspension bridge, features a looped main cable that alters the structure’s load transfer mechanism. The seismic response of this novel bridge type is not well understood, creating an urgent need for investigation to ensure its safety and performance. The global finite element model of this bridge was established by considering the interdependent behavior of the structure and the underlying soil. Based on the design seismic response spectrum, ground motion accelerations were selected, and the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yu Shen1, Yi Liu1, Hanchen Zhang2, Liuyang Li3,4, Kaiming Pan5, Qinghe Fang2,*
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072871
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Health Monitoring of Transportation Infrastructure Structure)
Abstract This study presents a systematic numerical analysis of wind loads on offshore photovoltaic (PV) panels. A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model, incorporating a free-surface wave boundary condition, is developed and validated against experimental data. Parametric investigations quantify the effects of wind speed, panel tilt angle, clearance, and wave characteristics on the aerodynamic coefficients (drag, lift, and moment). Results indicate that all force coefficients increase with wind speed, with the lift coefficient being most sensitive to wave action. While a larger tilt angle intensifies airflow disturbance and amplifies the coefficients, this effect is more pronounced over More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yajuan Lu*, Yongtao Hu, Jie Li, Jinping Zhang, Jingjing Si
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.071110
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Artificial Intelligence and Data Mining Applications in Fault Diagnosis and Damage Identification of Infrastructure)
Abstract To address challenges in wind turbine blade defect detection models, primarily due to insufficient feature extraction capabilities and the difficulty of deploying models on drone-type edge devices, this study proposes a wind turbine blade defect detection model, WtCS-YOLO11, that incorporates multiscale feature extraction and an attention mechanism. Firstly, the cross-stage partial with two kernels and a wavelet convolution module (C3k2_WTConv) is proposed by introducing wavelet convolution into the module. The cross-stage partial with two kernels (C3k2) module in the necking network is replaced with the C3k2_WTConv module to increase the model’s receptive field, enable multiscale… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yaguan Wang1, Linlin Kou2, Yang Gao3,*, Qiang Sun1, Yong Qin3, Genwang Peng3
Structural Durability & Health Monitoring, DOI:10.32604/sdhm.2025.072538
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: AI-Enhanced Low-Altitude Technology Applications in Structural Integrity Evaluation and Safety Management of Transportation Infrastructure Systems)
Abstract The fasteners employed in the railway tracks are susceptible to defects arising from their intricate composition. Foreign objects are frequently observed on the track bed in an open environment. These two types of defects pose potential threats to high-speed trains, thus necessitating timely and accurate track inspection. The majority of extant automatic inspection methods are predicated on the utilization of single visible light data, and the efficacy of the algorithmic processes is influenced by complex environments. Furthermore, due to the single information dimension, the detection accuracy of defects in similar, occluded, and small object categories… More >