 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Brassinosteroid Biosynthetic Gene CmDWF4 Regulates Bud Outgrowth in Chrysanthemum morifolium
State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Germplasm Enhancement and Utilization, Key Laboratory of Landscaping, Key Laboratory of Flower Biology and Germplasm Innovation (South), Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Key Laboratory of Biology of Ornamental Plants in East China, National Forestry and Grassland Administration, College of Horticulture, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, 210095, China
* Corresponding Author: Fadi Chen. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Molecular Genetics and Physiology towards a Better Understanding of Agricultural Crop Plants)
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany 2023, 92(6), 1681-1694. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2023.027870
Received 18 November 2022; Accepted 20 February 2023; Issue published 11 April 2023
Abstract
Brassinosteroids (BRs), a class of steroid phytohormones, play a critical role in plant growth and development. The DWF4 gene encodes a cytochrome P450 enzyme (CYP90B1), which is considered a rate-limiting enzyme in BR biosynthesis. Here, we identified a homologous gene of DWF4 in chrysanthemum, CmDWF4. This gene was predicted to encode 491 amino acid residues with a molecular weight of 56.2 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) of 9.10. Overexpression of CmDWF4 in chrysanthemum was found to significantly increase growth rate, number, and length of lateral buds. Transcriptome analysis showed that multiple xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase (XTH) family encoding genes associated with cell wall modification were up-regulated in CmDWF4-overexpressing lines. qRT-PCR assay confirmed the up-regulation of CmXTH6, CmXTH23, and CmXTH28 in CmDWF4-overexpression line. Overall, this work establishes a mechanism by which BR biosynthetic gene CmDWF4 promotes lateral bud outgrowth in chrysanthemum, possibly through regulating cell elongation and expansion.Keywords
Shoot branching is a major determinant of plant morphogenesis and a key trait that determines the yield potential of agricultural, horticultural, and forestry crops [1]. Optimizing shoot architecture significantly improves the ornamental value of cut flowers, especially that of chrysanthemums [2]. Shoot branching can be divided into two important stages, namely the formation of the axillary meristem (AM) and the outgrowth of axillary buds. The formation of AM is regulated by internal factors [3], while the outgrowth of axillary buds is controlled by both internal and external factors, including environment, phytohormones, developmental stage, and key genes [3–5].
Among a range of factors that regulate bud outgrowth, hormonal signaling plays a principal role. Auxin was the first phytohormone discovered to be involved in the regulation of shoot branching by maintaining apical dominance and inhibiting the growth of axillary buds [6,7]. In addition, strigolactone (SL) was found to inhibit bud outgrowth [8,9]. Cytokinin (CK) was reported to antagonize auxin and SL to promote bud outgrowth [10–12]. Auxin-CK-SL is a classic model to explain the control of bud outgrowth, which is summarized as ‘the second messenger model’ and/or ‘the auxin transport canalization-based model’ [13–15]. Apart from these three hormones, recent reports suggested that BR is also involved in the regulation of shoot branching development [16,17].
BRs, a class of steroid plant hormones, were originally characterized for their function in cell elongation [18]. They were discovered to have a crucial function in plant growth and development [19,20]. In rice, BR deficient mutants as well as BR signal transduction blocked mutants showed significantly reduced tiller numbers compared with the wild type [16,21]. Conversely, transgenic rice with enhanced BR signaling developed more tillers compared with the wild type [16]. In Arabidopsis, BES1, a positive regulator of the BR signaling pathway, regulates shoot branching through SLs-mediated signaling [22–24]. This leaves doubts about the branching regulation function of BRs in dicotyledonous plants. However, in the latest study, BRs have been found as the major signal integrating multiple pathways to control bud outgrowth in tomato [17]. In general, the function of BR in the regulation of bud outgrowth is still rarely reported. More evidence is needed to understand the role of BR in the regulation of shoot branching in dicots.
The biosynthesis of BR requires a variety of enzymes, which are encoded by the genes STE/DWF7, DWF5, DWF1/DIM, DWF4/CYP90B1, CPD/CYP90A1, DET2/DWF6, ROT3/CYP90C1, and CYP85A1/2/BR6OX1/2 [25,26]. In the process of steroid biosynthesis, these genes were obviously up-regulated [27]. The DWF4 gene encodes a cytochrome P450 enzyme (CYP90B1) that mediates multiple 22α-hydroxylation steps, which is a rate-limiting step in BR biosynthesis [28,29]. CYP90B1 forms a complex with uniconazole or brassinazole, further inhibits BR biosynthesis [30]. Overexpression of DWF4 leads to increased vegetative development, seed number, and seed yield in Arabidopsis and maize [31,32], as well as improved stress tolerance in Brassica napus and potato [33,34] and enhanced fruit quality in tomato [35]. However, the mechanism by which DWF4 regulates shoot branching remains unclear.
Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium) is a commercially important ornamental species with various branching types. However, remove lateral buds in chrysanthemum cultivation is labor and time consuming. Therefore, controlling chrysanthemum branch number is essential and has long been attracted the attention of breeders. Here, we identified a BR biosynthetic gene CmDWF4, and generated transgenic chrysanthemum, we found that CmDWF4 regulates shoot branching in chrysanthemum. Then, the regulatory mechanism of CmDWF4 was explored by transcriptome sequencing and quantitative analysis of transgenic lines. This study provides a further understanding of the function of the DWF4 gene and adds evidence for the role of BR in regulating shoot branching in chrysanthemum.
2.1 Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
The chrysanthemum cultivar ‘Jinba’ was used as the wild type (WT). Transgenic plants OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 were obtained via the Agrobacterium-mediated leaf disc method in the background of WT. Chrysanthemum was propagated asexually by cuttings. The cuttings were cultivated in 12 × 6 aperture disks with a mixture of vermiculite and nutritional soil (1:1, vol/vol). After rooting, the consistent plants were transferred to pots containing the same substrate. The plants were cultivated in a controlled environment (22°C ± 2°C, 16 h of light and 8 h of darkness, 200 μmol·m−2·s−1 light intensity, 70% relative humidity) [36]. When the plants were relocated to the pots for 30 days, water was supplied once a week using a nitrogen-rich nutrient solution.
2.2 Isolation of CmDWF4 and Sequence Analysis
The sequence information of the BR biosynthetic gene CmDWF4 was obtained from chrysanthemum transcriptome and TAIR website (https://www.arabidopsis.org/Blast/index.jsp). The full-length ORF sequence of CmDWF4 (1467 bp) was cloned with the primer pair CmDWF4-F and CmDWF4-R from the cDNA of ‘Jinba’. All primers used in this study (Table S1) were designed using the Primer Premier 5 software. Amino acid sequence alignment with functionally reported genes AtDWF4 [31], StDWF4 [34], GhDWF4 [35], and ZmDWF4 [32] was performed using DNAMAN software. The construction of a phylogenetic tree was carried out using the MEGA-X software [37].
2.3 Vector Construction and Chrysanthemum Transformation of pORE-R4-CmDWF4
Restriction enzyme sites BamH I and EcoR I were inserted into the cloned CmDWF4 gene by primers CmDWF4-BamH I-F and CmDWF4-EcoR I-R (Table S1). The PCR products and pORE-R4 vector were digested with 2.5 μL BamH I and 2.5 μL EcoR I (Takara, Japan). To join the target gene fragment with the target vector, 5.0 μL Solution I (Takara, Japan) was utilized. The generated vector pORE-R4-CmDWF4 was transferred into Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 using the electro-transformation approach. The Agrobacterium-mediated leaf disc transformation method [36] was used to infect pORE-R4-CmDWF4 into chrysanthemum ‘Jinba’. MS solid medium with 7 mg·L−1 kanamycin was used to screen for normal rooting lines. DNA was extracted from rooted seedlings for identification to obtain CmDWF4-overexpressing lines.
2.4 Treatment and Measurement of Lateral Buds
When the plants were 45 days old, the leaves and shoot apex above the third node were removed with a disinfection blade as a decapitation treatment. Nodes were numbered from top to bottom and the first fully expanded leaf was the first node. After decapitation for 6 days, the length of the first three lateral buds from the stem to the top of the bud was measured with a 20 cm measuring ruler as the total elongation. As we have found that the first three lateral buds elongated significantly after decapitation in chrysanthemum ‘Jinba’. Lateral bud length of intact plants was measured starting from the stem and was simulated from the 6th to the 39th node by HeatMap of TBtools software [38].
2.5 Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
After decapitation treatment in WT, the first three lateral buds were collected from each plant at 0, 12, 24, 36, 60, 84, and 108 h, respectively, and three plants were used as one biological replicate. The root, stem, leaf, top bud, and axillary bud of WT were also sampled for analysis of the expression pattern of CmDWF4, using three plants as a biological replicate. Transgenic plants OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 were extracted from the leaves, with three plants used as a biological replicate. Total RNA was extracted using the Quick RNA isolation Kit (Huayueyang, China) according to the operation manual. The chrysanthemum CmUbiquitin [39] gene was used as the reference sequence. The primer pair CmDWF4-RT-F and CmDWF4-RT-R and other quantitative primers used in this study are listed in Table S1. The qRT-PCR reaction system was as follows: 10 μL SYBR Premix Ex Taq™ II (Takara, Japan), 2 μL primer F/R (1 μM), 0.5 μL template cDNA (50 ng·μL−1), and 5.5 μL ddH2O. The 2−∆∆Ct method [40] was used to calculate relative expression levels. The results are shown as the average of three biological replicates.
Quantitatively validated transgenic lines OX-2, OX-10, OX-23, and WT were sent to the Annoroad Gene Tech. (Beijing) Co., Ltd. (China) for RNA sequencing. RNA was extracted from 30-day-old chrysanthemum leaves. To predict unigene expression levels in the four samples, we used the fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments (FPKM) method. FPKM of different samples was visualized by HeatMap of TBtools software [38]. The RNA-seq raw data of 12 samples generated in this study have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under accession number PRJNA915417.
The expression of CmDWF4 in different tissues and qRT-PCR analysis of CmDWF4 with the 20 mM sucrose treatment was performed by statistical variance analysis using the IBM SPSS Statistics 25 software. Other data were analyzed for significance using Student’s t-test. The differences between mean values were separated at a level of p < 0.05 or p < 0.01.
3.1 CmDWF4 Potentially Regulates Lateral Bud Outgrowth in Chrysanthemum
According to an effective culturing system using two-node stems [41], the BR biosynthetic gene CmDWF4 was up-regulated with the 20 mM sucrose treatment, which promoted the growth of the upper bud [42]. Our qRT-PCR verification showed that CmDWF4 was up-regulated by 4.01-folds in the upper buds treated with 20 mM sucrose (Fig. S1).
To further identify the potential role of CmDWF4 in lateral bud growth, 45-day-old chrysanthemum seedlings were used for decapitation treatment. We then analyzed CmDWF4 expression using the RNAs extracted from the axillary buds at 0, 12, 24, 36, 60, 84, and 108 h. Results showed that decapitation led to a rapid increase in the transcriptional level of CmDWF4 within 12 to 24 h (Fig. 1), indicating that CmDWF4 may play an important role in lateral bud outgrowth in chrysanthemum.
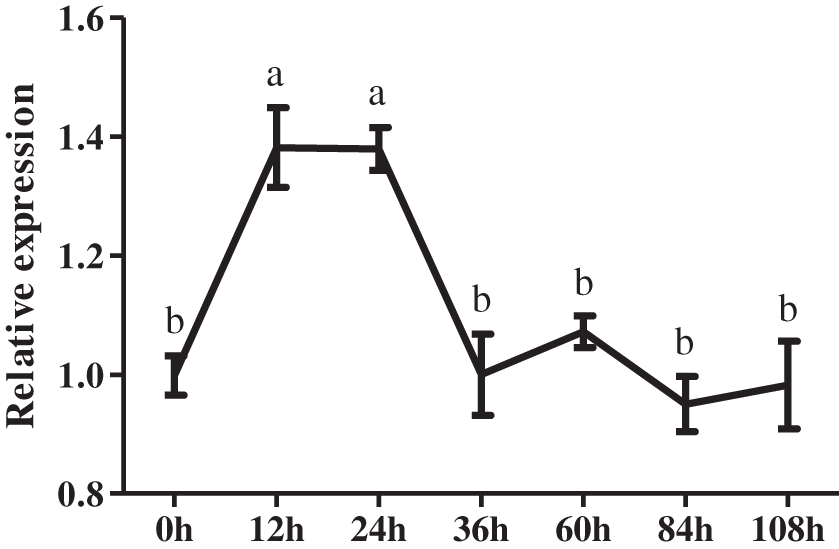
Figure 1: Expression pattern of the CmDWF4 gene in axillary buds in response to decapitation. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 3). Significant differences are indicated by different letters (p < 0.05)
3.2 Expression Pattern of CmDWF4
Next, we examineed the expression of CmDWF4 in root, stem, leaf, top bud, and axillary bud of the 45-day-old chrysanthemum seedlings. We found highest expression of CmDWF4 in leaves, which was 14.93 times than that in roots. Moreover, we found that the transcriptional level of CmDWF4 in axillary buds was 1.43 times higher than that in the top buds (Fig. 2).
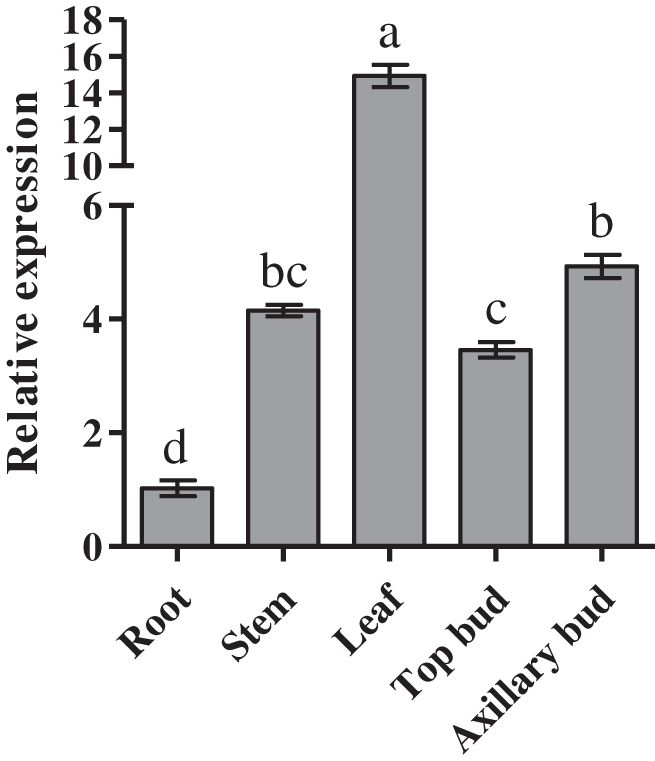
Figure 2: Expression profiles of CmDWF4 in different tissues of chrysanthemum. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 3). Significant differences are indicated by different letters (p < 0.05)
3.3 Cloning and Characterization of CmDWF4
The full-length CmDWF4 sequence was cloned by specific primers (CmDWF4-F and CmDWF4-R, Table S1) from the cultivar ‘Jinba’ cDNA. Sequence analysis revealed that the open reading frame (ORF) of CmDWF4 was 1476 bp, which was predicted to encode 491 amino acid residues with a molecular weight of 56.2 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) of 9.10. The predicted amino acid sequence of CmDWF4 contained four conserved features of the CYP450 family: domains A, B, and C and heme-binding domain (Fig. 3A). A phylogenetic analysis implied that CmDWF4 was most closely related to Artemisia annua protein AaDWF4 (Fig. 3B).
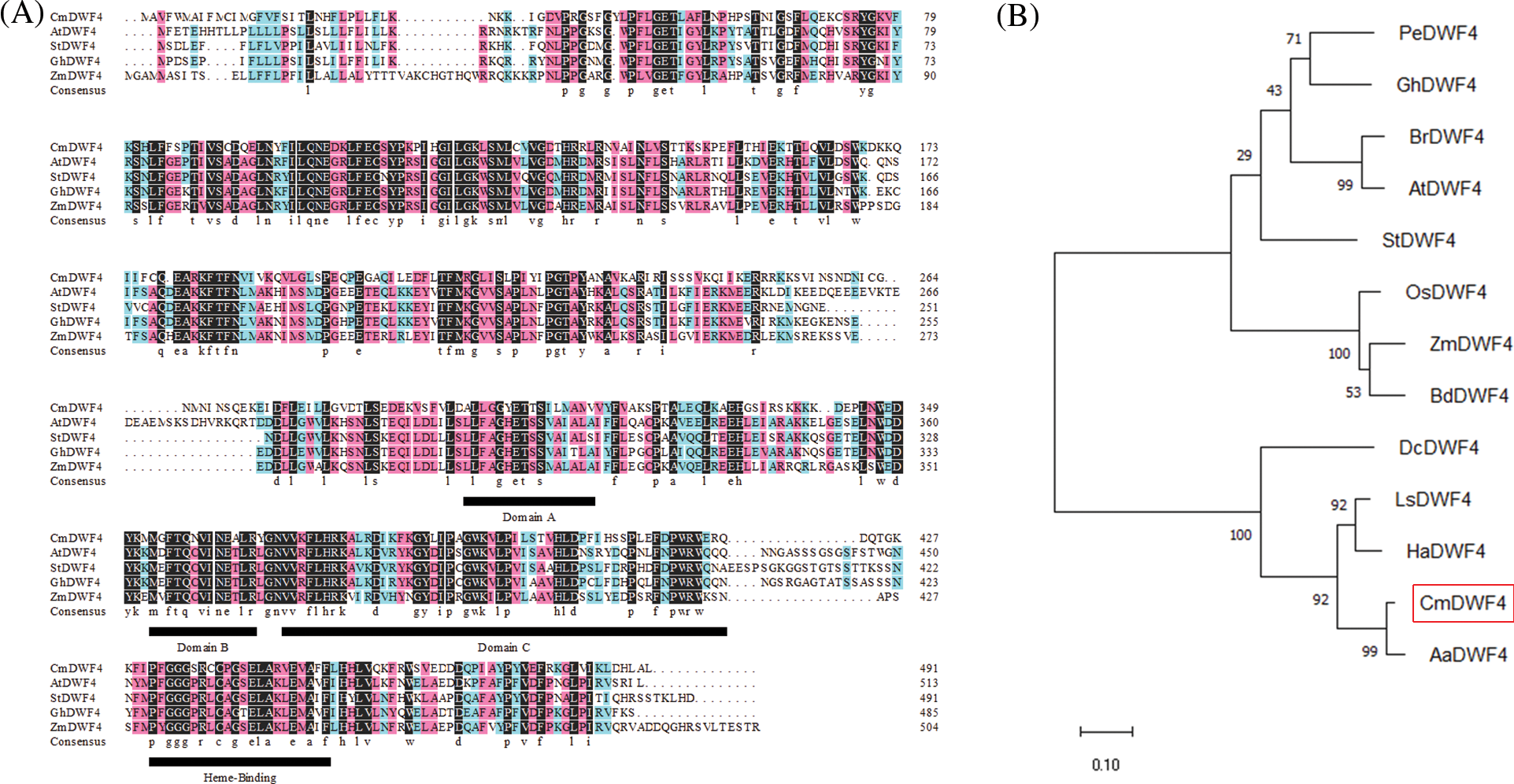
Figure 3: Sequence analysis of CmDWF4 and related DWF4s. (A) Polypeptide alignment of CmDWF4 with DWF4s from Arabidopsis, potato, cotton, and maize. The conserved features of the CYP450, domains A, B, and C, and heme-binding domain were indicated by underlining. (B) Phylogenetic tree of CmDWF4 and related DWF4s. The GenBank accession numbers of P450s are as follows: PeDWF4 (Populus euphratica, HQ452827.1), GhDWF4 (Gossypium hirsutum, NP_001313765.1), BrDWF4 (Brassica pekinensis Rupr., Bra030023.1), AtDWF4 (Arabidopsis thaliana, NP_190635.1), StDWF4 (Solanum tuberosum, XM_006340546.1), OsDWF4 (Oryza sativa, AB206579.1), ZmDWF4 (Zea mays, EF519871.1), BdDWF4 (Brachypodium distachyon, KQK22730.1), DcDWF4 (Daucus carota var. sativa Hoffm., DCAR_017553), LsDWF4 (Lactuca sativa, XP_023770054.1), HaDWF4 (Helianthus annuus, XP_021998202.1), and AaDWF4 (Artemisia annua, PWA81420.1)
3.4 Effects of CmDWF4 on Lateral Bud Initiation and Outgrowth
To further investigate the function of CmDWF4 in chrysanthemum, we generated the overexpression lines of CmDWF4 in the cultivar ‘Jinba’ by introducing the plasmid pORE-R4-CmDWF4. Positive transgenic lines were identified by conducting a genomic PCR assay using primers pORE-R4-F and CmDWF4-R2 (Table S1). Finally, three independent transgenic lines were obtained: OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 (Fig. S2). qRT-PCR analysis revealed that the transcriptional level of CmDWF4 in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 was 3.02, 5.19, and 8.19 times than that in WT, respectively (Fig. 4C).
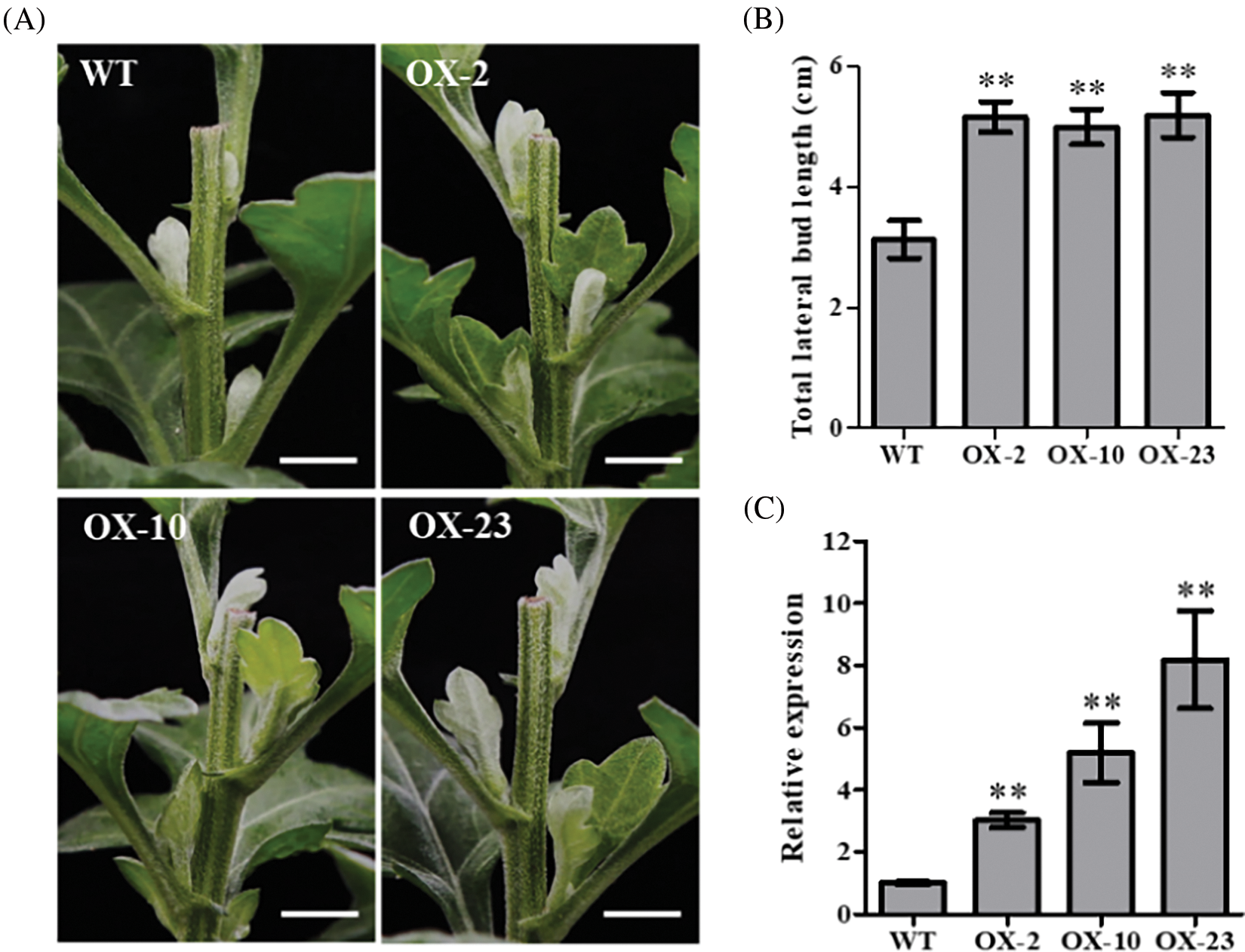
Figure 4: Effects of CmDWF4 on lateral bud initiation and outgrowth after decapitation. (A) Lateral bud outgrowth phenotypes of overexpressed CmDWF4 lines in the ‘Jinba’ background after decapitation for 6 days. Scale bars represent 1.0 cm. (B) Statistics of the total length of the first three lateral buds. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 6). (C) qRT-PCR analysis of relative expression of CmDWF4 in transgenic lines. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 3). Significant variations from WT are indicated with asterisks (**p < 0.01)
The 45-day-old CmDWF4 transgenic lines OX-2, OX-10, OX-23, and WT were decapitated at the same time. The growth of three lateral buds at the top of the plants was observed after 6 days in the long-day culture chamber. It was found that the first three lateral buds of the overexpression lines OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 were significantly longer than those in WT (Fig. 4A). Statistical analysis showed that the length of the total three lateral buds of OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 was 5.17, 5.00, and 5.20 cm, respectively, which were significantly greater than the 3.13 cm length of lateral buds in WT (Fig. 4B), indicating an essential role of CmDWF4 in lateral bud initiation and outgrowth in chrysanthemum.
3.5 Effects of CmDWF4 on the Number and Length of Lateral Buds
The phenotype of 65-day-old CmDWF4 transgenic lines was identified. It was found that the overexpressed lines OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 had more and longer buds compared with WT (Fig. 5A). The length of lateral buds at the same node (from node 6 to node 39, S6–S39) was compared by a color scale. The results showed that 73.52% of the buds of OX-2, 85.29% of the buds of OX-10, and 70.59% of the buds of OX-23 were longer than the buds of WT (Fig. 5B). Statistical analysis showed that the number of lateral buds greater than 0.5 cm in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 was 36.0, 35.5, and 38.0, respectively, which was significantly larger than 30.0 in WT (Fig. 5C). The total lateral bud length of OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 was 68.95, 69.33, and 58.30 cm, respectively, which was also significantly greater than 43.73 cm in WT (Fig. 5D). These results indicated that CmDWF4 positively regulates the growth of lateral bud in chrysanthemum plants.
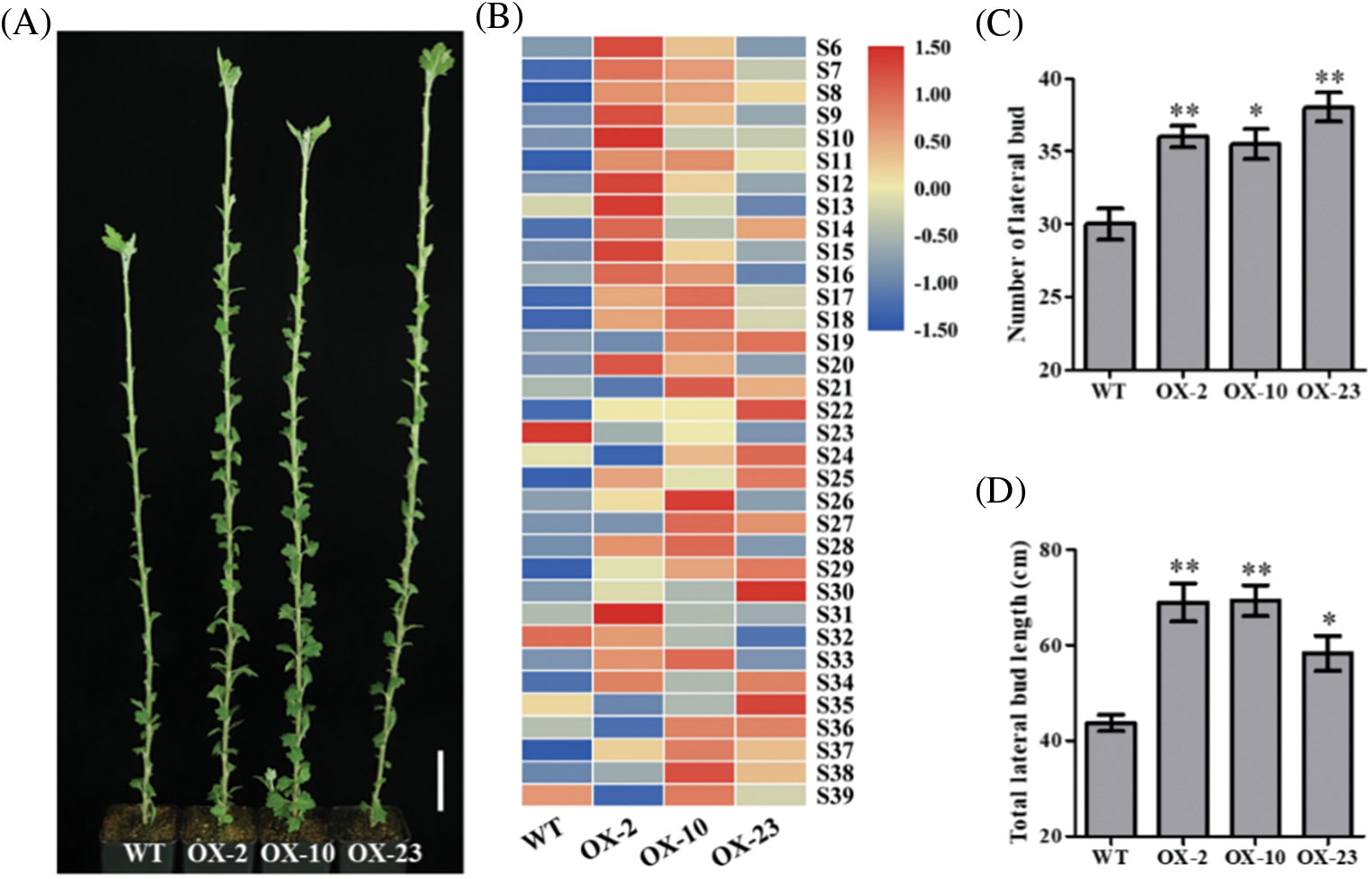
Figure 5: Effects of CmDWF4 on the number and length of lateral buds in intact chrysanthemum plants. (A) Lateral bud outgrowth phenotypes of overexpressed CmDWF4 lines. Scale bar represents 5.0 cm. (B) Comparison of lateral bud length at the same node with the color scale. S6–S39 represents the 6th to the 39th node. (C) The number of lateral buds longer than 0.5 cm in (A). (D) Total lateral bud length of the plants in (A). Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 4). Significant variations from WT are indicated with asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01)
3.6 CmDWF4 Promotes Lateral Bud Outgrowth through Regulating Cell Elongation and Expansion
To explore the mechanism of CmDWF4 in regulating chrysanthemum bud outgrowth, we performed transcriptome sequencing using CmDWF4-overexpressing lines OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23. Five differentially expressed genes related to BR signaling were identified, and their expression levels were up-regulated in CmDWF4-overexpressing lines (Fig. 6B). In addition, multiple xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase (XTH) family encoding genes were up-regulated in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 compared to WT (Fig. 6A). XTHs modify a major structural component of the plant cell wall, xyloglucan, and therefore may influence cell elongation and expansion [43–45]. qRT-PCR was used to verify the transcript levels of XTHs in CmDWF4-overexpressing transgenic lines. Result showed that three XTHs genes in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 lines were significantly up-regulated compared with WT plants (Figs. 6C–6E). The expression levels of CmXTH6/CmXTR10 in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 were 1.74, 1.47, and 1.89 times that of WT, respectively (Fig. 6C). The expression levels of CmXTH23/CmXTR6 in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 were 1.82, 1.78, and 2.87 times that of WT, respectively (Fig. 6D). The expression levels of CmXTH28/CmEXGT-A2 in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 were 2.05, 1.87, and 1.86 times that of WT, respectively (Fig. 6E). The data implied that overexpression of CmDWF4 might regulate the expression of cell wall-related genes to stimulate cell elongation and expansion to promote lateral bud outgrowth.
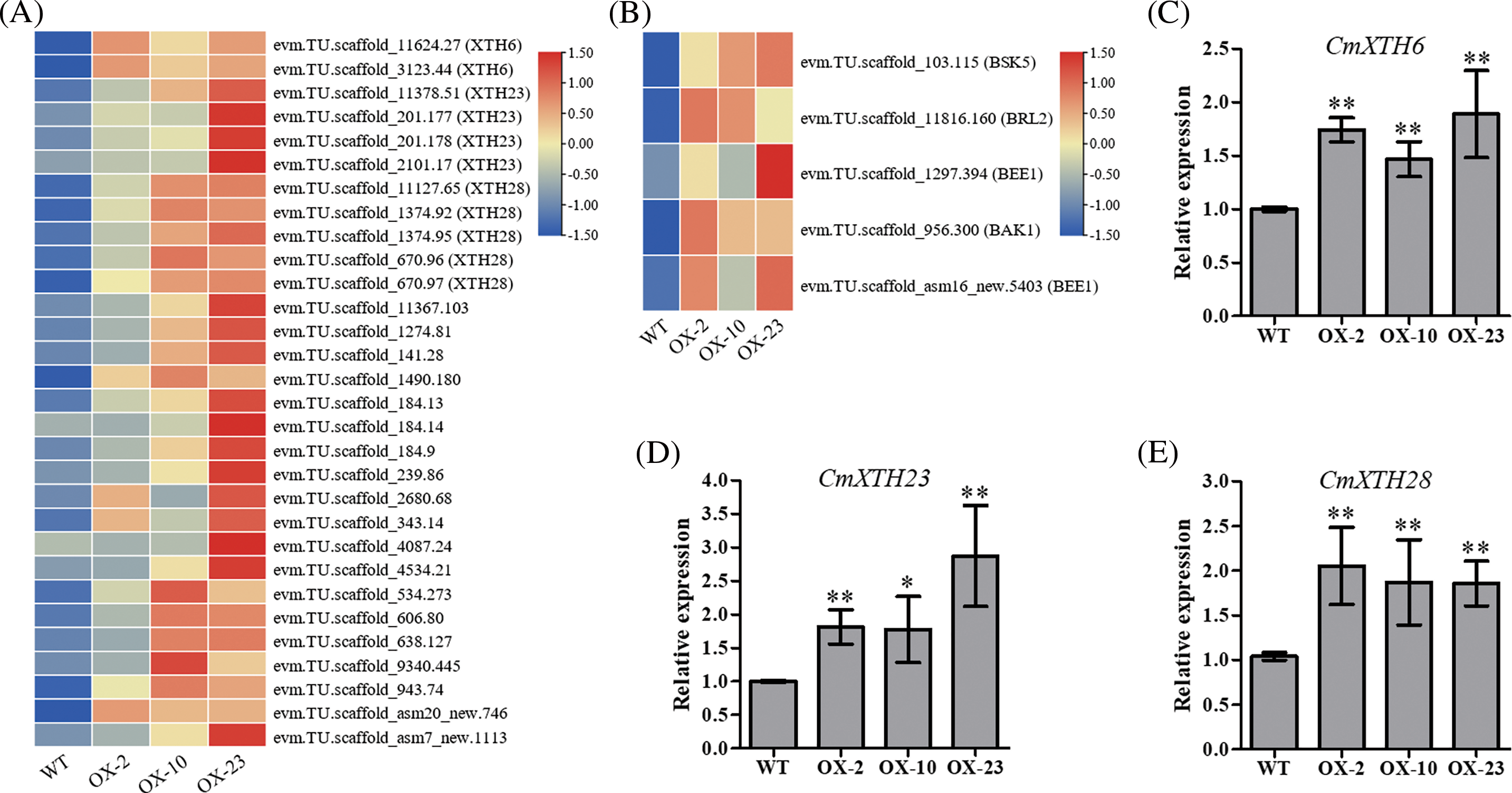
Figure 6: Transcriptome analysis and quantitative validation of CmDWF4 overexpressing lines. (A) Expression levels of XTHs genes in WT, OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 RNA-seq data. (B) BR signaling-related genes expression levels in WT, OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 RNA-seq data. Data are presented as means (n = 3) of FPKM by log2 scale and row scale. (C) The relative expression level of CmXTH6 by qRT-PCR analysis. (D) The relative expression level of CmXTH23 by qRT-PCR analysis. (E) The relative expression level of CmXTH28 by qRT-PCR analysis. Data are presented as means ± SE (n = 3). Significant variations from WT are indicated with asterisks (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01)
Plant growth and development are aided by BRs, a class of plant-specific steroid hormones. BRs promote tillering in rice [16] and bud outgrowth in tomato [17]. The cytochrome P450 enzyme (CYP90B1) encoded by the DWF4 gene is a rate-limiting step in BR biosynthesis [28–30]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the BR biosynthetic gene CmDWF4 was up-regulated in the growing bud with the 20 mM sucrose treatment (Fig. S1) [41,42]. The role of sucrose in promoting plant bud outgrowth has been widely reported [46,47]. In this study, the expression of CmDWF4 increased in lateral buds of WT within 12 to 24 h in response to decapitation treatment (Fig. 1). Therefore, we speculated that CmDWF4 was involved in the regulation of lateral bud outgrowth in chrysanthemum.
Transgenic experiments were conducted to verify whether CmDWF4 was involved in the regulation of lateral bud outgrowth. After obtaining CmDWF4 overexpressing lines OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23, the growth rate, number, and length of the lateral buds were observed in the intact plants or decapitated plants. The results showed that the initiation and sustained growth of lateral buds were promoted in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 lines (Figs. 4 and 5). In Arabidopsis, AtDWF4 functions to increase vegetative growth and seed yield [31]. In maize, ZmDWF4 improves photosynthetic ability and enhances yield [32], indicating that CmDWF4 has functional similarity with AtDWF4 in Arabidopsis and ZmDWF4 in maize in shoot branching regulation. However, in Arabidopsis and maize, no reports showed how DWF4 regulates the lateral bud outgrowth. In other species, the function of DWF4 in regulating lateral bud outgrowth has not been reported. This study provides new clues on the shoot branching regulation of the DWF4 gene in different species by the homologous transformation of CmDWF4 in chrysanthemum.
Transcriptome analysis of CmDWF4 overexpressing lines showed that multiple xyloglucan endotransglucosylases/hydrolases (XTHs) encoding genes were up-regulated (Fig. 6A). Enzymologically, xyloglucan endotransglucosylase (XET) and xyloglucan endohydrolase (XEH) activities are used to describe the XTHs family of enzymes. XTHs modify a major structural component of the plant cell wall, xyloglucan, and thus may affect cell elongation and expansion [43–45]. It has been reported that exogenous BL promotes the expression of XTHs genes [48,49]. The key brassinosteroid signaling pathway transcription factor BES1 acts directly upstream of XTH19 and XTH23 to control their expression [50]. However, the regulatory relationship of DWF4 on XTHs is rarely reported. The family of 33 Arabidopsis XTHs genes is divided into three major groups according to the genetic structure. XTH6 [51], XTH23 [50], and XTH28 [44] belong to group 1, group 2, and group 3, respectively [45]. Quantitative validation in our study showed that the expression of CmXTH6, CmXTH23, and CmXTH28 was significantly increased in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 lines (Figs. 6C–6E), suggesting that overexpression of CmDWF4 might result in cell elongation and expansion by upregulating the expression of the XTHs gene. Eventually promoted chrysanthemum shoot branching.
BR is widely known to promote cell elongation [18,52]. The response of XTH23 to BR regulation has been recorded [50]. In this study, the transcriptional level of CmDWF4 was significantly increased in OX-2, OX-10, and OX-23 lines (Fig. 4C). The expression levels of BR signaling-related genes were up-regulated in CmDWF4-overexpressing lines, including BAK1 (BRI1 associated receptor kinase 1) [53,54], BSK5 (brassinosteroid-signaling kinase 5) [55], BEE1 (BR enhanced expression 1) [56], and BRL2 (BRI1-like receptor kinase 2) [57] (Fig. 6B). This indicated that BR content in CmDWF4-overexpressing lines was indeed increased. Together, these data provide strong evidence that the lateral bud outgrowth phenotypes and associated gene expression level changes in transgenic lines are due to elevated BR levels.
Funding Statement: This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872149, 32172609), China Agriculture Research System (CARS-23-A18), the “JBGS” Project of Seed Industry Revitalization in Jiangsu Province (JBGS[2021]020), the earmarked fund for Jiangsu Agricultural Industry Technology System, and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author Contributions: Xianrong Fu performed most of the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Aiping Song and Fadi Chen directed experiments and revised the manuscript. Bo Peng, Song Li, Weixin Liu and Lingling Zhang assisted in the experiments. Fadi Chen, Jiafu Jiang and Sumei Chen supervised the research.
Ethics Approval: The authors declare that this article is in compliance with ethical standards of the journal.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
References
1. Mathan, J., Bhattacharya, J., Ranjan, A. (2016). Enhancing crop yield by optimizing plant developmental features. Development, 143(18), 3283–3294. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.134072 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
2. Ahmad, S., Yuan, C., Yang, Q., Yang, Y., Cheng, T. et al. (2020). Morpho-physiological integrators, transcriptome and coexpression network analyses signify the novel molecular signatures associated with axillary bud in chrysanthemum. BMC Plant Biology, 20(1), 145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02336-0 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
3. Janssen, B. J., Drummond, R. S., Snowden, K. C. (2014). Regulation of axillary shoot development. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 17, 28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2013.11.004 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
4. Rameau, C., Bertheloot, J., Leduc, N., Andrieu, B., Foucher, F. et al. (2015). Multiple pathways regulate shoot branching. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5, 741. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00741 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
5. Barbier, F. F., Dun, E. A., Kerr, S. C., Chabikwa, T. G., Beveridge, C. A. (2019). An update on the signals controlling shoot branching. Trends in Plant Science, 24(3), 220–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2018.12.001 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
6. Thimann, K. V., Skoog, F. (1933). Studies on the growth hormone of plants. III. The inhibiting action of the growth substance on bud development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 19(7), 714–716. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.19.7.714 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
7. Balla, J., Kalousek, P., Reinohl, V., Friml, J., Prochazka, S. (2011). Competitive canalization of PIN-dependent auxin flow from axillary buds controls pea bud outgrowth. The Plant Journal, 65(4), 571–577. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04443.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
8. Gomez-Roldan, V., Fermas, S., Brewer, P. B., Puech-Pages, V., Dun, E. A. et al. (2008). Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature, 455(7210), 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07271 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
9. Umehara, M., Hanada, A., Yoshida, S., Akiyama, K., Arite, T. et al. (2008). Inhibition of shoot branching by new terpenoid plant hormones. Nature, 455(7210), 195–200. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07272 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
10. Wickson, M., Thimann, K. V. (1958). The antagonism of auxin and kinetin in apical dominance. Physiologia Plantarum, 11(1), 62–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1958.tb08426.x [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
11. Dun, E. A., de Saint Germain, A., Rameau, C., Beveridge, C. A. (2012). Antagonistic action of strigolactone and cytokinin in bud outgrowth control. Plant Physiology, 158(1), 487–498. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.186783 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
12. Müller, D., Waldie, T., Miyawaki, K., To, J. P., Melnyk, C. W. et al. (2015). Cytokinin is required for escape but not release from auxin mediated apical dominance. The Plant Journal, 82(5), 874–886. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12862 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
13. Domagalska, M. A., Leyser, O. (2011). Signal integration in the control of shoot branching. Nature Reviews: Molecular Cell Biology, 12(4), 211–221. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3088 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
14. Waldie, T., Leyser, O. (2018). Cytokinin targets auxin transport to promote shoot branching. Plant Physiology, 177(2), 803–818. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.01691 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
15. van Rongen, M., Bennett, T., Ticchiarelli, F., Leyser, O. (2019). Connective auxin transport contributes to strigolactone-mediated shoot branching control independent of the transcription factor BRC1. PLoS Genetics, 15(3), e1008023. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008023 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
16. Fang, Z., Ji, Y., Hu, J., Guo, R., Sun, S. et al. (2020). Strigolactones and brassinosteroids antagonistically regulate the stability of the D53-OsBZR1 complex to determine FC1 expression in rice tillering. Molecular Plant, 13(4), 586–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2019.12.005 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
17. Xia, X., Dong, H., Yin, Y., Song, X., Gu, X. et al. (2021). Brassinosteroid signaling integrates multiple pathways to release apical dominance in tomato. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 118(11), e2004384118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2004384118 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
18. Szekeres, M., Németh, K., Koncz-Kálmán, Z., Mathur, J., Kauschmann, A. et al. (1996). Brassinosteroids rescue the deficiency of CYP90, a cytochrome P450, controlling cell elongation and de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Cell, 85(2), 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81094-6 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
19. Clouse, S. D., Langford, M., McMorris, T. C. (1996). A brassinosteroid-insensitive mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibits multiple defects in growth and development. Plant Physiology, 111(3), 671–678. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.3.671 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
20. Nolan, T. M., Vukasinovic, N., Liu, D., Russinova, E., Yin, Y. (2019). Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. The Plant Cell, 32(2), 295–318. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00335 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
21. Tong, H., Jin, Y., Liu, W., Li, F., Fang, J. et al. (2009). DWARF AND LOW-TILLERING, a new member of the GRAS family, plays positive roles in brassinosteroid signaling in rice. The Plant Journal, 58(5), 803–816. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03825.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
22. Yin, Y., Wang, Z., Mora-Garcia, S., Li, J., Yoshida, S. et al. (2002). BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation. Cell, 109(2), 181–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00721-3 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
23. Wang, Y., Sun, S., Zhu, W., Jia, K., Yang, H. et al. (2013). Strigolactone/MAX2-induced degradation of brassinosteroid transcriptional effector BES1 regulates shoot branching. Developmental Cell, 27(6), 681–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2013.11.010 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
24. Hu, J., Ji, Y., Hu, X., Sun, S., Wang, X. (2020). BES1 functions as the co-regulator of D53-like SMXLs to inhibit BRC1 expression in strigolactone-regulated shoot branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Communications, 1(3), 100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2019.100014 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
25. Vriet, C., Russinova, E., Reuzeau, C. (2013). From squalene to brassinolide: The steroid metabolic and signaling pathways across the plant kingdom. Molecular Plant, 6(6), 1738–1757. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst096 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
26. Bajguz, A., Chmur, M., Gruszka, D. (2020). Comprehensive overview of the brassinosteroid biosynthesis pathways: Substrates, products, inhibitors, and connections. Frontiers in Plant Science, 11, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.01034 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
27. Zhang, Y. Y., Elam, E., Ni, Z. J., Zhang, F., Thakur, K. et al. (2022). LC-MS/MS targeting analysis of terpenoid metabolism in Carya cathayensis at different developmental stages. Food Chemistry, 366(5), 130583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130583 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
28. Choe, S., Dilkes, B. P., Fujioka, S., Takatsuto, S., Sakurai, A. et al. (1998). The DWF4 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a cytochrome P450 that mediates multiple 22α-hydroxylation steps in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. The Plant Cell, 10(2), 231–243. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.10.2.231 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
29. Fujita, S., Ohnishi, T., Watanabe, B., Yokota, T., Takatsuto, S. et al. (2006). Arabidopsis CYP90B1 catalyses the early C-22 hydroxylation of C27, C28 and C29 sterols. The Plant Journal, 45(5), 765–774. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02639.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
30. Fujiyama, K., Hino, T., Kanadani, M., Watanabe, B., Jae Lee, H. et al. (2019). Structural insights into a key step of brassinosteroid biosynthesis and its inhibition. Nature Plants, 5(6), 589–594. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41477-019-0436-6 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
31. Choe, S., Fujioka, S., Noguchi, T., Takatsuto, S., Yoshida, S. et al. (2001). Overexpression of DWARF4 in the brassinosteroid biosynthetic pathway results in increased vegetative growth and seed yield in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 26(6), 573–582. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01055.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
32. Liu, N., Zhao, Y. J., Wu, J. W., Wei, Y. M., Ren, R. C. et al. (2020). Overexpression of ZmDWF4 improves major agronomic traits and enhances yield in maize. Molecular Breeding, 40(8), 71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-020-01152-6 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
33. Sahni, S., Prasad, B. D., Liu, Q., Grbic, V., Sharpe, A. et al. (2016). Overexpression of the brassinosteroid biosynthetic gene DWF4 in Brassica napus simultaneously increases seed yield and stress tolerance. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 28298. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28298 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
34. Zhou, X., Zhang, N., Yang, J., Tang, X., Wen, Y. et al. (2018). Functional analysis of StDWF4 gene in response to salt stress in potato. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 125(1), 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.01.027 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
35. Ye, S., Li, F., Li, X., Hong, Q., Zhai, Y. et al. (2015). Over-expression of GhDWF4 gene improved tomato fruit quality and accelerated fruit ripening. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 14(10), 1980–1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2095-3119(15)61059-0 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
36. Zhu, L., Guan, Y., Zhang, Z., Song, A., Chen, S. et al. (2020). CmMYB8 encodes an R2R3 MYB transcription factor which represses lignin and flavonoid synthesis in chrysanthemum. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 149(10), 217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.010 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
37. Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., Tamura, K. et al. (2018). MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35(6), 1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
38. Chen, C., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H. R., Frank, M. H. et al. (2020). TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molecular Plant, 13(8), 1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
39. Wei, Q., Ma, C., Xu, Y., Wang, T., Chen, Y. et al. (2017). Control of chrysanthemum flowering through integration with an aging pathway. Nature Communications, 8(1), 829. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00812-0 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
40. Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
41. Liu, W., Peng, B., Song, A., Zhang, Y., Jiang, J. et al. (2022). Sucrose-induced bud outgrowth in Chrysanthemum morifolium involves changes of auxin transport and gene expression. Scientia Horticulturae, 296(25), 110904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2022.110904 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
42. Liu, W., Peng, B., Song, A., Jiang, J., Chen, F. (2020). Sugar transporter, CmSWEET17, promotes bud outgrowth in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Genes, 11(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010026 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
43. Xu, W., Campbell, P., Vargheese, A. K., Braam, J. (1996). The Arabidopsis XET-related gene family: Environmental and hormonal regulation of expression. The Plant Journal, 9(6), 879–889. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1996.9060879.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
44. Campbell, P., Braam, J. (1999). In vitro activities of four xyloglucan endotransglycosylases from Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 18(4), 371–382. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00459.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
45. Rose, J. K., Braam, J., Fry, S. C., Nishitani, K. (2002). The XTH family of enzymes involved in xyloglucan endotransglucosylation and endohydrolysis: Current perspectives and a new unifying nomenclature. Plant and Cell Physiology, 43(12), 1421–1435. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcf171 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
46. Barbier, F., Peron, T., Lecerf, M., Perez-Garcia, M. D., Barriere, Q. et al. (2015). Sucrose is an early modulator of the key hormonal mechanisms controlling bud outgrowth in Rosa hybrida. Journal of Experimental Botany, 66(9), 2569–2582. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv047 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
47. Bertheloot, J., Barbier, F., Boudon, F., Perez-Garcia, M. D., Peron, T. et al. (2019). Sugar availability suppresses the auxin-induced strigolactone pathway to promote bud outgrowth. New Phytologist, 225(2), 866–879. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16201 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
48. Li, Y., Zheng, X., Wang, C., Hou, D., Li, T. et al. (2021). Pear xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolases PcBRU1 promotes stem growth through regulating cell wall elongation. Plant Science, 312, 111026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.111026 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
49. Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Khan, R., Wu, X., Zhou, L. et al. (2021). Exogenous application of brassinosteroids regulates tobacco leaf size and expansion via modulation of endogenous hormones content and gene expression. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 27(4), 847–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-00971-x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
50. Xu, P., Fang, S., Chen, H., Cai, W. (2020). The brassinosteroid-responsive xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase 19 (XTH19) and XTH23 genes are involved in lateral root development under salt stress in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 104(1), 59–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14905 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
51. Sasidharan, R., Chinnappa, C. C., Staal, M., Elzenga, J. T., Yokoyama, R. et al. (2010). Light quality-mediated petiole elongation in Arabidopsis during shade avoidance involves cell wall modification by xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolases. Plant Physiology, 154(2), 978–990. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.162057 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
52. Sun, Y., Fan, X., Cao, D., Tang, W., He, K. et al. (2010). Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Developmental Cell, 19(5), 765–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.010 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
53. Li, J., Wen, J., Lease, K. A., Doke, J. T., Tax, F. E. et al. (2002). BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell, 110(2), 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00812-7 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
54. Nam, K. H., Li, J. (2002). BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell, 110(2), 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00814-0 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
55. Li, Z., Xu, Z., He, G., Yang, G., Chen, M. et al. (2012). A mutation in Arabidopsis BSK5 encoding a brassinosteroid-signaling kinase protein affects responses to salinity and abscisic acid. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 426(4), 522–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.118 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
56. Wang, F., Gao, Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Gu, X. et al. (2019). BES1-regulated BEE1 controls photoperiodic flowering downstream of blue light signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. New Phytologist, 223(3), 1407–1419. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15866 [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
57. Ceserani, T., Trofka, A., Gandotra, N., Nelson, T. (2009). VH1/BRL2 receptor-like kinase interacts with vascular-specific adaptor proteins VIT and VIK to influence leaf venation. The Plant Journal, 57(6), 1000–1014. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03742.x [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [CrossRef]
Supplementary Materials
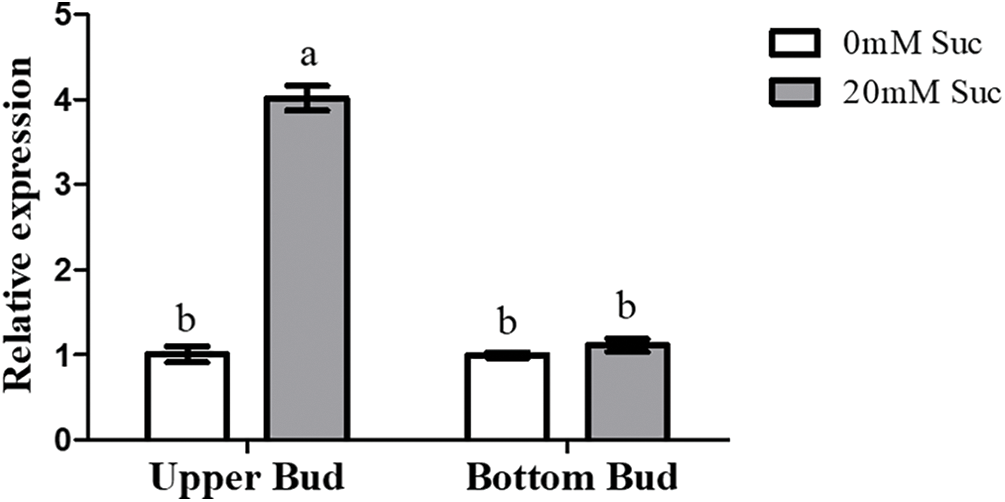
Figure S1: qRT-PCR analysis of CmDWF4 with the 20 mM sucrose treatment. Data are presented as the means ± SE (n = 3). Significant differences are indicated by different letters (p < 0.05)
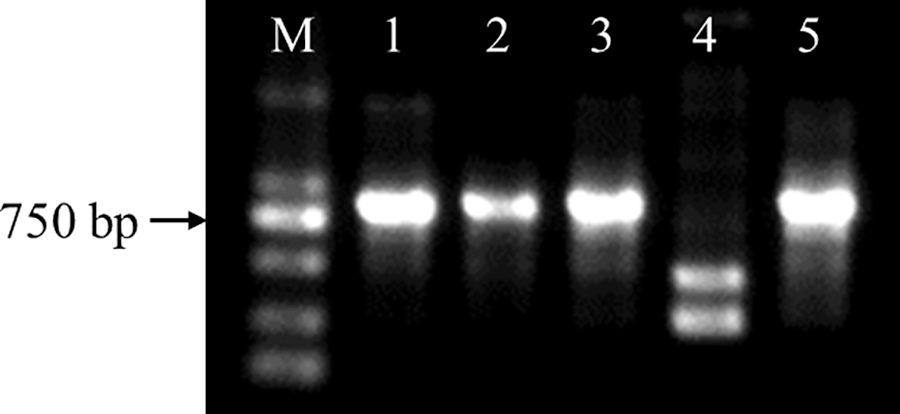
Figure S2: Identification of CmDWF4 transgenic lines at the DNA level. M: DL2000 DNA Marker (TaKaRa); 1: OX-2; 2: OX-10; 3: OX-23; 4: WT; 5: plasmid pORE-R4-CmDWF4
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools