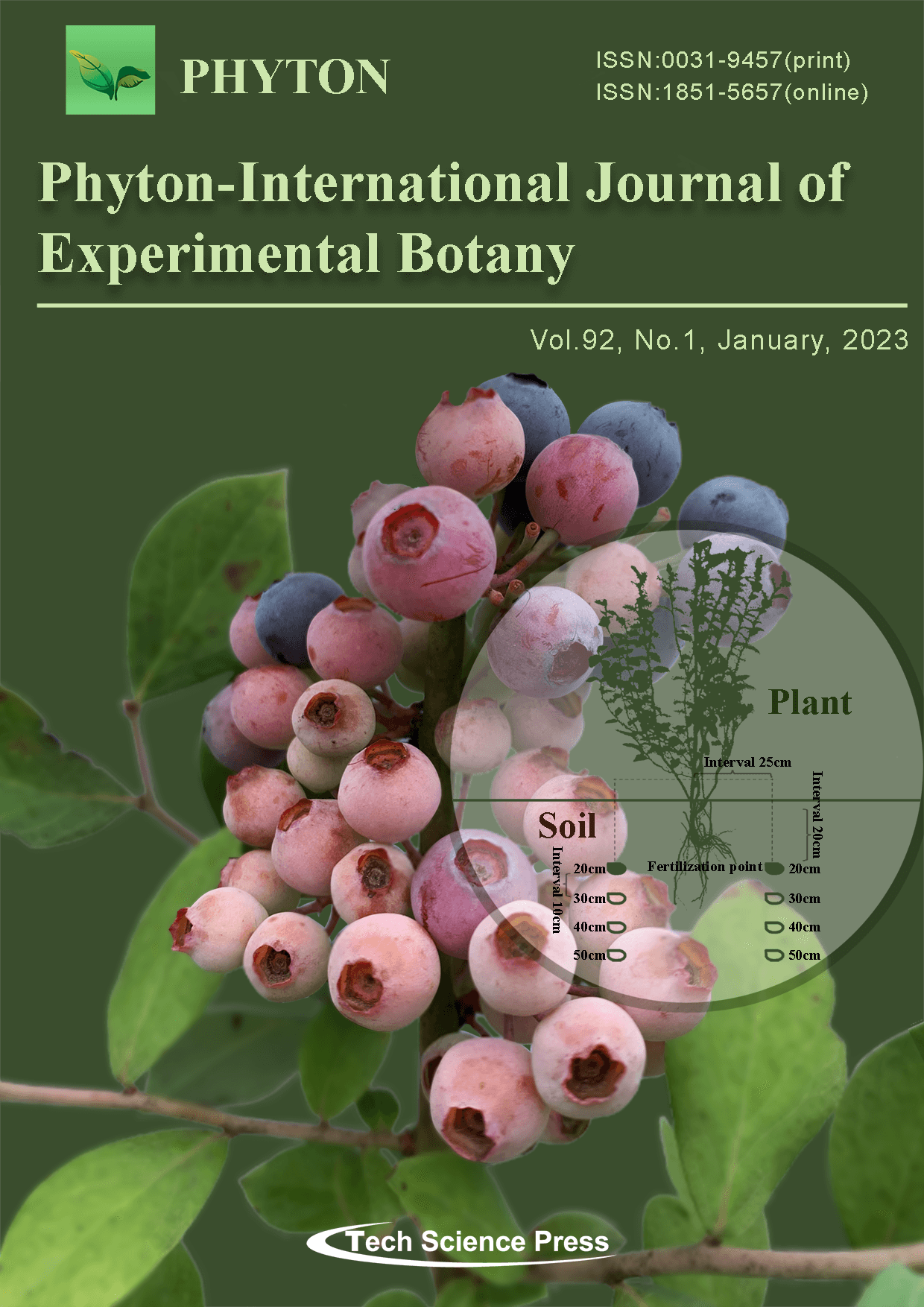
The blueberry is an important economic fruit crop in China and has played a key role in increasing agricultural income. The county of Majiang in Guizhou is an important blueberry production region, but water shortages and low fertilizer utilization rates hamper blueberry production. Therefore, it is very urgent to take appropriate irrigation and fertilization strategies to increase the yield of blueberries. Thus, In this study, two factors of water and fertilizer, 4 irrigation levels, 3 fertilization levels and a control field experiment design were used to study the effects of different water and nitrogen treatments on blueberry plant physiology and fruit yield. The research showed that low N and moderate water treatments resulted in high fruit yields and reduced nitrate N retention in the soil. The findings provide a scientific basis and practical Guidance for using appropriate water and N management to obtain high yields of blueberries in this region. The results also provide practical and technical guidance for Minimizing environmental degradation and improving farmers’ incomes.
View this paper