

 | Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany |  |
DOI: 10.32604/phyton.2022.018462
ARTICLE
Overexpression of a Glycosyltransferase Gene from a Metabolically Poly-Resistant Beckmannia syzigachne Population Alters Growth and Confers Herbicide Resistance to Brachypodium distachyon
1College of Food Science and Pharmaceutical Engineering, Zaozhuang University, Zaozhuang, 277160, China
2Institute of Apicultural Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, 100093, China
3Key Laboratory of Pesticide Toxicology and Application Technique, College of Plant Protection, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, 271018, China
4College of Life Sciences, Zaozhuang University, Zaozhuang, 277160, China
*Corresponding Authors: Wei Li. Email: 13615382586@163.com; Jinxin Wang. Email: wangjx@sdau.edu.cn
Received: 26 July 2021; Accepted: 26 September 2021
Abstract: Beckmannia syzigachne is a noxious weed for rice-wheat rotations in China. The B. syzigachne (AH-02) population evolved metabolic resistance to fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl. To investigate the function of GT73C1 in this population, the GT73C1 gene was amplified by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, and the sequence was 100% consistent with the transcriptome data. Its phylogenetic tree was displayed and annotated using FigTree v1.4.4. The plant overexpression vector of GT73C1 gene was constructed and used to transform Brachypodium distachyon plants. Furthermore, the expression of GT73C1 was significantly induced by fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl, which was consistent with the findings from the whole plant bioassay. These results indicate that GT73C1 is closely related to the metabolic resistance of B. distachyon.
Keywords: Beckmannia syzigachne; GT73C1 gene; phylogenetic analyses; Brachypodium distachyon; genetic transformation
Agricultural weeds are mostly annual or short-lived wild plant species, which thrive in agricultural ecosystems, competing with other crops for nutrients, water, light and space, and some are even intermediate hosts of pests [1]. American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne Steud.) is a diploid, self-pollinated, hygrophilous annual weed from the family Poaceae. It is widely distributed in wheat rotated with rice or rice rotated with oilseed rape on fields in the Yangtze Delta and the south-western region of China [2].
Herbicide is a major tool for controlling weeds and protecting crop yields [3]. The herbicides including the acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) and acetolactate synthetase (ALS) inhibitors are commonly used to selectively control grass weeds in wheat. Among them, fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl are widely applied with herbicides for the control of grass weeds, such as B. syzigachne [4,5]. Due to their frequent usage, multiple B. syzigachne populations have been reported to evolve resistance to both fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl. This has resulted in a multiple resistance and a great difficulty for controlling B. syzigachne [5,6].
Herbicide-resistant weeds can survive to herbicide treatments through a variety of mechanisms. The general two are target-site resistance (TSR) and non-target-site resistance (NTSR) [7,8]. TSR is due to changes in herbicide-binding sites or differences in the expression of target enzymes [9,10]. However, NTSR is more complicated, and it is often caused by either elevated constitutive or herbicide-induced expression of a set of genes encoding herbicide detoxification enzymes [7,8]. Furthermore, the expressions of these enzymes differ among weed species and among different biotypes of the same weed [11–14]. Therefore, searching and functional verification of genes encoding these enzymes have been widely conducted during recent years [15–20]. A laccase gene isolated from B. syzigachne was found related to the fenoxaprop-P-ethyl resistance, which was verified by genetic transformation of Oryza sativa [21]. Considering the complexity of metabolic resistance, current research is far from sufficient for a clear understanding of NTSR.
Brachypodium distachyon is the first species of Poaceae with a complete genome sequence, which has become an important species for verifying the function of genes [22,23]. In an unpublished study, a number of genes related to metabolic resistance to herbicides were identified from the second generation of B. syzigachne (AH-02) through RNA-Seq. This second generation of B. syzigachne evolved resistance to both fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl, but it had no amino acid substitution in the target enzymes [24]. This study focused on determining the function of GT73C1, because the glycosyltransferase gene family encodes a class of enzymes that play key roles in the detoxification process of exogenous and xenobiotic compounds, such as herbicides, in plants [25].
The aims of this work were: (1) to obtain the GT73C1 gene by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR); (2) to analyze the sequence information on the GT73C1 gene and its encoded protein; (3) to construct a plant overexpression vector of GT73C1 for transformation into B. distachyon; and (4) to functionally validate the role of the enzyme encoded by GT73C1 in NTSR for obtaining the positive transgenic B. distachyon.
2.1 Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
Resistant and susceptible biotypes (RF3 and SF3) of B. syzigachne were used in this study. The seeds were first stored at −20°C for 7 days to break dormancy, and then deposited in 9-cm diameter Petri dishes containing two layers of qualitative-grade filter circles soaked with 5 mL distilled water [5,24]. The dishes were placed in a growth chamber at 22/15°C (12 h light, 200 µmol m−2 s−1 photosynthetic photon flux, and 75% relative humidity). After germination, the seeds were sown in 10-cm side plastic pots containing loam soils. All plants were grown in the growth chamber at 22 (light)/15°C (darkness) (12 h light, 12 h light, 200 µmol m−2 s−1 photosynthetic photon flux, and 75% relative humidity) unless otherwise stated [24].
Brachypodium distachyon (ecotype Bd21), which was kindly provided by professor Hailong An from the Shandong Agricultural University, was used to verify the function of the GT73C1 gene in this study. Mature seeds of B. distachyon were placed on two layers of a damp filter paper. The dishes were kept in 4°C refrigerator for 7 days under dark conditions in dark at 4°C to break dormancy and subsequently exposed to 22°C (16 h light/8 h darkness) for 5 days [22]. Germinated seedlings were transplanted to 10-cm wide and 8.5-cm high plastic pots. All plants were grown in the growth chamber at 22°C under long-day (LD) conditions (18 h light/6 h darkness) unless otherwise stated [22].
2.2 RNA Extraction and Synthesis of the First Strand of cDNA of GT73C1
The B. syzigachne (RF3 and SF3) were cultivated as described above, and at the three-four leaf stage, total RNA (RF3 and SF3) was extracted with TranZol® Reagent (TRANSGEN BIOTECH, Beijing, China, ET101) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA degradation and contamination were monitored using 1% agarose gels. Reverse transcription was performed with the TransScript® II One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (TRANSGEN BIOTECH, AH311) using 5 μg total RNA as the template.
The sequences of the GT73C1 gene (RF3 and SF3) were obtained from previous B. syzigachne transcriptome sequencing data (unpublished). The unigene was compared to the priority sequence of the Nr protein libraries and Swissprot protein library to obtain the open reading frame (ORF) of GT73C1. Then, the unigene was predicted by the ORF Finder in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, http://www.nc-bi.Nlm.nih.gov) database. Finally, the ORF of GT73C1 was obtained and used in subsequent experiments (Supplementary Text 1).
The primers (Table 1) were designed based on the ORF of GT73C1 for gene amplification, using cDNA as the template. PCR was performed in a final volume of 25 µL, including 1 µL of cDNA, 0.5 µL of each primer (20 µM), 0.5 µL of Trans Start® FastPfu Fly DNA Polymerase, 5 µL of 5 × Trans Start® FastPfu Fly Buffer, 2 µL of dNTP Mixture, and 15.5 µL of ddH2O. The reaction was subjected to a 5-min denaturation at 94°C, followed by 32 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 58°C for 30 s, 72°C for 45 s, and a final extension cycle at 72 °C for 10 min.
The PCR amplification products were confirmed and separated on a 2% agarose gel. The amplified fragments were purified using the TIANgel Midi Purification Kit and directly cloned into the pEASY-T1 vector (TransGen Biotech, China). The plasmids were extracted from a positive Escherichia coli suspension with the EasyPure® Plasmid MiniPrep Kit (TRANSGEN BIOTECH, EM101) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. They were then sequenced in forward and reverse directions by the Shanghai Sangon Biological Engineering Technology & Services Co., Ltd. (China). The sequencing data were compared with the result from RNA-Seq using DNAMAN version 5.2.2 software (Lynnon Biosoft, Quebec, Canada).
2.4 The Bioinformatic Analysis of GT73C1
Conservative regions identified by CDD were aligned between GT73C1 and other related glycosyltransferase genes using MUSCLE v3.8.31 [26]. All ambiguously aligned regions were subsequently removed using TrimAl v1.2rev59 [27]. The best-fit model of amino acid substitution in each dataset was determined using ModelTest [28]. Phylogenetic trees were then inferred through the maximum likelihood method implemented in RaxML with 1000 bootstrap replicates [29]. The phylogenetic trees were displayed and annotated using FigTree v1.4.4. The pI and molecular weight of the GT73C1 protein were predicted by expasy (http://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/).
2.5 Functional Verification of GT73C1
2.5.1 Induction of Embryogenic Calluses
Immature seeds of B. distachyon were harvested approximately 6–8 weeks after potting when most of the seeds were sufficiently large to contain immature embryos. The seeds were treated with 10% sodium hypochlorite plus 0.05% Tween 20 for 5 min and then rinsed three times with sterile water. Immature embryos were isolated from the surface-sterilized seeds, and placed on callus induction medium (CIM) for 6 weeks to induce embryogenic calluses. The compact and nodular calluses were collected for subculture on CIM to obtain more embryogenic calluses [22].
2.5.2 Construction of the Plant Overexpression Vector
The positive plasmids verified by sequencing were digested by KpnI and MluI, which was performed in a final volume of 50 µL including 2 µg of positive plasmids, 1 µL of FlyCut™ KpnI, 1 µL of FlyCut™ MluI (20 µM), 5 µL of 10 × FlyCut™ Buffer, and up to 50 µL of ddH2O. Then, the target fragment was ligated to the Agrobacterium binary vector pPZP211, which carries the maize (Zea mays) Ubi1 promoter, and it was digested by KpnI and MluI as mentioned above [30,31]. The positive plant overexpression vector was used for genetic transformation.
The positive plant overexpression vectors were transformed into the chemically competent Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105, and the positive bacterial suspension was used for transformation. The collected calluses were immersed into the Agrobacterium cell suspension (0.6 < OD600 < 1.0) for 6 min and gently shaken at intervals. The excess Agrobacterium suspension around the calluses was first removed using sterile filter papers, and they were then placed on a freshly sterilized filter paper for 2–3 days. The infected calluses were selected on MS solid medium, and selected with 80 mg/L of G418 at 28°C in complete darkness. After two rounds of selection (6–8 weeks), resistant calluses generated on the surface of the original calluses were collected. Then, the resistant calluses were transferred to the differential medium for plant regeneration under light for 3 weeks. The transgenic plants of B. distachyon were transferred into soil for seed production, and the transgenic plants with empty carrier were also obtained [22].
2.5.4 Detection of Transgenic Plants
RNA extraction and synthesis of cDNA were conducted as described above. RT-PCR was performed as described above to screen positive transgenic plants of B. distachyon. These plants (T0) were cultivated to obtain their progenies (T1). The offspring (NT1 and WT1) of the non-transformed plants (NT0) and wild plants (WT0) were also obtained.
2.5.5 Bioassay of the Positive Transgenic Plants
Germinated seeds (T1, NT1 and WT1) of B. distachyon were transplanted to 10-cm wide and 8.5-cm high plastic pots with five germinated seeds per pot. When reaching the 3–4 leaf stage, the T1 plants were subjected to RT-PCR analysis to screen the positive transgenic plants and remove the negative ones. The positive transgenic plants were then sprayed with fenoxaprop-P-ethyl at 62.1 g a.i. ha−1 and mesosulfuron-methyl at 9 g a.i. ha−1 (i.e., field-recommended rates), using compressed air, moving nozzle cabinet sprayer equipped with a Teejet 9503 EVS flat fan nozzle. The sprayer was calibrated to deliver 450 L ha−1 water at 0.28 MPa. The transgenic plants without herbicide damage at 21 days after treatment were saved for further study.
2.5.6 Expression Patterns of GT73C1
Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was conducted to assess the transcriptional level of GT73C1 in the positive T1 plants of B. distachyon. The qRT-PCR was carried out based on the Bio-RAD CFX ConnectTM (Hercules, CA, USA) using the Power SYBR® Green PCR Master Mix (ABI Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ubiquitin (UBQ) was used as the internal control gene to normalize the transcriptional levels of GT73C1. Each reaction was conducted with three replicates for each cDNA sample, and two biological repeats were assayed, giving similar trends. The reaction conditions were 95°C for 10 min and 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s and 60°C for 60 s. Error bars were calculated based on the values from the three replicates. The relative expression levels of the target gene to the internal control were calculated using the 2–ΔΔCT method [32].
The T1 plants of B. distachyon were also subjected to RT-PCR, and those without the transgene were removed. When the positive T1 plants reached the 3–4 leaf stage, they were sprayed with fenoxaprop-P-ethyl at 62.1 g a.i. ha−1 and mesosulfuron-methyl at 9 g a.i. ha−1 (i.e., field-recommended rates) [25]. The RNA extraction (0, 12, 24, and 36 h after the herbicide treatment) and cDNA synthesis were performed as described above.
The RNA results showed that it was not degraded and met the experimental requirements. Through database comparison and using the ORF Finder tool, the ORF of the GT73C1 gene was obtained, which was 1491 bp, encoding 496 amino acids. The agarose gel electrophoresis results of the PCR products showed a single band at about 1500 bp, as predicted (Fig. 1). There were no amino acid differences between RF3 and SF3 GT73C1, and the gene was as predicted by ORF of transcriptome sequencing (Supplementary Fig. 1).
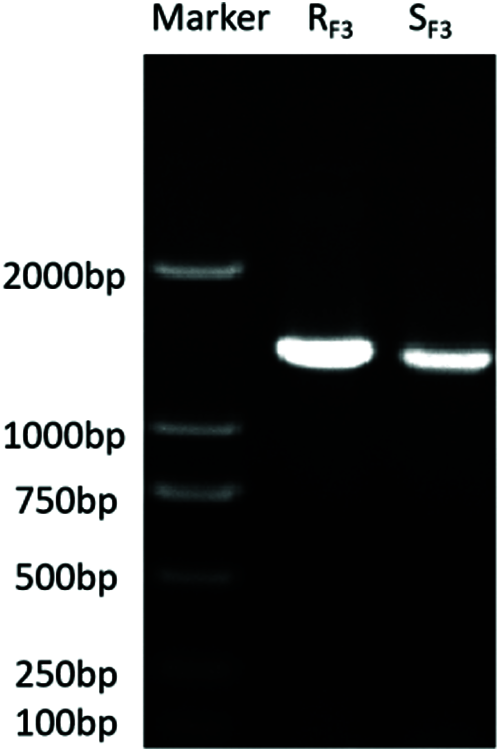
Figure 1: Electrophoresis of the GT73C1 gene amplified by RT-PCR
3.2 Sequence Analysis of the GT73C1 Gene
The phylogenetic tree showed that GT73C1 was closely related to the other GT family proteins (Fig. 2). The pI of the GT73C1 protein was 5.23 and the molecular weight was 54878.23 Daltons (Supplementary Fig. 2).
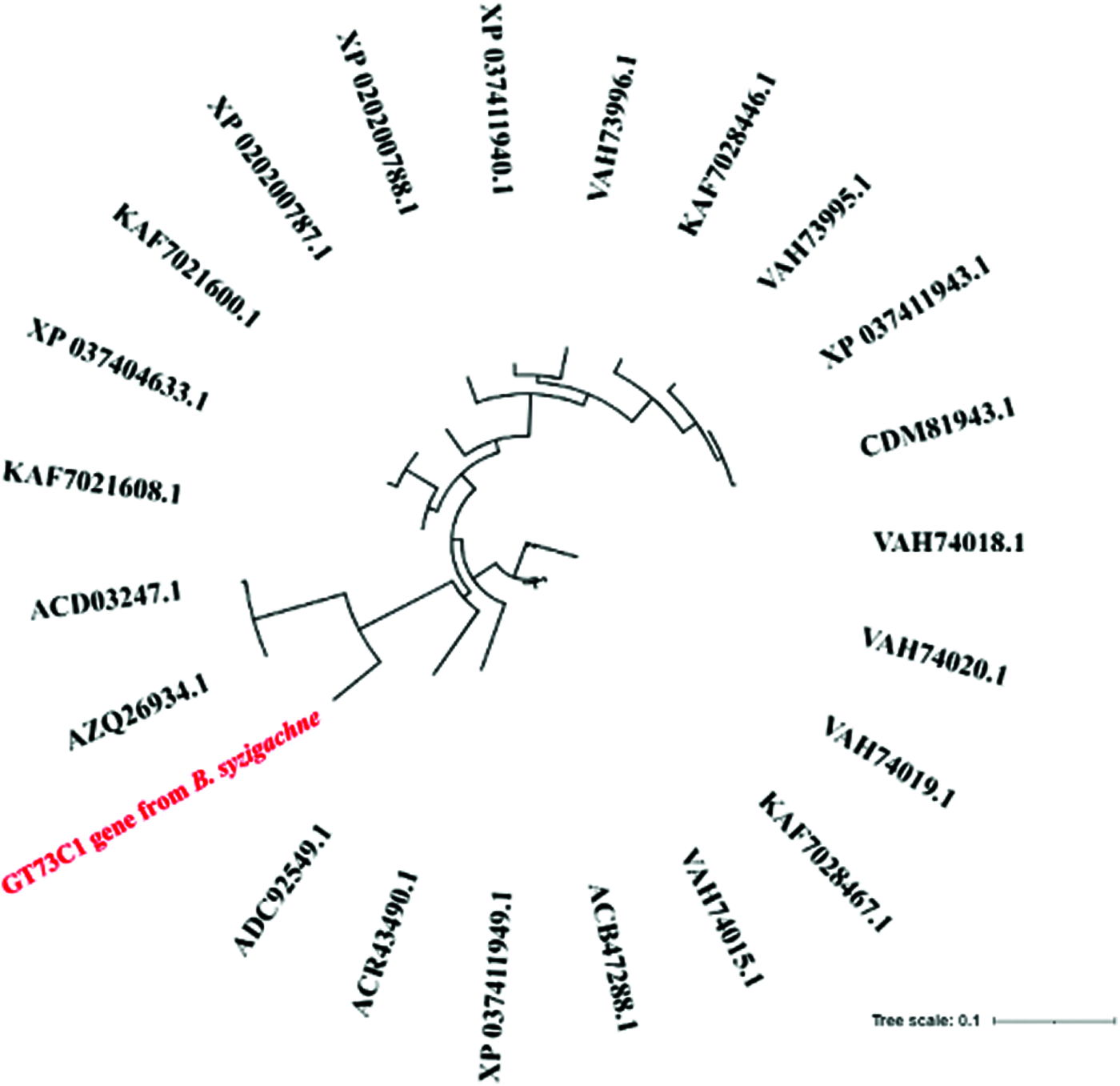
Figure 2: Phylogenetic analysis of the GT73C1 gene extracted from B. syzigachne
3.3 Induction of Embryogenic Callus and Construction of Plant Overexpression Vector
Compact and globular calluses of B. distachyon of about 5 mm in diameter were collected for Agrobacterium infection. The enzyme-digested products of positive plasmids and pPZP211 vector were examined through agarose gel electrophoresis, confirming the completion of digestion (Fig. 3a). The EHA105 suspension was also examined by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the positive bacterial suspension was selected for transformation (Fig. 3b).
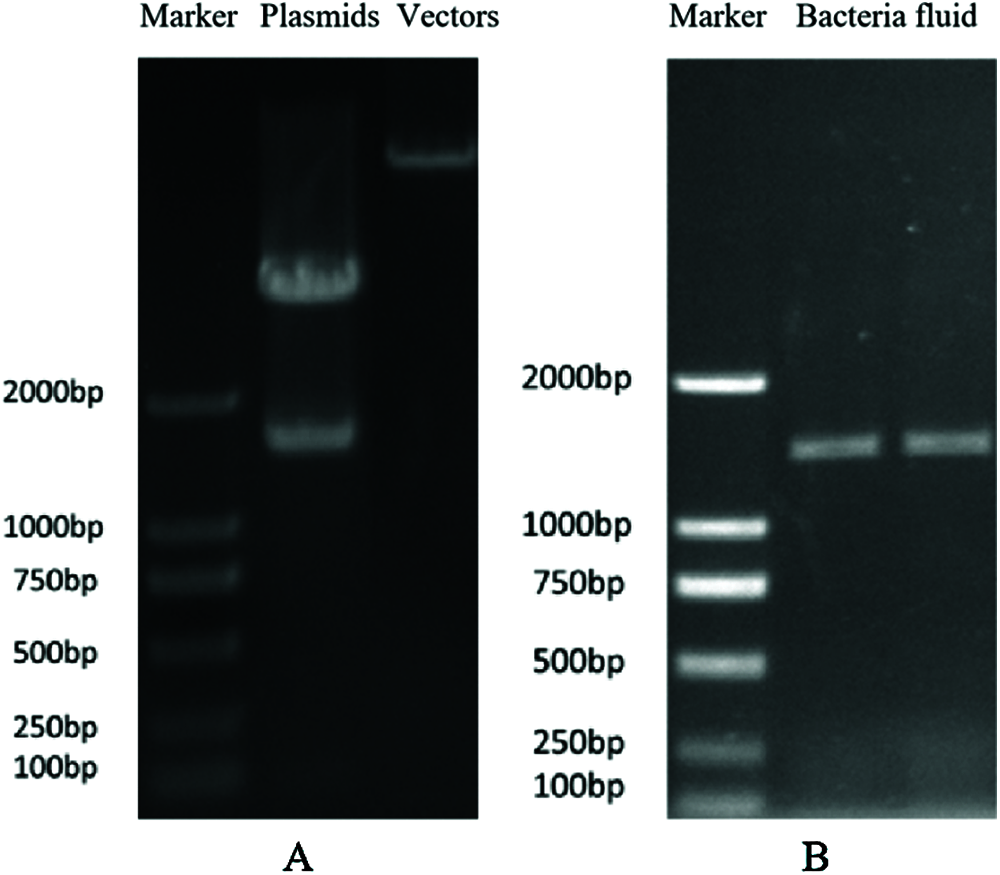
Figure 3: Construction of plant overexpression vector. (A) The identification of restriction enzyme digestion of plasmids and vectors; (B) The detection of positive bacterial suspension by PCR amplification
3.4 Acquisition of Transgenic Plants
A total of 22 transgenic plants of B. distachyon were generated from 30 hygromycin-resistant calluses. The RT-PCR result showed that 17 out of the 22 plants were positive for GT73C1. The 17 positive plants (T0) were cultivated under the same conditions for obtaining progenies (T1). The offspring of the non-transformed plants (NT0) and wild plants (WT0) were also obtained.
3.5 The Bioassay of Positive Transgenic Plants
The whole plant bioassay results showed no visible injury symptoms in T1 plants of B. distachyon. However, the NT1 and WT1 plants appeared in general less robust and shorter than T1 plants, which was independent of the fenoxaprop-P-ethyl or mesosulfuron-methyl treatment (Fig. 4).
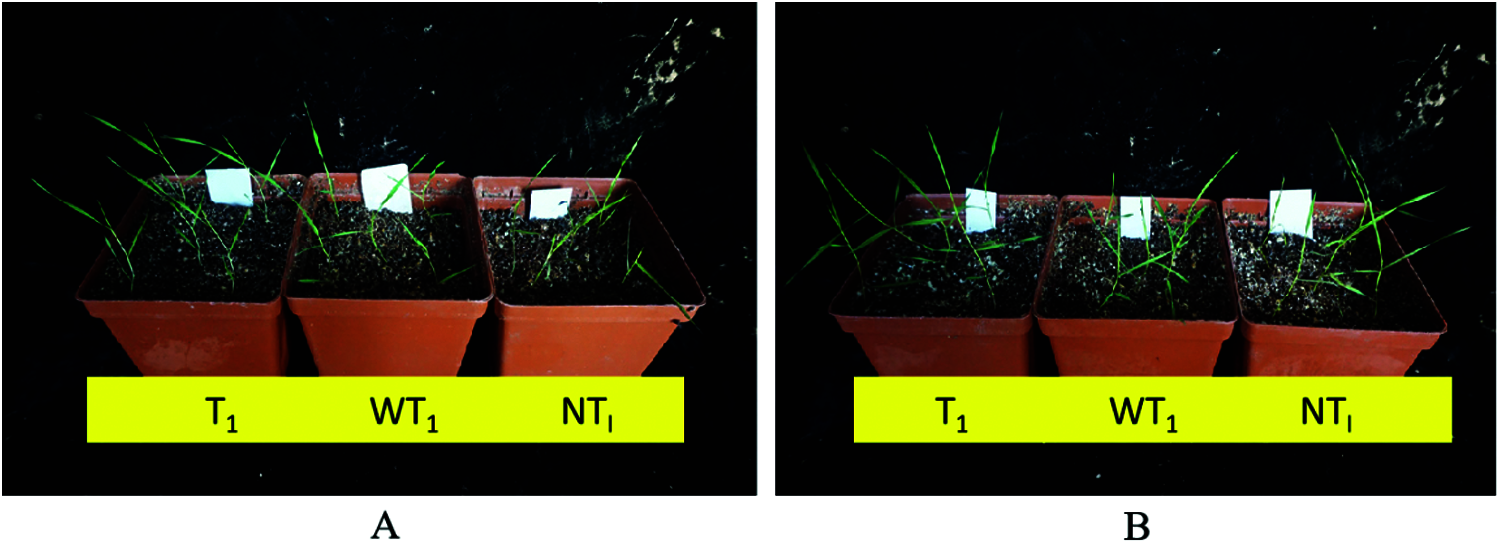
Figure 4: The bioassay of positive transgenic plants. (A) The bioassay of positive transgenic plants at 21 d after fenoxaprop-P-ethyl field-recommended rate treatment; (B) The bioassay of positive transgenic plants at 21 d after mesosulfuron-methyl field-recommended rate treatment
3.6 Expression Patterns of the GT73C1 Gene
The 22 positive T1 B. distachyon plants were used to analyze the expression patterns of GT73C1. The results of qRT-PCR showed that fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl could induce a high expression of the GT73C1 gene. This indicated that GT73C1 mediates the metabolic resistance to fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl (Fig. 5).
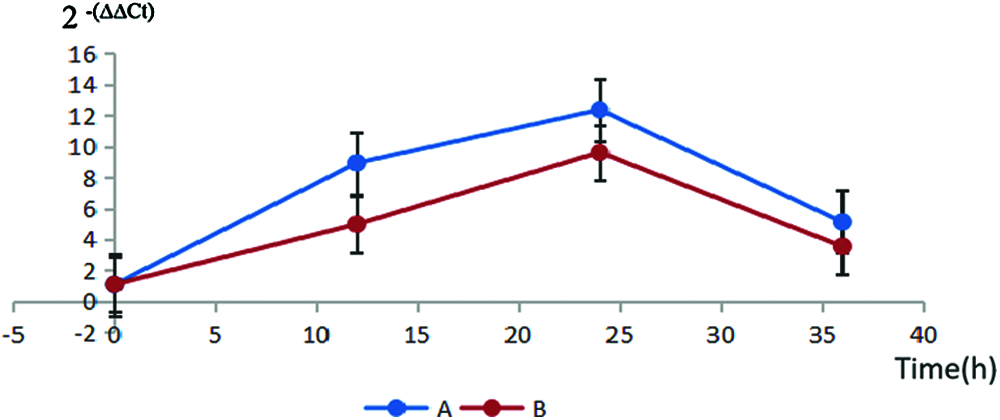
Figure 5: Transcriptional level of the GT73C1 gene in positive B. distachyon. (A) The fenoxaprop-P-ethyl field-recommended rate treatment; (B) The mesosulfuron-methyl field-recommended rate treatment; Error bars indicate standard deviations
Multiple studies have reported NTSR to herbicides by metabolic detoxification, based on the results from transcriptomics and proteomics. The miR397 gene from B. syzigachne (referred to as bsy-miR397) was functionally characterized to determine its role in regulating fenoxaprop-P-ethyl resistance by transgenic technology (Nicotiana tabacum L. and Oryza sativa L.) [21]. In the present study, a solely NTSR-based population with no TSR involvement was selected for identifying herbicide metabolic detoxification genes [24]. For further gene function verification, we utilized transgenic B. distachyon to characterize the role of a metabolic gene. Brachypodium distachyon, a member of the Pooideae subfamily, is a small grass with biological attributes (small genome, diploid accessions, small stature and many tillers) suitable to be used as a model system.
Glycosylation, which is mediated by the UDP-glycosyltransferase, participates in plant resistance against xenobiotic compounds (such as herbicides) [25]. Therefore, this study selected GT73C1 as the target gene. The phylogenetic tree showed that GT73C1 is closely related to other GT family proteins, which have evolved as part of the resistance mechanisms in many plants, such as in Triticum aestivum [13]. Bioinformatics software and online tools can provide useful information for determining the functions of unknown proteins. Sequence analysis of GT73C1 showed no amino acid differences between RF3 and SF3. This result indicated that the high expression of GT73C1 might be one of the important causes of resistance in B. syzigachne, rather than the mutations in metabolizing genes.
Transgene technology is effective in verifying the functions of unknown genes. The RT-PCR detection of T1 plants of Brachypodium showed that 77% of the seedlings were positive, which indicated a potential separation of the GT73C1 gene. The expression of GT73C1 in the transformed plants of Brachypodium was induced by fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl, indicating that this gene might be closely related to the metabolic resistance towards fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl. The whole plant bioassay further supported this hypothesis.
We successfully isolated and amplified the metabolic resistance gene (GT73C1). The phylogenetic tree showed that GT73C1 is closely related to other GT family proteins. The overexpression of GT73C1 in the positive B. distachyon plants indicated that GT73C1 is closely related to the metabolic poly-resistance towards fenoxaprop-P-ethyl and mesosulfuron-methyl, which was further verified by the whole plant bioassay.
Acknowledgement: We thank Professor Hailong An (Shandong Agricultural University) for providing B. distachyon (ecotype Bd21) and acknowledge TopEdit LLC for the linguistic editing and proofreading during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding Statement: This study was supported by the (1) Scientific Research Foundation for Ph.D. Programs of Zaozhuang University (21/1020708), (2) Science and Technology Program of Zaozhuang (2020NS20), (3) Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (J18KA134), and (4) Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2019PC011).
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
1. Kaur, T., Kaur, N., Bhullar, M. S. (2018). Ecological methods for weed management. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews, 31, 179–216. DOI DOI10.1007/978-3-319-94232-2_4. [Google Scholar]
2. Li, L., Du, L., Liu, W., Yuan, G., Wang, J. (2014). Target-site mechanism of ACCase-inhibitors resistance in American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne Steud.) from China. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology, 110, 57–62. DOI 10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.03.001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
3. Whitehead, C. W., Switzer, C. M. (1963). The differential response of strains of wild carrot to 2, 4-D and related herbicides. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 43(3), 255–262. DOI 10.4141/cjps63-052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
4. Wang, M., Liu, B., Li, Y., Luo, X., Li, L. (2019). Non-target site based resistance to the ALS-inhibiting herbicide mesosulfuron-methyl in American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne). Weed Science, 67(5), 527–533. DOI 10.1017/wsc.2019.22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
5. Li, L., Bi, Y., Liu, W., Yuan, G., Wang, J. (2013). Molecular basis for resistance to fenoxaprop-P-ethyl in American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne Steud.). Pesticide Biochemistry Physiology, 105, 118–121. DOI 10.1016/j.pestbp.2012.12.007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
6. Li, L., Liu, W., Chi, Y., Guo, W., Luo, X. et al. (2015). Molecular mechanism of mesosulfuron-methyl resistance in multiply-resistant American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne). Weed Science, 63(4), 781–787. DOI 10.1614/WS-D-15-00026.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
7. Neve, P., Vila-Aiub, M., Roux, F. (2009). Evolutionary-thinking in agricultural weed management. New Phytologist, 184, 783–793. DOI 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03034.x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
8. Dayan, F. E., Barker, A., Bough, R., Ortiz, M., Takano, H. et al. (2019). Herbicide mechanisms of action and resistance. In: Moo-Young, M. (Ed.Comprehensive biotechnology. 3rd ed, pp. 36–48. Oxford: Pergamon Press. DOI 10.1016/B978-0-444-64046-8.00211-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
9. Powles, S. B., Yu, Q. (2010). Evolution in action: Plants resistant to herbicides. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 61, 317–347. DOI 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
10. Délye, C. (2005). Weed resistance to acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase inhibitors: An update. Weed Science, 53, 728–746. DOI 10.1614/WS-04-203R.1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
11. Délye, C. (2013). Unravelling the genetic bases of non-target-site-based resistance (NTSR) to herbicides: A major challenge for weed science in the forthcoming decade. Pest Management Science, 69, 176–187. DOI 10.1002/ps.3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
12. Han, H., Yu, Q., Vila-Aiub, M., Powles, S. B. (2014). Genetic inheritance of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolic resistance to chlorsulfuron in a multiple herbicide resistant Lolium rigidum population. Crop Protection, 65, 57–63. DOI 10.1016/j.cropro.2014.06.026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
13. Yu, Q., Han, H., Li, M., Purba, E., Walsh, M. J. et al. (2012). Resistance evaluation for herbicide resistance endowing acetolactate synthase (ALS) gene mutations using Raphanus raphanistrum populations homozygous for specific ALS mutations. Weed Research, 52, 178–186. DOI 10.1111/j.1365-3180.2012.00902.x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
14. Martin, J. A., Wang, Z. (2011). Next-generation transcriptome assembly. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12, 671–682. DOI 10.1038/nrg3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
15. Pan, L., Gao, H., Xia, W., Zhang, T., Dong, L. (2016). Establishing a herbicide-metabolizing enzyme library in Beckmannia syzigachne to identify genes associated with metabolic resistance. Journal of Experimental Botany, 67, 1745–1757. DOI 10.1093/jxb/erv565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
16. Rey-Caballero, J., Menéndez, J., Osuna, M. D., Salas, M., Torra, J. (2017). Target-site and non-target-site resistance mechanisms to ALS inhibiting herbicides in Papaver rhoeas. Pesticide Biochemistry Physiology, 138, 57–65. DOI 10.1016/j.pestbp.2017.03.001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
17. Ozsolak, F., Milos, P. M. (2011). RNA sequencing: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12, 87–98. DOI 10.1038/nrg2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
18. Liu, W., Bai, S., Zhao, N., Jia, S., Li, W. et al. (2018). Non-target site-based resistance to tribenuron-methyl and essential involved genes in Myosoton aauaticum (L.). Plant Biology, 18, 225–238. DOI 10.1186/s12870-018-1451-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
19. Zhao, N., Yan, Y., Wang, H., Bai, S., Wang, Q. et al. (2018). Acetolactate synthase overexpression in mesosulfuron-methyl-resistant shortawn foxtail (Alopecurus aequalis Sobol.Reference gene selection and herbicide target gene expression analysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 66, 9624–9634. DOI 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
20. Wang, J., Li, X., Li, D., Han, Y., Li, Z. et al. (2018). Non-target-site and targetsite resistance to AHAS inhibitors in American sloughgrass (Beckmannia syzigachne). Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 17, 30345–30347. DOI 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62021-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
21. Pan, L., Zhao, H., Yu, Q., Bai, L., Dong, L. (2017). MiR397/Laccase gene mediated network improves tolerance to fenoxaprop-P-ethyl in Beckmannia syzigachne and Oryza sativa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 879. DOI 10.3389/fpls.2017.00879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
22. Li, Q., Wang, Y., Wang, F., Guo, Y., Duan, X. et al. (2016). Functional conservation and diversification of APETALA1/FRUITFULL genes in Brachypodium distachyon. Physiologia Plantarum, 157(4), 507–518. DOI 10.1111/ppl.12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
23. Draper, J., Mur, L., Jenkins, G., Ghosh-Biswas, G., Bablak, P. et al. (2001). Brachypodium distachyon. A new model system for functional genomics in grasses. Plant Physiology, 127, 1539–1555. DOI 10.1104/pp.010196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
24. Li, W., Zhang, L., Zhao, N., Guo, W., Liu, W. et al. (2017). Multiple resistance to ACCase and ALS-inhibiting herbicides in Beckmannia syzigachne (Steud.) Fernald without mutations in the target enzymes. Chilean Journal of Agricultural Research, 77(3), 257–265. DOI 10.4067/S0718-58392017000300257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
25. Gaines, T. A., Duke, S. O., Morran, S., Rigon, C. A., Tranel, P. J. et al. (2020). Mechanisms of evolved herbicide resistance. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 295(30), 10307–10330. DOI 10.1074/jbc.REV120.013572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
26. Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Research, 32(5), 1792–1797. DOI 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
27. Capella-Gutiérrez, S., Silla-Martínez, J. M., Gabaldón, T. (2009). TrimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics, 25(15), 1972–1973. DOI 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
28. Darriba, D., Posada, D., Kozlov, A. M., Stamatakis, A., Morel, B. et al. (2020). ModelTest-NG: A new and scalable tool for the selection of DNA and protein evolutionary models. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 37(1), 291–294. DOI 10.1093/molbev/msz189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
29. Kozlov, A. M., Darriba, D., Flouri, T., Morel, B., Stamatakis, A. (2019). RAxML-NG: A fast, scalable and user-friendly tool for maximum likelihood phylogenetic inference. Bioinformatics, 35(21), 4453–4455. DOI 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
30. Hajdukiewicz, P., Svab, Z., Maliga, P. (1994). The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Molecular Biology, 25(6), 989–994. DOI 10.1007/BF00014672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
31. Christensen, A. H., Sharrock, R. A., Quail, P. H. (1992). Maize polyubiquitin genes: Structure, thermal perturbation of expression and transcript splicing, and promoter activity following transfer to protoplasts by electroporation. Plant Molecular Biology, 18(4), 675–689. DOI 10.1007/BF00020010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
32. Livak, K. J., Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(t)) method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408. DOI 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
ATGACCTTCGCCGGCGGCGGCAATGGCCAGATCGGCTCCACGAGGGCGCACTTCGTGCTGGTCCCAATGATGGCGCAGGGCCACACCATCCCCATGACGGACATGGCGCGCCTCCTGGCCGAGCATGGCGCGCAGGTCAGCTTCATCACCACACCGGTGAACGCCTCCAGGTTGGCAGGCTTCGCCGCCGATGTGGAGAGAGCGGGACTGGCGGTCCGGCTCGTGGAGCTCCGCTTCCCGGCCGCCGAGTTCGGCCTACCGGACGGGTGCGAGAACCTCGACTTGATCCAGTCCAAGGGTCTGTTCCTGAACTTCATGGAGGCCTGCGCCGCGCTGAGGGAGCCGTTAATGACGCACCTCCGTGAGCAGCAGCTCTCGCCCCCAAGCTGCATCATTTCTGACATGATGCACTGGTGGACCGGTGACATTGCAAGGGAGCTCGGTATCCCGAGGCTCACCTTTATCGGCTTCTGTGGCTTCTCCTCCCTTGCCAGGTACATCATCTCTCAGAACAACTTGCTGGAAAACGTCACAGATGAAAATGAGCTTGTCAGGATTCCAGGGTTCCCTACACAACTAGAGTTGACGAAGGATAAATGTCCTGGAAGCCTTTCCGTTCCAGGCATGGAGAAAATCCGTGAGAAGATGATTGAGGAGGAGCTGAGATGCGATGGTGAGGTCGTTAACACTTTCCAAGAGCTAGAGACATTGTACATTGAATCCCTTGAGCAAGTGACAAGGAAGAAGGTCTGGACGGTCGGGCCAATGTGCCTCTCCCACCGAGACAGCAACACAATGTCCGCAAGAGGAAACAAGGCATCGATGGATGAGGCACAGTGCTTGCAGTGGCTTGATTCAATGAAGCCAGGCTCAGTAATCTTTGTCAGCTTTGGCAGCCTCGCTGCCACTACACCTCAACAGCTTGTTGAGCTGGGACTGGGACTTGAAGCCTCCAAGAAACCGTTTATTTGGGTGATCAAAGCAGGGGCTAAGTTTCCAGAGGTCGAGGAATGGCTCGCAGATGGGTTCGAGGAGCGTGTCAAAGACAGAGGCATGATCATAAGAGGCTGGGCGCCACAGGTAATGATCTTGTGGCACCAAGCCATTGGGGGATTTGTGACGCACTGTGGGTGGAACTCAACAATAGAGGGCATCTGTGCAGGTGTGCCCATGATCACATGGCCACACTTTGCGGAGCAATTTTTGAATGAGAAGCTGGTTGTCGATGTGCTGAAAATTGGGTTGGAGGTTGGAGTGAAAGGAGTTACACAGTGGGGAAACGAACAACAAGAGGTTATGGTTACAAGAGATGCTGTGGAGACAGCAGTGTACACCTTGATGGGTGAGGGGGAGGCTGCAAAGGAGTTGAGAATGCGAGCAAAAGACTATGCCATTAAGGCAAGGAGGGCTTTCGACGAGGAAGGTTCTTCATATAACAACGTAAAGCTATTAATTCAAGAAATGGGAAATAAGACGAATGCAGGTGGCTGA
Figure S1: The alignment of amplified GT73C1 gene (from RF3 and SF3) and RNA-seq of B. syzigachne
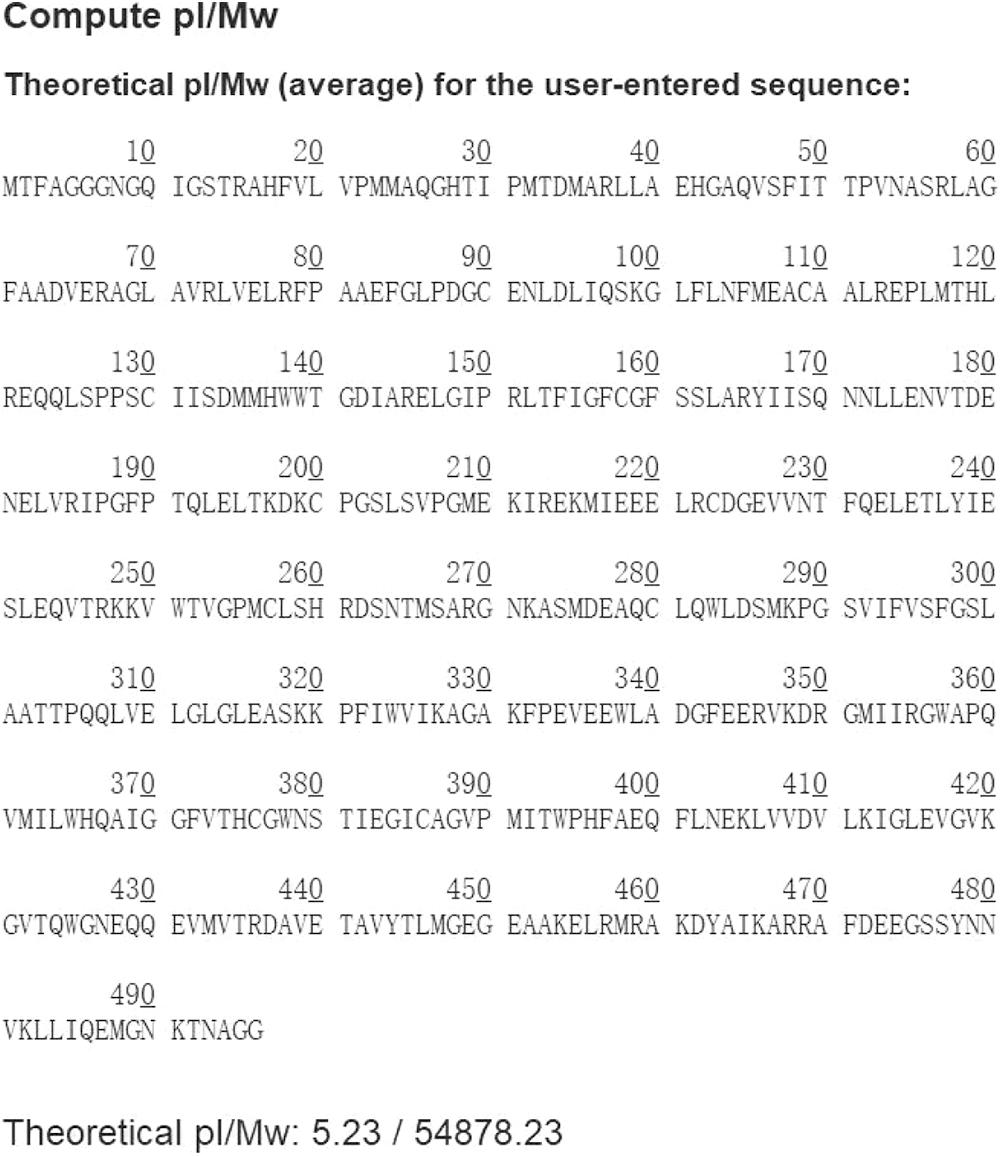
Figure S2: The pI and molecular weight of GT73C1 protein
 | This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. |