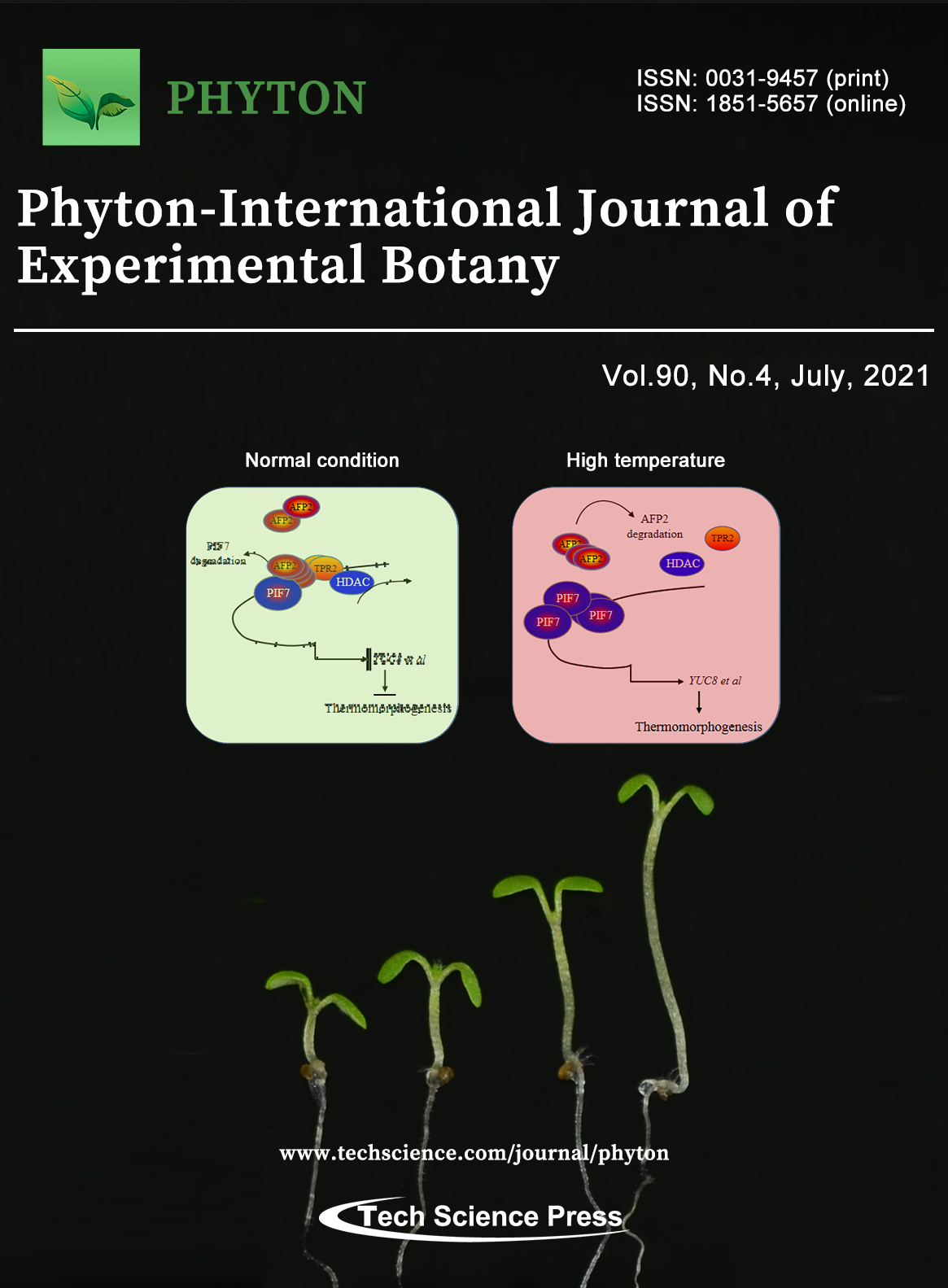
Ambient temperature induces the hypocotyl elongation of seedling, called as thermomorphogenesis. In this issue, Deng et al. found that the canonical bHLH transcriptional factor PIF7 mediates the seedling thermomorphogenesis in the model plant Arabidopsis. During this process, an essential regulator AFP2, which is previously reported to be associated with abscisic acid signal, interacts with PIF7, thus fine turns the transcriptional activity, subsequently precisely modulates downstream auxin biosynthesis to coordinate hypocotyl elongation.
View this paper