 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Genome-Wide Identification of the MYB Gene Family and Screening of Potential Genes Involved in Fatty Acid Biosynthesis in Walnut
1 College of Horticulture and Gardening, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, 434025, China
2 Lhasa Municipal Forestry and Grassland Bureau, Lhasa, 850000, China
3 Agro-Tech Extension and Service Center, Shannan, 856000, China
* Corresponding Author: Feng Xu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Plant Secondary Metabolism and Functional Biology)
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany 2024, 93(9), 2317-2337. https://doi.org/10.32604/phyton.2024.055350
Received 24 July 2024; Accepted 19 August 2024; Issue published 30 September 2024
Abstract
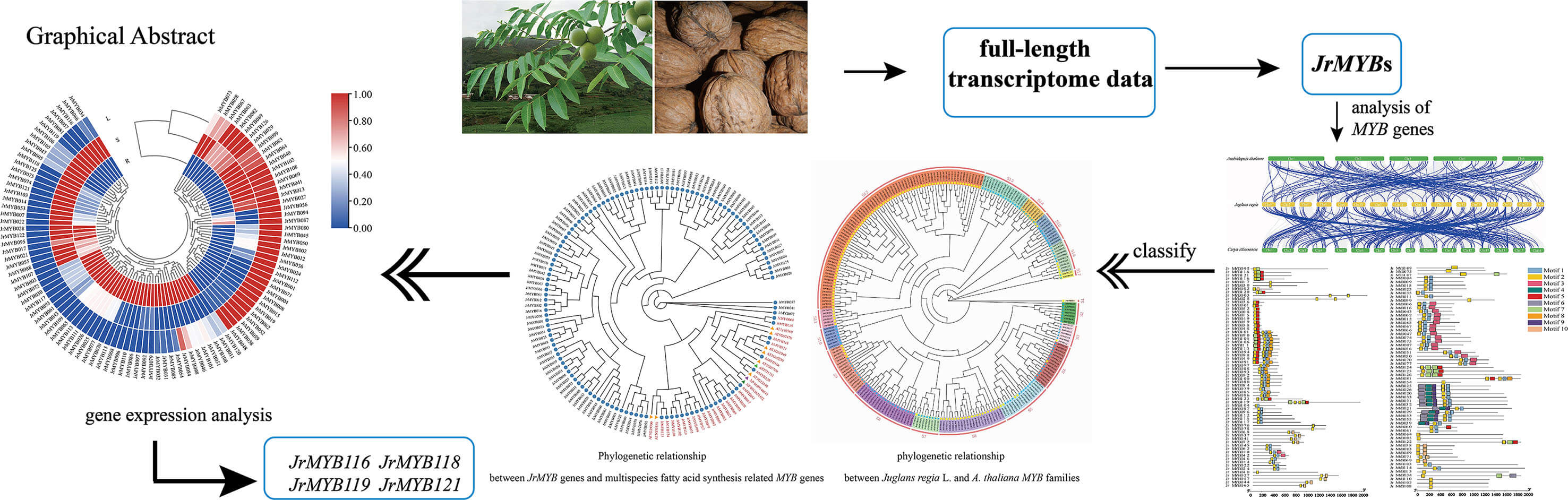
The multifaceted roles of MYB transcriptional regulators are pivotal in orchestrating the complex processes of secondary metabolism, stress tolerance mechanisms, and life cycle progression and development. This study extensively examined the JrMYB genes using whole genome and transcriptomic data, focusing on identifying putative MYB genes associated with fatty acid metabolism. 126 MYB genes were identified within the walnut genome, characterized by hydrophilic proteins spanning lengths ranging from 78 to 1890 base pairs. Analysis of cis-acting elements within the promoter regions of MYB genes revealed many elements linked to cell development, environmental stress, and phytohormones. Transcriptomic data was utilized to examine the role of JrMYB genes in the biosynthesis of fatty acids in walnuts. The results revealed diverse expression of these genes across various tissue sites, displaying varying levels and distinct expression patterns. Furthermore, by integrating the results of the phylogenetic tree with the correlation of expression levels, a total of 10 genes potentially involved in the regulation of fatty acid synthesis were screened. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis was conducted on these 10 genes and further identified 4 candidate genes, and a transcription regulatory network involved in fatty acids metabolism was constructed. This study presents a systematic analysis of JrMYB genes, laying the groundwork for an in-depth exploration of the JrMYB genes family’s function in regulating fatty acid synthesis.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools