 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ruikang Ma1, Guangfei Wei2, Songzi Li2, Tongle Li1, Fugang Wei3, Yong Wang4, Guozhuang Zhang2,*, Linlin Dong1,2,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.075657
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Endophytic Microbiota: Prospects and Challenges for Application Towards Sustainable Agriculture and Environmental Management)
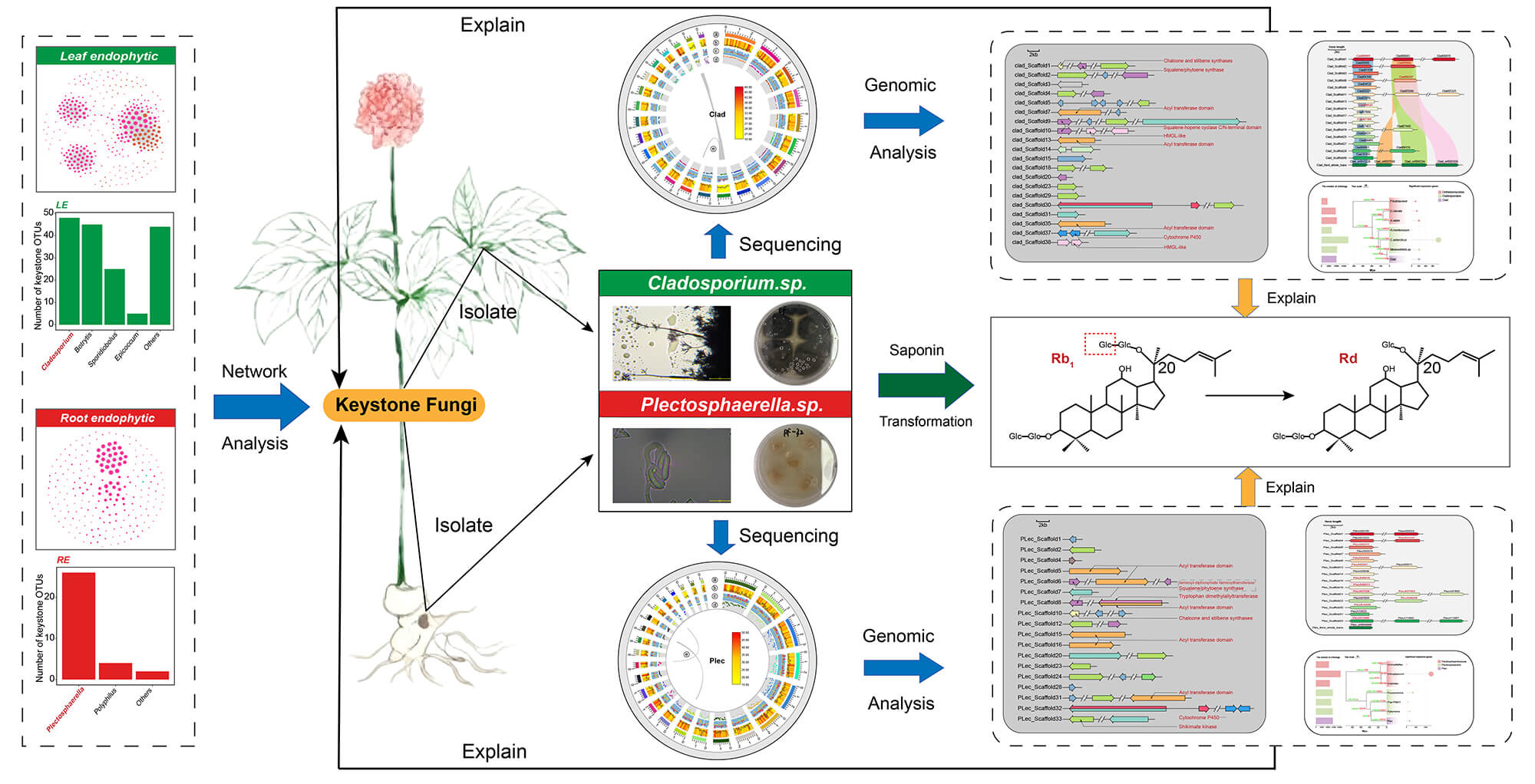
Abstract Keystone taxa are critical for microbial community homeostasis and ecological niche interactions. However, the functions and genomic traits of endophytic keystone fungi in plant tissues remain unclear. Via network analysis, this study identified keystone fungi Plectosphaerella (Plec) and Cladosporium (Clad) in roots/leaves of medicinal Panax plants (P. ginseng, P. quinquefolius, P. notoginseng). Both correlated strongly positively with ginsenoside Rd content in respective tissues (ρ > 0.6, p < 0.001). Co-cultivation confirmed their ability to convert ginsenoside Rb1 to Rd, linked to β-glucosidase activity. Whole-genome sequencing/assembly/evolutionary analysis of the two strains elucidated genomic features for their keystone roles and saponin biotransformation. More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiao Wang*, E Liang, Xiaohui Song, Deyan Li
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.075656
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Plant Responses and Adaptations to Environmental Stresses)
Abstract Three-year-old Panax japonicus was exposed to elevated CO2 concentrations using open-top chambers: ambient CO2 (aCO2), moderately elevated (e1CO2, 550 μmol/mol), and highly elevated (e2CO2, 750 μmol/mol). Gas exchange parameters, photosynthetic pigments, sugar accumulation, and total saponin content were measured to assess the effects of CO2 enrichment on photosynthesis, sugar metabolism, and saponin biosynthesis. The e1CO2 treatment significantly increased net photosynthetic rate (by 17.22% at 36 days and 69.62% at 92 days), chlorophyll a content, and soluble sugar, sucrose, and starch accumulation. Key sugar metabolism enzymes, including sucrose phosphate synthase (SPS), also showed enhanced activity. Consequently, underground rhizome total saponins rose More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Li Wang1,2, Jinfeng Zhang2, Binbin Li2, Zhengbo Pen3, Zhiyuan Yang3,*, Anshu Rastogi4,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.075709
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Crop Managements and Crop Adversity: Strategies, Mechanisms, and Implements)
Abstract Chilo suppressalis (Walker) is one of the most important rice pests worldwide, posing a significant challenge to effective control. To develop a precision-timed, eco-friendly management strategy, overwintering population investigation and dynamic monitoring of C. suppressalis populations were conducted in the Meishan region of Sichuan, China, from 2023 to 2024. The optimal timing for insecticide application was estimated, followed by field trials evaluating the efficacy of different insecticides. Results demonstrated that the peak emergence of first-generation adults typically occurred in early July (under the environmental conditions of the Meishan region), with the ambient humidity below 75% and temperature… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Miguel Ángel De los Santos-Santos1, Rosendo Balois-Morales1,2, Juan Esteban Bello-Lara2, José Orlando Jiménez-Zurita2, Graciela Guadalupe López-Guzmán2, Efigenia Montalvo-González3, Guillermo Berumen-Varela4, Carlos Azhael Rodríguez-Guzmán2, Andrés Eloy León-Fernández2,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.076197
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in the Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Fruit Ripening in Tropical Fruits)
Abstract Acetogenins are lipidic polyketides with antioxidant, antimicrobial, cytotoxic, and antitumor properties, mainly found in the roots, stems, bark, leaves, and fruits (particularly the seeds) of Annonaceae species. Previous studies have identified acetogenins in the peel and pulp of soursop (Annona muricata L.) fruits. In this research, acetogenins present in starch and pectin extracted from these fruits were analyzed and identified, given their potential importance in the pharmaceutical and possibly in the food industries. The objective was to identify and quantify acetogenins in starch and pectin of soursop fruits. Extraction of both polysaccharides was performed using conventional… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hui Zhang1, Yingchun He1, Min Hong2, Yang Wang3, Mingzhang Li1, Qiguo Zhuang1, Kui Du1, Yue Xie1,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.074974
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Plant Breeding and Genetic Improvement: Leveraging Molecular Markers and Novel Genetic Strategies)
Abstract The genus Actinidia is primarily functionally dioecious, and early sex identification plays a crucial role in improving breeding efficiency and reducing production costs. In this study, the accuracy of three sex-linked molecular markers (SyGI [Shy Girl], FrBy [Friendly Boy], and SmY1) in sex identification was evaluated in various Actinidia species. The selected marker products were subsequently cloned and sequenced in six wild Actinidia species. Ninety-six wild A. chinensis chinensis accessions and 74 A. chinensis deliciosa accessions, most of which were wild, with only one cultivated, were used for comprehensive primer validation. Thirty-three juvenile A. chinensis chinensis hybrid seedlings were used for practical application… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Geng Zhang1, Xiangyu Ding2, Zidan Wen2, Chao Liu2, Duyen T. P. Nguyen3, Jinxiu Song4, Zejin Zhang5, Zhiming Yan1,6, Yuanhua Wang1,*, Zhengnan Yan2,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.077381
Abstract As a pivotal environmental factor, light, comprising intensity, photoperiod, and spectrum, governs the entire life cycle of strawberries by mediating alterations in the plant’s morphological, physiological, and biochemical traits. Although extensive research has been conducted on light-mediated growth regulation in horticultural crops, most reviews focus primarily on leafy and fruiting vegetables, with limited attention given to berry crops such as strawberries. Additionally, most existing reviews concentrate on one or several growth stages, failing to systematically characterize light’s effects throughout the entire growth cycle and postharvest stage. This review briefly summarizes the regulatory roles of light More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shaimaa R. Ahmed1,*, Omnia M. Hendawy2, Sumera Qasim2, Hanan Khojah3, Ambreen Malik Uttra4
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.075718
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Plant-Derived Natural Products: Phytochemical Diversity and Functional Properties)
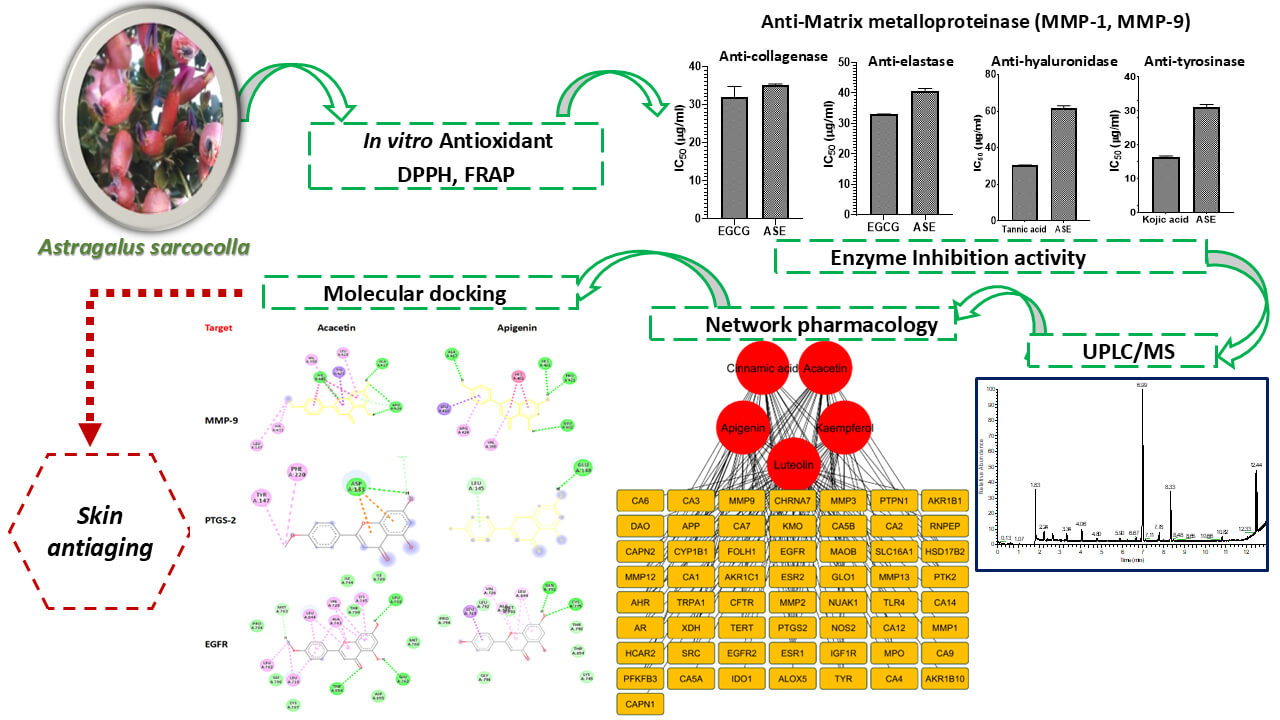
Abstract The study evaluated the skin anti-aging activity of Astragalus sarcocolla leaves extract (ASE) by assessing its antioxidant and inhibitory effect activity on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), collagenase, elastase, hyaluronidase, and tyrosinase in relation to its chemical composition. Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) identified 27 metabolites (15 flavonoids, 8 phenolic acids and their derivatives, and 4 coumarins). ASE showed strong antioxidant capacity in DPPH (IC50 value of 26.05 µg/mL) and FRAP (2433 µM FeSO4/g extract) assays. The extract inhibited MMP-1 and MMP-9 in a concentration-dependent manner and suppressed collagenase, elastase, hyaluronidase, and tyrosinase activities (IC50 = 35.038, 40.748, 61.389,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Manar Bouhchich1, Abdessadek Rahimi1, Rhizlan Abdnim2, Amine Elbouzidi3,*, Mohamed Addi3, Mostafa Mimouni1
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.074293
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Medicinal Plants and Natural Bioactives: From Pharmacology to Cosmeceutical Innovation)
Abstract Date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) seeds, often discarded as by-products during date fruit processing, represent approximately 6–20% of the fruit’s mass depending on cultivar and maturity stage. Although traditionally used for producing activated charcoal and in environmental remediation, their pharmacological potential remains underexplored. This study aimed to evaluate the chemical composition, biological activity, and potential commercial value of seeds from four widely consumed Saharan cultivars (Assiane, Boufegouss, Aziza, and Majhoul) collected in the Figuig region. Soxhlet extraction was employed to obtain seed extracts, which were subsequently characterized by qualitative and quantitative phytochemical screening. The analyses revealed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Lu Lu1,#, Zewei Lu1,#, Wenwu Zou2,3,#, Kun Li1, Jing Liu2, Jiahao Pan4, Mintao Sun1, Jun Wang1, Yansu Li1,*, Yan Yan1,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.074706
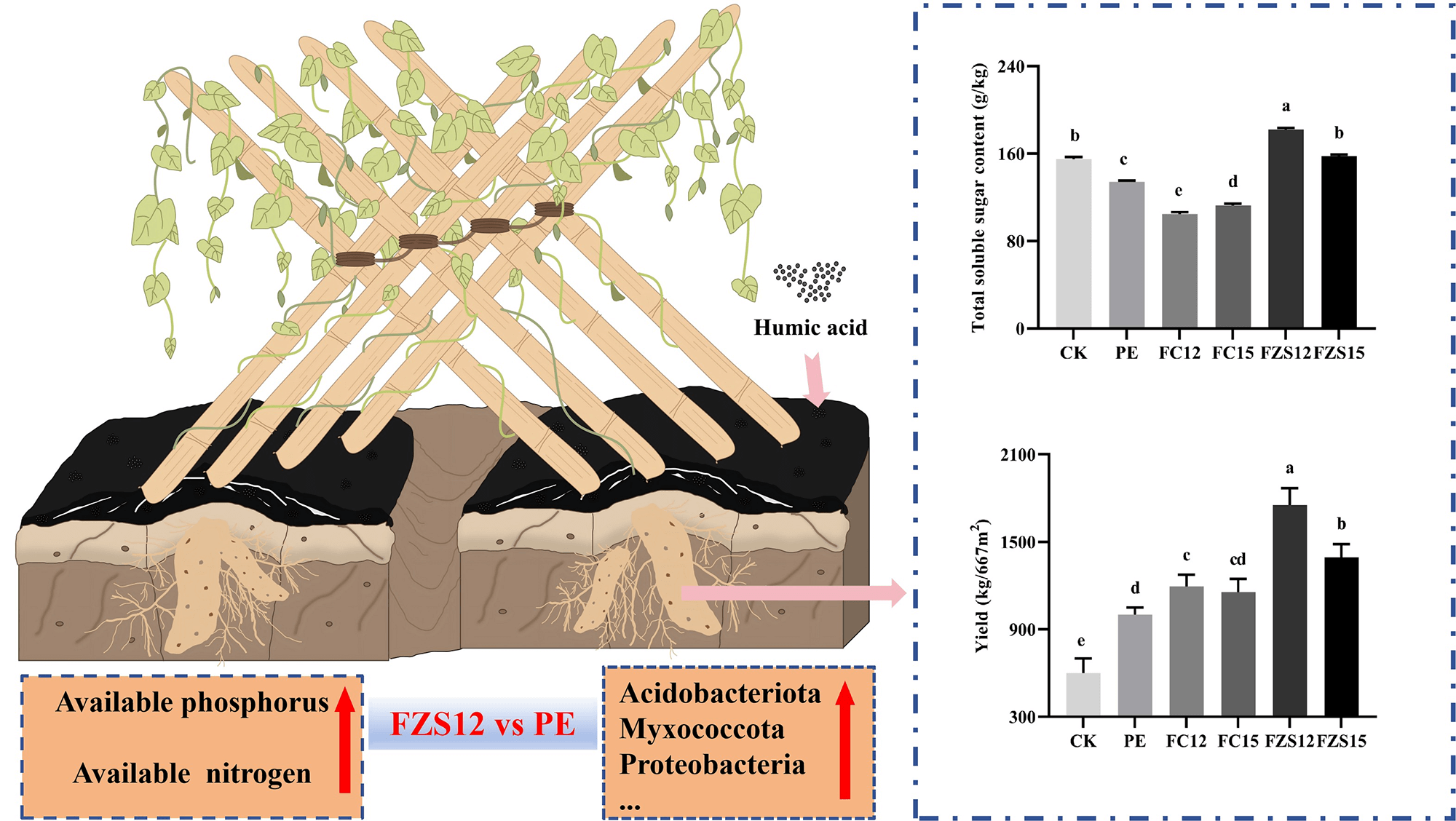
Abstract To address the issue of residual pollution caused by polyethylene mulch, this study explored the effects of different mulching methods on the soil environment of the yam field, as well as on yam yield and quality. The experiment comprised six treatments in total: one non-mulched treatment served as the control (CK), along with five different film-mulched treatments, namely PE, FZS12, FZS15, FC12, and FC15. The degradation of these films and their effects on soil physicochemical properties, microbial community, yam yield and quality were compared. The results showed that the FZS12 treatment achieved grade 5 degradation… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shizhou Yu1,2, Jie Zhang1, Linggai Cao1, Jie Liu1, Peng Lu3, Jiemeng Tao3, Xueliang Ren1, Zhixiao Yang1,2,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.073509
Abstract Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum, 2n = 48) is a key non-food economic crop, yet its stress response and gene regulatory mechanisms remain poorly understood. By analyzing 603 transcriptome datasets, this study identified 1405 tissue-specific genes, revealing tissue-specific synthesis of terpenoids and other ecologically important secondary metabolites in sepals and other tissues. Comparative stress-response analysis highlighted distinct gene expression patterns in leaves and roots under biotic and abiotic stresses. Additionally, 28,396 expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) were mapped in leaves, offering valuable genetic regulatory markers. These findings provide crucial insights into tobacco’s gene expression characteristics and their functional More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Christian Pérez-Chablé1, Daisy Pérez-Brito1,*, Anuar Magaña-Alvarez1, Jairo Cristóbal-Alejo2, Irma L. Medina-Baizabal1, Marcela Gamboa-Angulo1,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.072668
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Plant-Derived Antimicrobials: Phytochemical Defense, Plant Metabolism, and Ecological Roles)
Abstract Acalypha gaumeri (Euphorbiaceae) is the only endemic species of the genus in the Yucatan Peninsula. It is dioecious and has antifungal properties against various phytopathogens. In the present study, molecular identification of A. gaumeri was performed using the rbcL region, confirming its belonging to the Acalypha genus. Its genetic diversity was evaluated using 10 SPAR markers (ISSR and DAMD) from 60 individuals collected from female and male plants of the Kiuic, Tinum and Yaxcaba ex-situ populations. The results showed a high level of genetic polymorphism (PIC = 0.980) and significant differences among the populations. Ethanol and aqueous extracts from… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Erna Karalija1, Sabina Dahija1, Sajra Prijić1, Dunja Šamec2,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.072517
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Abiotic Stresses and Plant Defences in Climate Change)
Abstract Salinity is one of the major abiotic stresses limiting chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) productivity, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions where soil salinization is intensifying. Developing cost-effective and practical strategies to enhance seedling establishment and early vigor under saline conditions is therefore essential. In this study, we compared two seed-priming agents—1 mM proline and 25 mM NaCl—under identical hydroponic conditions to elucidate tissue-specific responses to 25 mM NaCl stress. Proline priming significantly improved shoot length (by ~23%), total chlorophyll content (by ~19%), and ascorbate peroxidase (ASPOX) activity. In contrast, NaCl priming enhanced root biomass retention (by More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Xiaofeng Mao1,#, Fenni Lv1,2,#, Shaofeng Li3, Lulu Gao1,2, Wenjun Ma4, Donglai Liu1, Binpeng Wu1, Yanan Wu1, Peng Wang1,2,*, Naiwei Li1,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.072636
Abstract Catalpa bungei, a fast-growing timber tree, is threatened by the lepidopteran pest Omphisa plagialis. Previous studies in our laboratory successfully generated transgenic C. bungei lines overexpressing Cry genes (Cry1Ab, Cry2A, and Cry9-2) that exhibited resistance to O. plagialis, but their potential impact on soil bacterial communities remains unclear. In this study, we analyzed nine transgenic C. bungei lines (three independent lines for each Cry gene) to characterize their rhizosphere bacterial communities using high-throughput sequencing of the 16S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) V4–V5 regions. A total of 628 amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) were shared among all transgenic and wild-type (WT) lines, forming a stable core… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Priscilla Yamilhet Montes-Orona1, Mercedes Georgina Ramírez-Aragón2, Isaela Villalpando-De La Torre3, Urbano Nava-Camberos1, Jared Ceniceros-García1, José Luis García-Hernández1,*
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2026.074379
Abstract Mexican oregano (Lippia graveolens Kunth) is an aromatic species of high culinary and medicinal relevance. In Mexico, more than 40 taxa with characteristic aroma and flavor are commercially recognized as oregano, with L. graveolens being the most widely distributed and economically important. Despite its relevance, few domesticated or semi-domesticated cultivars exist, and wild populations remain the main source of raw material, raising concerns regarding sustainability and quality standardization. The essential oil and oleoresins of L. graveolens possess recognized bioactivity, including antioxidant, antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties, largely attributed to phenolic compounds such as thymol and carvacrol. Given the… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Muhammad Nazim1,2,*, Abdul Ghafoor3,*, Abida Hussain4, Mehwish Tabassum5, Aamir Nawaz6, Muhammad Ahmad7, Murad Muhammad1,2, Muqarrab Ali4
Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany, DOI:10.32604/phyton.2024.058970
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Soil Microbe-Plant Interactions: Unveiling Mechanisms of Biostimulants in Stress Tolerance)
Abstract In recent years, the world has faced rising global temperatures, accumulative pollution, and energy crises, stimulating scientists worldwide to strive for eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions. Biochar has materialized as a
favorable tool for environmental remediation, indicating efficacy as an efficient sorbent substance for both
inorganic and organic pollutants in environmental field. These unique properties exclude improved surface
functionality, porous morphology, large specific surface area (SSA), cation exchange capacity (CEC), robust
adsorption capabilities, environmental stability, and embedded micronutrients. Biochar exhibited potential
characteristics for environmental oversight, greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction, and soil fertility improvement. This review… More >