 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
ERLNs augment simultaneous delivery of GFSV into PC-3 cells: Influence of drug combination on SDH, GPX-4, 5α-RD, and cytotoxicity
1 Department of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11451, Saudi Arabia
2 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11451, Saudi Arabia
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, King Saud University, Riyadh, 11451, Saudi Arabia
* Corresponding Author: GAMALELDIN I. HARISA. Email:
Oncology Research 2025, 33(4), 919-935. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.054537
Received 31 May 2024; Accepted 04 November 2024; Issue published 19 March 2025
Abstract
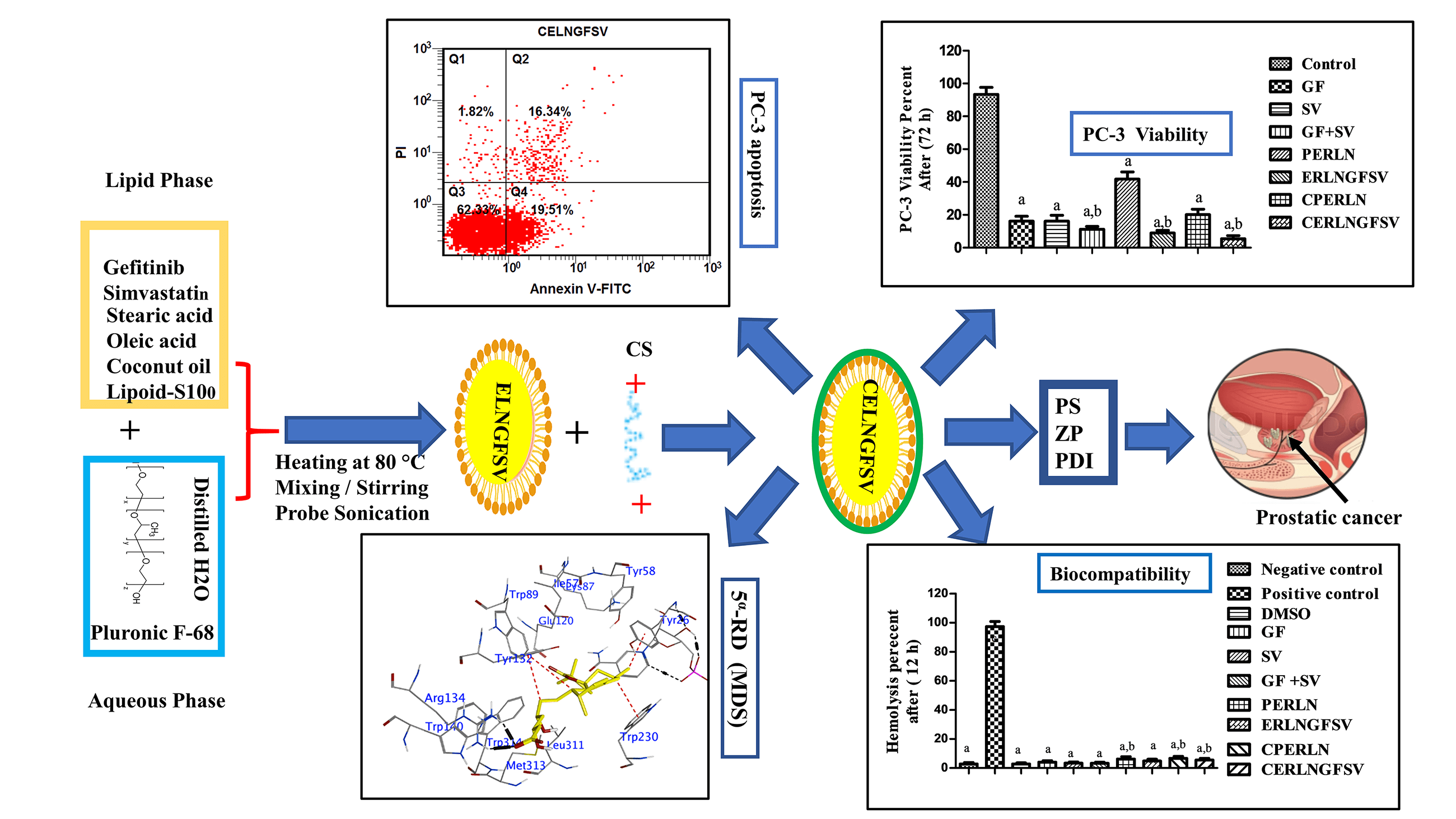
Objective: Prostate cancer (PCA) is the second most widespread cancer among men globally, with a rising mortality rate. Enzyme-responsive lipid nanoparticles (ERLNs) are promising vectors for the selective delivery of anticancer agents to tumor cells. The goal of this study is to fabricate ERLNs for dual delivery of gefitinib (GF) and simvastatin (SV) to PCA cells. Methods: ERLNs loaded with GF and SV (ERLNGFSV) were assembled using bottom-up and top-down techniques. Subsequently, these ERLN cargoes were coated with triacylglycerol, and phospholipids and capped with chitosan (CS). The ERLNGFSV, and CS engineered ERLNGFSV (CERLNGFSV) formulations were characterized for particle size (PS), zeta potential (ZP), and polydispersity index (PDI). The biocompatibility, and cytotoxicity of the plain and GF plus SV-loaded ERLN cargoes were assessed using erythrocytes and PC-3 cell line. Additionally, molecular docking simulations (MDS) were conducted to examine the influence of GF and SV on succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), glutathione peroxidase-4 (GPX-4), and 5α-reductase (5α-RD). Results: These results showed that plain, ERLNGFSV, and CERLNGFSV cargoes have a nanoscale size and homogeneous appearance. Moreover, ERLNGFSV and CERLNGFSV were biocompatible, with no detrimental effects on erythrocytes. Treatment with GF, SV, GF plus SV, ERLNGFSV, and CERLNGFSV significantly reduced the viability of PC-3 cells compared to control cells. Particularly, the blend of GF and SV, as well as ERLNGFSV and CERLNGFSV augmented PC-3 cell death. Also, treating PC-3 cells with free drugs, their combination, ERLNGFSV, and CERLNGFSV formulations elevated the percentage of apoptotic cells. MDS studies demonstrated that GF and SV interact with the active sites of SDH, GPX-4, and 5α-reductase. Conclusions: This study concludes that SVGF combination and ERLNs loading induce particular delivery, and synergism on PC-3 death through action on multiple pathways involved in cell proliferation, and apoptosis, besides the interaction with SDH, GPX-4, and 5α-RD. Therefore, GFSV-loaded ERLN cargoes are a promising strategy for PCA treatment. In vivo studies are necessary to confirm these findings for clinical applications.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools