 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Biological roles and molecular mechanism of circular RNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastrointestinal malignancies
1 School of Basic Medical Sciences, Health Science Center, Ningbo University, Ningbo, 315211, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, Ningbo, 315020, China
* Corresponding Authors: YONGFU SHAO. Email: ; GUOLIANG YE. Email:
,
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(3), 549-566. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.051589
Received 09 March 2024; Accepted 13 June 2024; Issue published 28 February 2025
Abstract
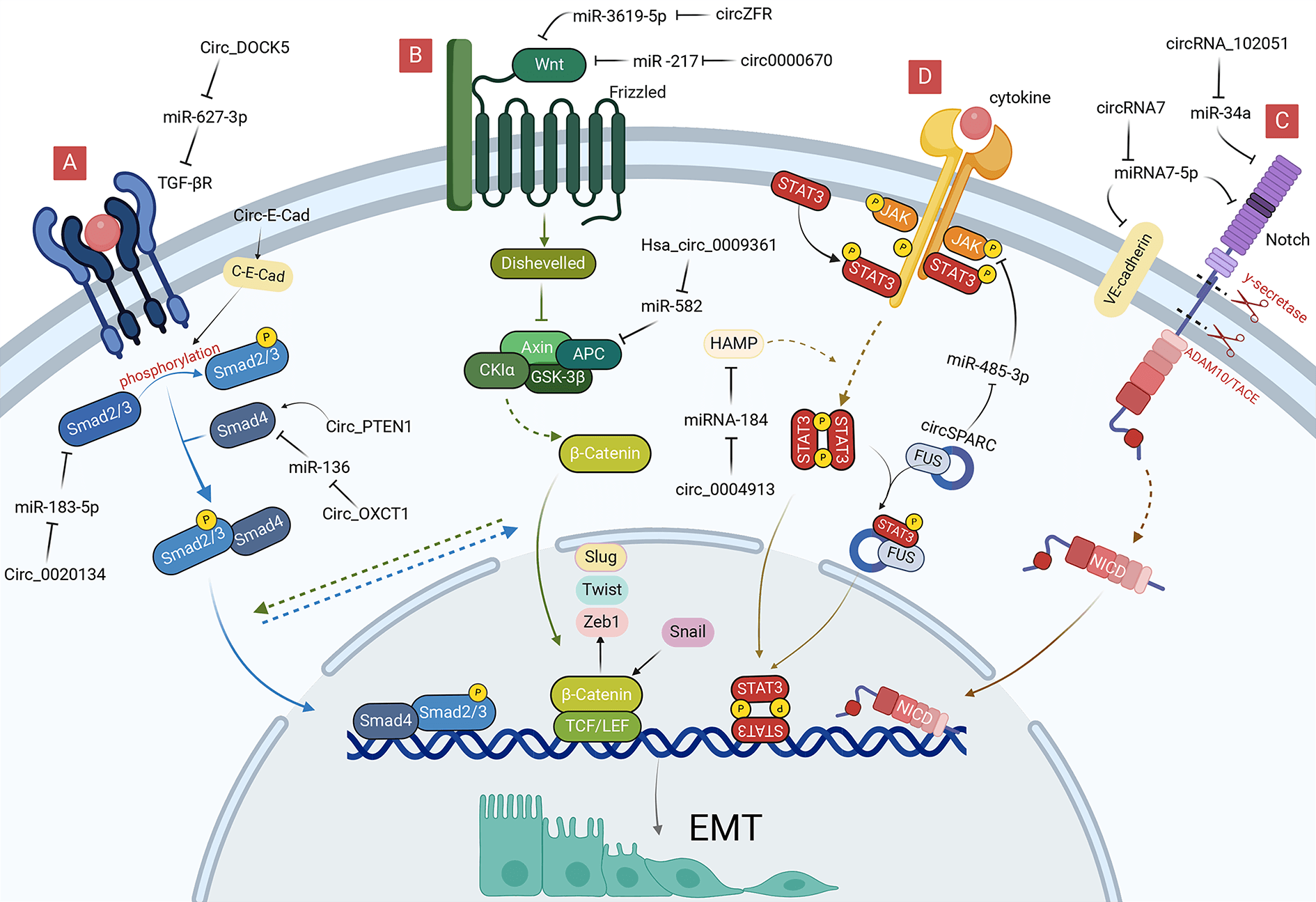
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are formed by splicing of precursor RNAs and covalently linked at the 5′ and 3′ ends. Dysregulated circRNAs are closely related to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of gastrointestinal malignancies. CircRNAs, including circRNA_0008717, circGOT1, circ-DOCK5, circVPS33B, circPVT1, circMET, circ-OXCT1, circ_67835, circRTN4, circ_0087502, circFNDC38, circ_PTEN1, circPGPEP1, and circ-E-Cad are involved in the EMT process of gastrointestinal malignancies through a variety of mechanisms, such as regulating EMT-inducing transcription factors, signaling pathways, and tumor microenvironments. Gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies are common malignant tumors worldwide, and the heterogeneity and easy metastasis of gastrointestinal malignancies limit the effectiveness of medical treatments. Therefore, investigating the molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal malignancies is essential for clinical treatment. This article summarizes the biological roles and molecular mechanism of circRNAs in EMT of gastrointestinal malignancies, providing a theoretical basis for applying EMT-related circRNAs in targeted therapy.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools