 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
EMP2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion by activating cellular autophagy
1 Department of Pharmacy, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Southwestern Chinese Medicine Resources, College of Medical Technology and School of Pharmacy, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, 611137, China
3 Department of Radiation Oncology, Radiation Oncology Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Sichuan Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Sichuan Cancer Hospital & Institute, Sichuan Cancer Center, Affliated Cancer Hospital of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, 610041, China
* Corresponding Authors: GU HE. Email: ; PENG ZHANG. Email:
# These authors contributed equally
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics)
Oncology Research 2025, 33(2), 443-464. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.043948
Received 17 July 2023; Accepted 13 May 2024; Issue published 16 January 2025
Abstract
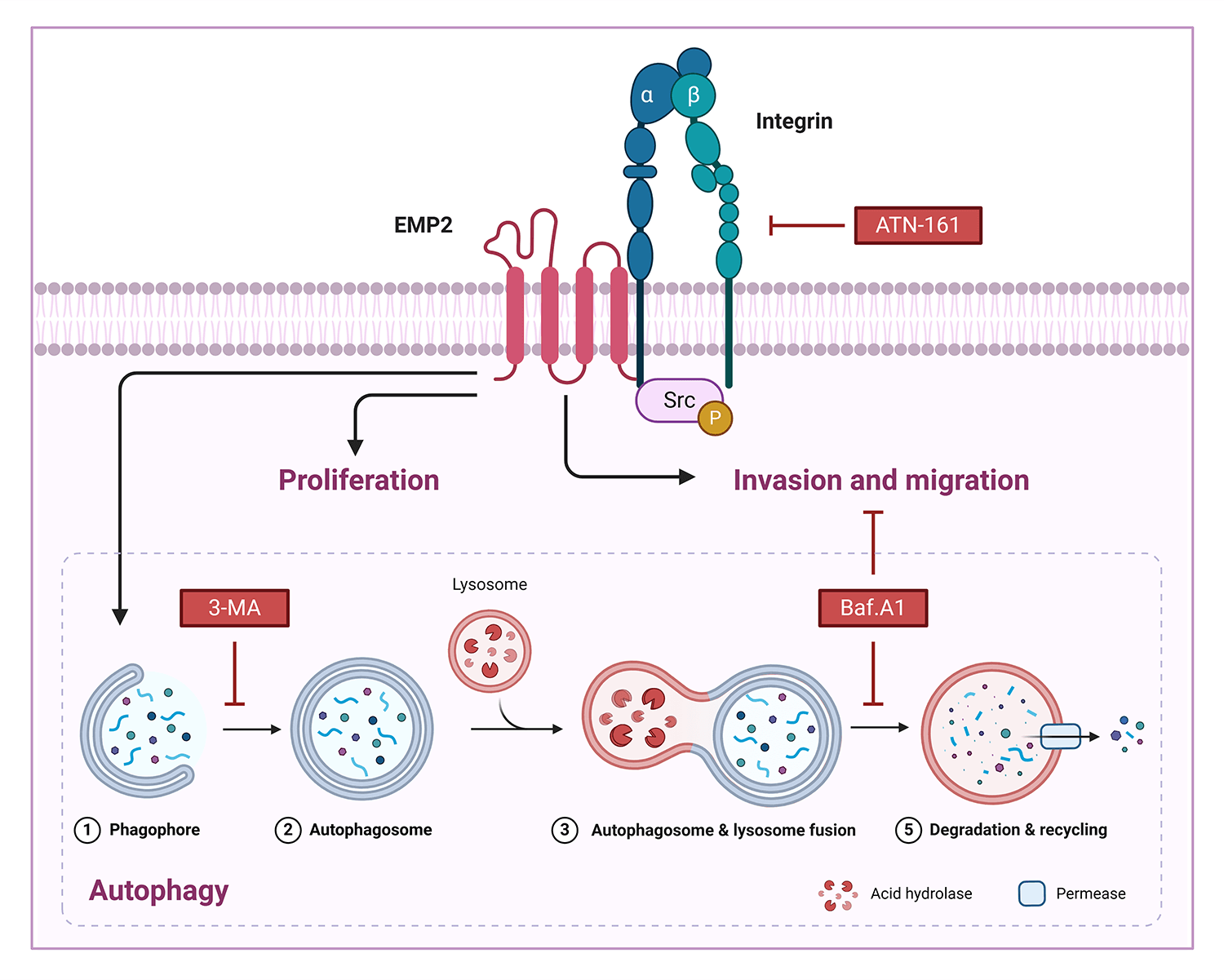
Background: EMP2 is a tumor-associated membrane protein belonging to the GAS-3/PMP22 gene family. EMP2 expression demonstrates significant tissue specificity and heterogeneity in various human tissues and tumor tissues, where it may play a role in either promoting or inhibiting tumor growth. This study aimed to investigate the expression level, biological functions, and molecular mechanisms of EMP2 in liver cancer. Methods: we analyzed the mRNA expression levels of EMPs family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and normal liver tissues based on the TCGA database and immunohistochemical analysis of tissue microarrays. Subsequently, we constructed HCC cell lines with either knockdown or overexpression of EMP2 to examine the biological functions and molecular mechanisms of EMP2 in tumorigenesis in vivo and in vitro. Results: Bioinformatic and immunohistochemical analysis of tissue microarrays have confirmed the significant upregulation of EMP2 in HCC tissues. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that downregulation of EMP2 results in a moderate reduction in the proliferation and invasive capacity of HCC cells. Conversely, overexpression of EMP2 enhances the invasive capacity of HCC cells and induces autophagy. Initial investigations into the molecular mechanisms underlying EMP2-mediated enhancement of HCC cell invasion have revealed the dual regulation of EMP2-induced autophagy and the integrin pathway, which synergistically influence the invasive and metastatic potential of HCC cells. Conclusion: EMP2 holds promise as a diagnostic marker for HCC metastasis and a potential target for targeted therapy.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools