 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Research advancements in nanoparticles and cell-based drug delivery systems for the targeted killing of cancer cells
Department of Biology, College of Science, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, 123, Oman
* Corresponding Authors: SIRIN A. ADHAM. Email: ,
Oncology Research 2025, 33(1), 27-44. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.056955
Received 04 August 2024; Accepted 07 November 2024; Issue published 20 December 2024
Abstract
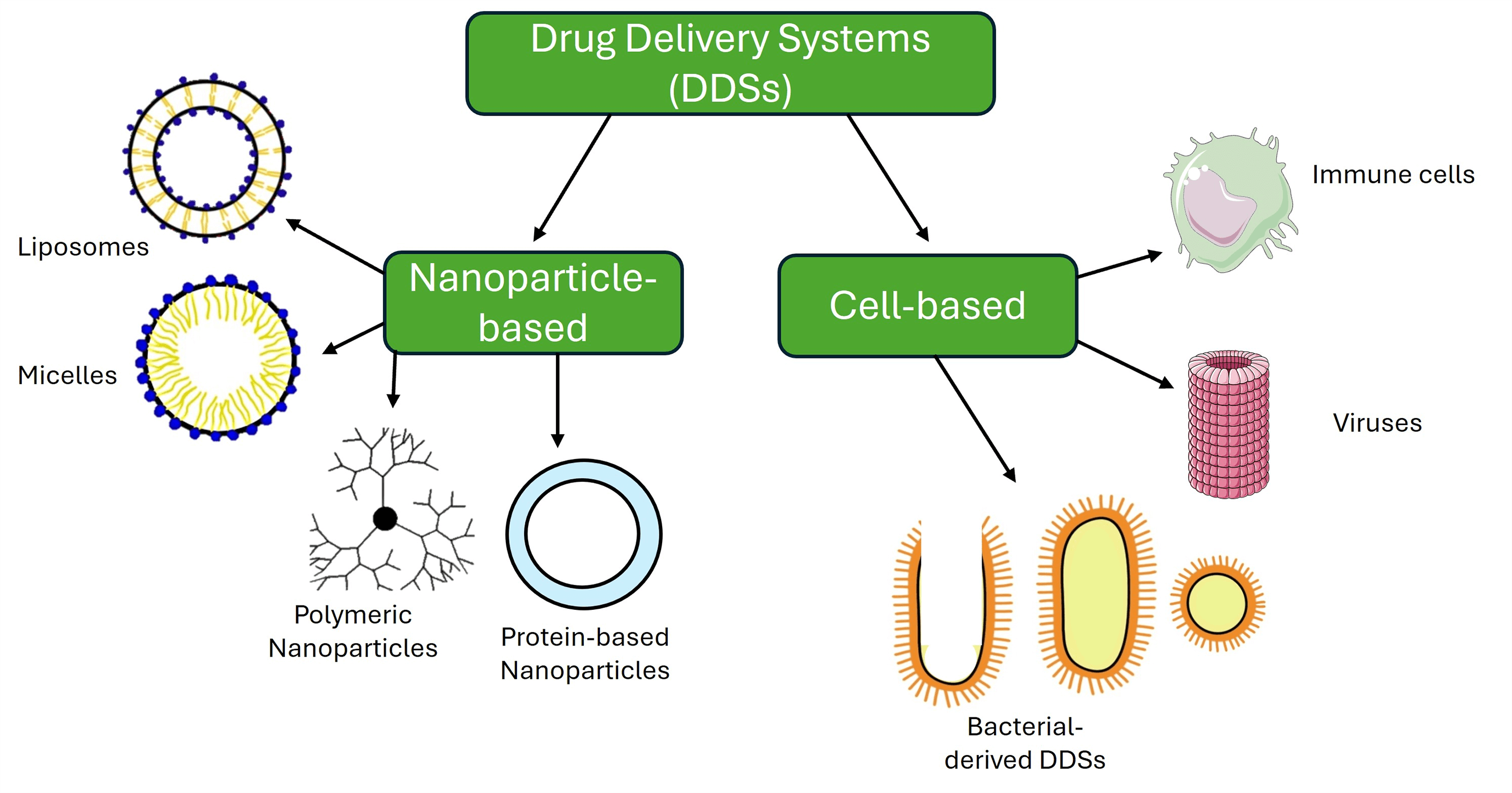
Nanotechnology in cancer therapy has significantly advanced treatment precision, effectiveness, and safety, improving patient outcomes and personalized care. Engineered smart nanoparticles and cell-based therapies are designed to target tumor cells, precisely sensing the tumor microenvironment (TME) and sparing normal cells. These nanoparticles enhance drug accumulation in tumors by solubilizing insoluble compounds or preventing their degradation, and they can also overcome therapy resistance and deliver multiple drugs simultaneously. Despite these benefits, challenges remain in patient-specific responses and regulatory approvals for cell-based or nanoparticle therapies. Cell-based drug delivery systems (DDSs) that primarily utilize the immune-recognition principle between ligands and receptors have shown promise in selectively targeting and destroying cancer cells. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of various nanoparticle and cell-based drug delivery system types used in cancer research. It covers approved and experimental nanoparticle therapies, including liposomes, micelles, protein-based and polymeric nanoparticles, as well as cell-based DDSs like macrophages, T-lymphocytes, dendritic cells, viruses, bacterial ghosts, minicells, SimCells, and outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). The review also explains the role of TME and its impact on developing smart DDSs in combination therapies and integrating nanoparticles with cell-based systems for targeting cancer cells. By detailing DDSs at different stages of development, from laboratory research to clinical trials and approved treatments, this review provides the latest insights and a collection of valuable citations of the innovative strategies that can be improved for the precise treatment of cancer.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools