 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Combination of fruquintinib with venetoclax for the treatment of colorectal cancer
1 Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, 210029, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing, 210023, China
3 Department of Oncology, The Affiliated Taizhou People’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Taizhou, 225300, China
* Corresponding Authors: WENJIE GUO. Email: ; YANHONG GU. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
Oncology Research 2025, 33(1), 225-234. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.050047
Received 25 January 2024; Accepted 17 April 2024; Issue published 20 December 2024
Abstract
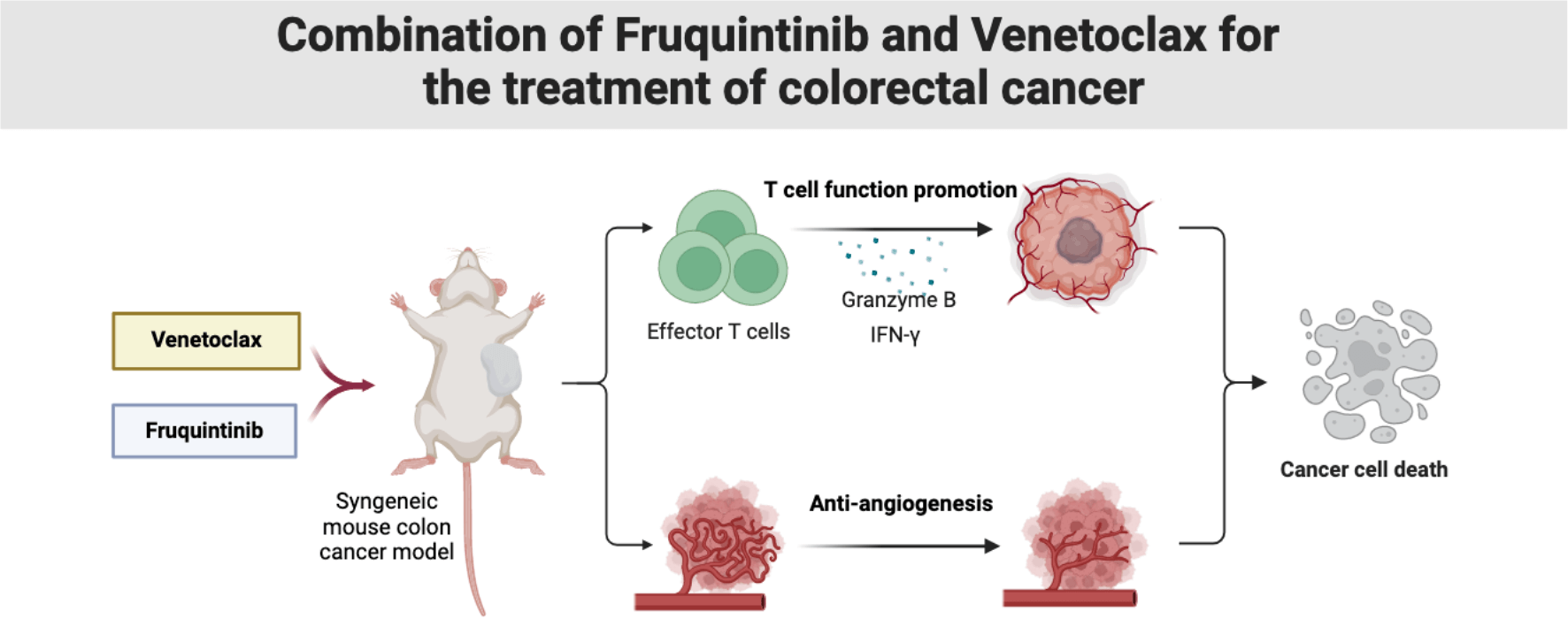
Background: As a novel blocker of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), fruquintinib has been approved for treating colorectal cancer (CRC). However, its dosage and therapeutic efficacy are limited by its widespread adverse reactions. Venetoclax, recognized as the initial inhibitor of B-cell lymphoma protein 2 (BCL2), has shown potential in boosting the effectiveness of immunotherapy against CRC. This study investigated the efficacy and mechanisms of fruquintinib combined with venetoclax in treating CRC. Methods and Materials: We developed a colon cancer mouse model with the CT26 colon cell line to demonstrate fruquintinib and venetoclax’s efficacy against tumors. Then we employed various techniques to evaluate different aspects of the experimental outcomes. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect cell proliferation and angiogenesis in tumor tissues. Western blot analysis was utilized to examine the occurrence of cell apoptosis, and flow cytometry to quantitate immune cells within the tumor tissues. Moreover, immunofluorescence was employed to measure cytokine levels. Results: The strongest inhibition on tumor growth was achieved by the combination of fruquintinib with venetoclax, as opposed to individual drug use. Venetoclax was found to amplify the impact of fruquintinib, leading to decreased cancer cell proliferation, increased cancer cell apoptosis, lowered angiogenesis, better vascular structure normalization, and improved immune cell infiltration. Conclusion: Our findings indicate that the addition of venetoclax enhances the impact of fruquintinib on vascular normalization and modulation of the tumor immune microenvironment. Our study presents the justification for utilizing the fruquintinib and venetoclax combination in treating CRC. Venetoclax holds promise in being assimilated into anticancer medications for CRC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools