 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Genomic profiling of colorectal cancer in large-scale Chinese patients: amplification and somatic mutations in ERBB2
1 Department of Oncology, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Cancer Institute, Department of Oncology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
3 Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China
4 3D Medicines Inc., Shanghai, China
* Corresponding Authors: YONG GAO. Email: ; MING QUAN. Email:
Oncology Research 2024, 32(9), 1429-1438. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.047309
Received 01 November 2023; Accepted 01 March 2024; Issue published 23 August 2024
Abstract
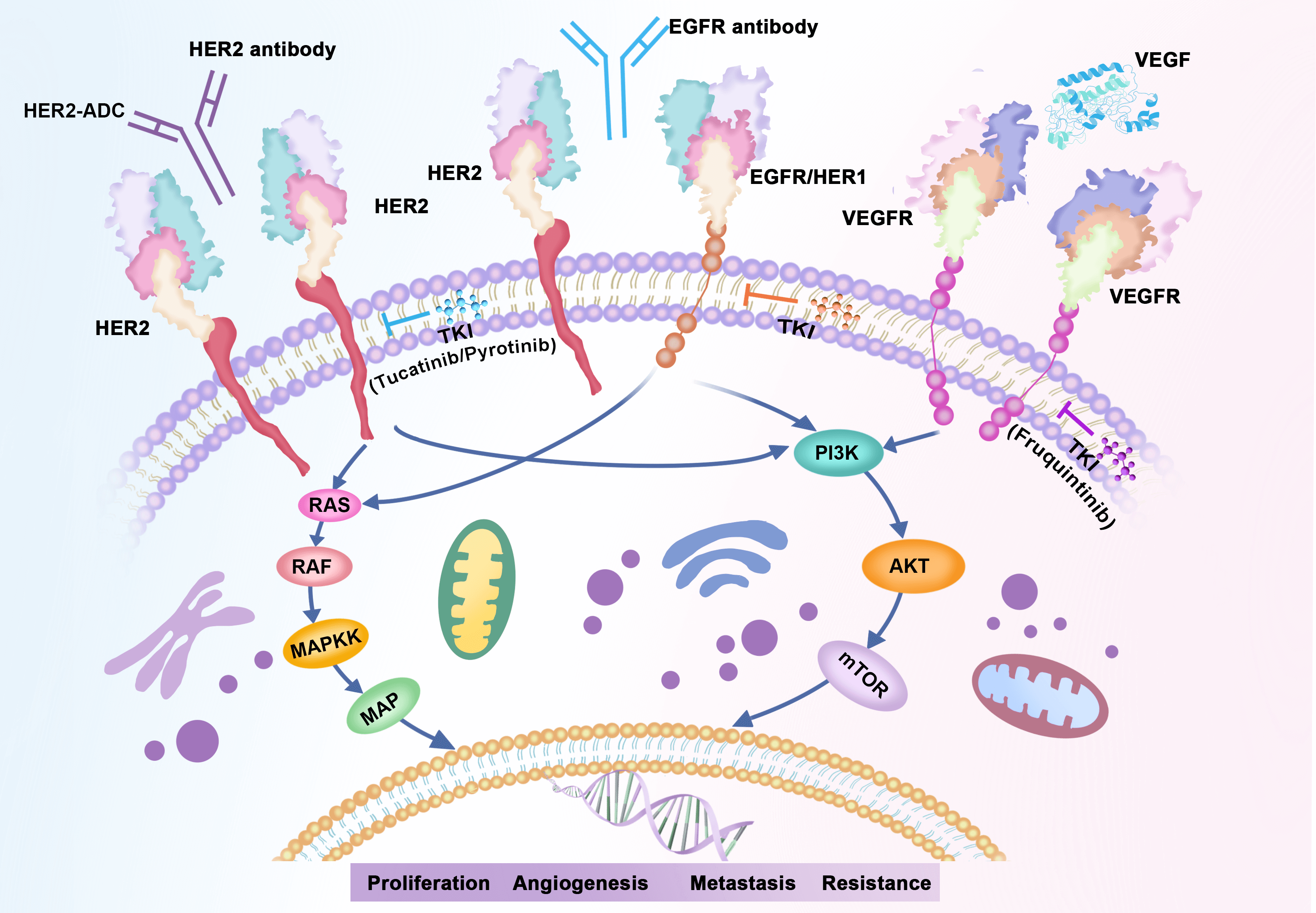
Objectives: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-targeted therapies have demonstrated potential benefits for metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients with HER2 amplification, but are not satisfactory in cases of HER2 mutant CRCs. Methods: Consequently, further elucidation of amplifications and somatic mutations in erythroblastic oncogene B-2 (ERBB2) is imperative. Comprehensive genomic profiling was conducted on 2454 Chinese CRC cases to evaluate genomic alterations in 733 cancer-related genes, tumor mutational burden, microsatellite instability, and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression. Results: Among 2454 CRC patients, 85 cases (3.46%) exhibited ERBB2 amplification, and 55 cases (2.24%) carried ERBB2 mutation. p.R678Q (28%), p.V8421 (24%), and p.S310F/Y (12%) were the most prevalent of the 16 detected mutation sites. In comparison to the ERBB2 altered (alt) group, KRAS/BRAF mutations were more prevalent in ERBB2 wild-type (wt) samples (ERBB2wt vs. ERBB2alt, KRAS: 50.9% vs. 25.6%, p < 0.05; BRAF: 8.5% vs. 2.3%, p < 0.05). 32.7% (18/55) of CRCs with ERBB2 mutation exhibited microsatellite instability high (MSI-H), while no cases with HER2 amplification displayed MSI-H. Mutant genes varied between ERBB2 copy number variation (CNV) and ERBB2 single nucleotide variant (SNV); TP53 alterations tended to co-occur with ERBB2 amplification (92.3%) as opposed to ERBB2 mutation (58.3%). KRAS and PIK3CA alterations were more prevalent in ERBB2 SNV cases (KRAS/PIK3CA: 45.8%/31.2%) compared to ERBB2 amplification cases (KRAS/PIK3CA: 14.1%/7.7%). Conclusion: Our study delineates the landscape of HER2 alterations in a large-scale cohort of CRC patients from China. These findings enhance our understanding of the molecular features of Chinese CRC patients and offer valuable implications for further investigation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools