 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
LncRNA PCGEM1 facilitates cervical cancer progression via miR-642a-5p/KIF5B axis
1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092, China
2 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The Second People’s Hospital of Nantong City, Nantong, 226002, China
3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong, 226002, China
* Corresponding Authors: DANDAN ZHANG. Email: ; HUIQIN LIU. Email:
Oncology Research 2024, 32(7), 1221-1229. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.047454
Received 06 November 2023; Accepted 10 January 2024; Issue published 20 June 2024
A correction of this article was approved in:
Correction: LncRNA PCGEM1 facilitates cervical cancer progression via miR-642a-5p/KIF5B axis
Read correction
Abstract
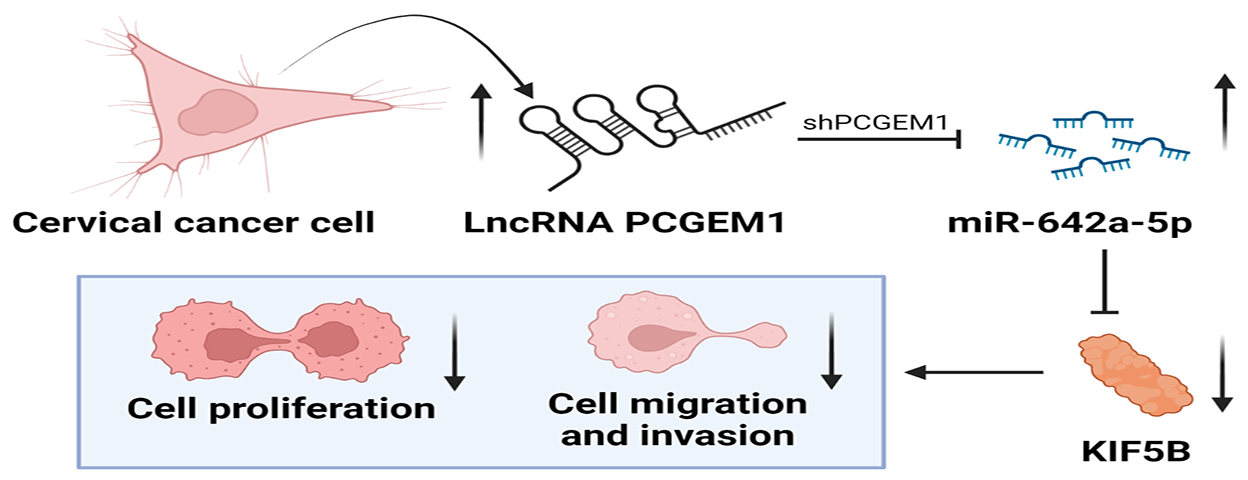
At present, the role of many long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as tumor suppressors in the formation and development of cervical cancer (CC) has been studied. However, lncRNA prostate cancer gene expression marker 1 (PCGEM1), whose high expression not only aggravates ovarian cancer but also can induce tumorigenesis and endometrial cancer progression, has not been studied in CC. The objective of this study was to investigate the expression and the underlying role of PCGEM1 in CC. The relative expression of PCGEM1 in CC cells was detected by real-time PCR. After the suppression of PCGEM1 expression by shRNA, the changes in the proliferation, migration, and invasion capacities were detected via CCK-8 assay, EdU assay, and colony formation assay wound healing assay. Transwell assay and the changes in expressions of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers were determined by western blot and immunofluorescence. The interplay among PCGEM1, miR-642a-5p, and kinesin family member 5B (KIF5B) was confirmed by bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter assay. Results showed that PCGEM1 expressions were up-regulated within CC cells. Cell viabilities, migration, and invasion were remarkably reduced after the suppression of PCGEM1 expression by shRNA in Hela and SiHa cells. N-cadherin was silenced, but E-cadherin expression was elevated by sh-PCGEM1. Moreover, by sponging miR-642a-5p in CC, PCGEM1 was verified as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) that modulates KIF5B levels. MiR-642a-5p down-regulation partially rescued sh-PCGEM1’s inhibitory effects on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT process. In conclusion, the PCGEM1/miR-642a-5p/KIF5B signaling axis might be a novel therapeutic target in CC. This study provides a research basis and new direction for targeted therapy of CC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools