 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
IQGAP3 promotes the progression of glioma as an immune and prognostic marker
1 Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Diabetic Cardiovascular Diseases, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning, 437100, China
2 School of Stomatology and Ophthalmology, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning, 437100, China
3 School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning, 437100, China
4 School of Pharmacy, Xianning Medical College, Hubei University of Science and Technology, Xianning, 437100, China
5 Department of Neurosurgery, The General Hospital of Chinese PLA Central Theater Command, Wuhan, 430070, China
* Corresponding Authors: ZHENWANG ZHANG. Email: ; LONG WANG. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics)
Oncology Research 2024, 32(4), 659-678. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.046712
Received 12 October 2023; Accepted 01 December 2023; Issue published 20 March 2024
Abstract
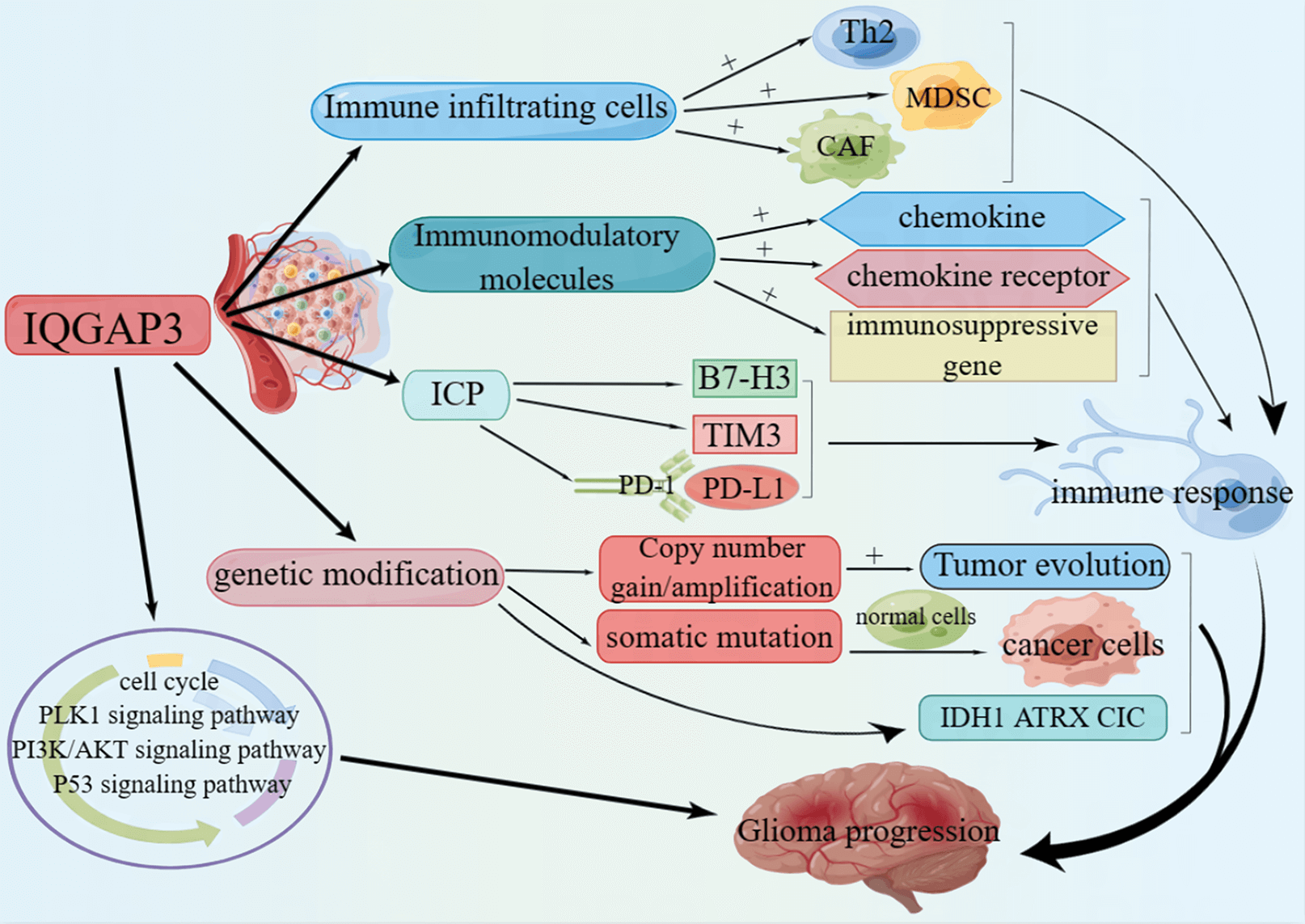
Background: IQGAP3 plays a crucial role in regulating cell proliferation, division, and cytoskeletal organization. Abnormal expression of IQGAP3 has been linked to various tumors, but its function in glioma is not well understood. Methods: Various methods, including genetic differential analysis, single-cell analysis, ROC curve analysis, Cox regression, Kaplan-Meier analysis, and enrichment analysis, were employed to analyze the expression patterns, diagnostic potential, prognostic implications, and biological processes involving IQGAP3 in normal and tumor tissues. The impact of IQGAP3 on immune infiltration and the immune microenvironment in gliomas was evaluated using immunofluorescence. Additionally, the cBioPortal database was used to analyze copy number variations and mutation sites of IQGAP3. Experimental validation was also performed to assess the effects of IQGAP3 on glioma cells and explore underlying mechanisms. Results: High IQGAP3 expression in gliomas is associated with an unfavorable prognosis, particularly in wild-type IDH and 1p/19q non-codeleted gliomas. Enrichment analysis revealed that IQGAP3 is involved in regulating the cell cycle, PI3K/AKT signaling, p53 signaling, and PLK1-related pathways. Furthermore, IQGAP3 expression may be closely related to the immunosuppressive microenvironment of glioblastoma. BRD-K88742110 and LY-303511 are potential drugs for targeting IQGAP3 in anti-glioma therapy. In vitro experiments showed that downregulation of IQGAP3 inhibits the proliferation and migration of glioma cells, with the PLK1/PI3K/AKT pathway potentially playing a crucial role in IQGAP3-mediated glioma progression. Conclusion: IQGAP3 shows promise as a valuable biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, and immunotherapeutic strategies in gliomas.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools