 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Clinical implications of single cell sequencing for bladder cancer
1 UroScience, School of Medical Sciences, University of Campinas, UNICAMP, Campinas, Sao Paulo, 13083-872, Brazil
2 ImmunOncology, Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas, PUC-Campinas, Campinas, Sao Paulo, 13087-571, Brazil
* Corresponding Author: LEONARDO OLIVEIRA REIS. Email:
# These authors contributed equally
Oncology Research 2024, 32(4), 597-605. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.045442
Received 27 August 2023; Accepted 08 January 2024; Issue published 20 March 2024
Abstract
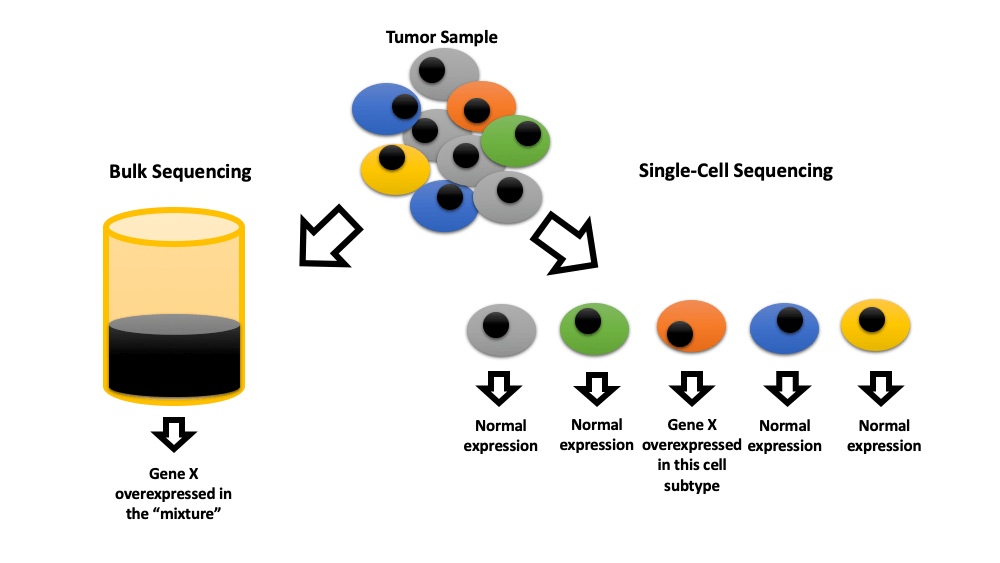
Bladder cancer (BC) is the 10th most common cancer worldwide, with about 0.5 million reported new cases and about 0.2 million deaths per year. In this scoping review, we summarize the current evidence regarding the clinical implications of single-cell sequencing for bladder cancer based on PRISMA guidelines. We searched PubMed, CENTRAL, Embase, and supplemented with manual searches through the Scopus, and Web of Science for published studies until February 2023. We included original studies that used at least one single-cell technology to study bladder cancer. Forty-one publications were included in the review. Twenty-nine studies showed that this technology can identify cell subtypes in the tumor microenvironment that may predict prognosis or response to immune checkpoint inhibition therapy. Two studies were able to diagnose BC by identifying neoplastic cells through single-cell sequencing urine samples. The remaining studies were mainly a preclinical exploration of tumor microenvironment at single cell level. Single-cell sequencing technology can discriminate heterogeneity in bladder tumor cells and determine the key molecular properties that can lead to the discovery of novel perspectives on cancer management. This nascent tool can advance the early diagnosis, prognosis judgment, and targeted therapy of bladder cancer.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools