 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
NAD+ associated genes as potential biomarkers for predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer
1 Henan Key Laboratory for Helicobacter Pylori & Microbiota and GI Cancer, Marshall Medical Research Center, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
2 Department of Gastroenterology, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
* Corresponding Authors: PENGYUAN ZHENG. Email: ; YANG MI. Email:
# Xiangdong Sun and Huijuan Wen contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics)
Oncology Research 2024, 32(2), 283-296. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.044618
Received 04 August 2023; Accepted 25 October 2023; Issue published 28 December 2023
Abstract
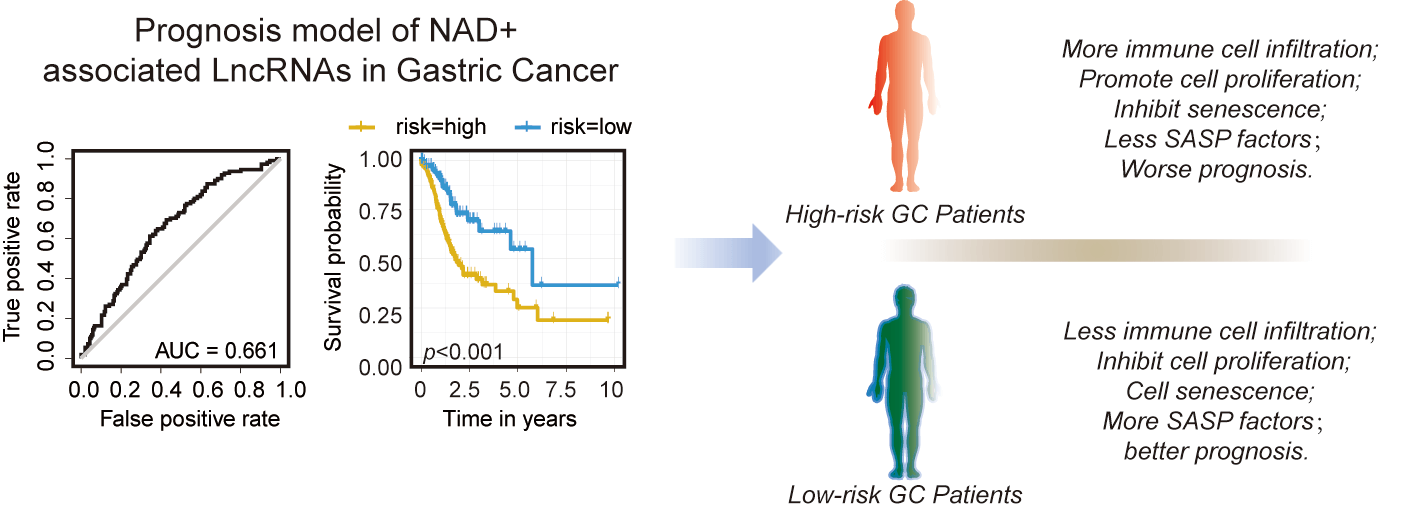
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) plays an essential role in cellular metabolism, mitochondrial homeostasis, inflammation, and senescence. However, the role of NAD+-regulated genes, including coding and long non-coding genes in cancer development is poorly understood. We constructed a prediction model based on the expression level of NAD+ metabolism-related genes (NMRGs). Furthermore, we validated the expression of NMRGs in gastric cancer (GC) tissues and cell lines; additionally, β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), a precursor of NAD+, was used to treat the GC cell lines to analyze its effects on the expression level of NMRGs lncRNAs and cellular proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). A total of 13 NMRGs-related lncRNAs were selected to construct prognostic risk signatures, and patients with high-risk scores had a poor prognosis. Some immune checkpoint genes were upregulated in the high-risk group. In addition, cell cycle, epigenetics, and senescence were significantly downregulated in the high-risk group. Notably, we found that the levels of immune cell infiltration, including CD8 T cells, CD4 naïve T cells, CD4 memory-activated T cells, B memory cells, and naïve B cells, were significantly associated with risk scores. Furthermore, the treatment of NMN showed increased proliferation of AGS and MKN45 cells. In addition, the expression of SASP factors (IL6, IL8, IL10, TGF-β, and TNF-α) was significantly decreased after NMN treatment. We conclude that the lncRNAs associated with NAD+ metabolism can potentially be used as biomarkers for predicting clinical outcomes of GC patients.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools