 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
GIPC1 promotes tumor growth and migration in gastric cancer via activating PDGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling
1 Cancer Research Center, School of Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361000, China
2 Department of Pharmacy, Xiamen Mental Health Center, Xiamen Xianyue Hospital, Xiamen, 361000, China
* Corresponding Authors: TING WU. Email: ; GANG SONG. Email:
; FANGHONG LUO. Email:
Oncology Research 2024, 32(2), 361-371. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.043807
Received 12 July 2023; Accepted 20 October 2023; Issue published 28 December 2023
Abstract
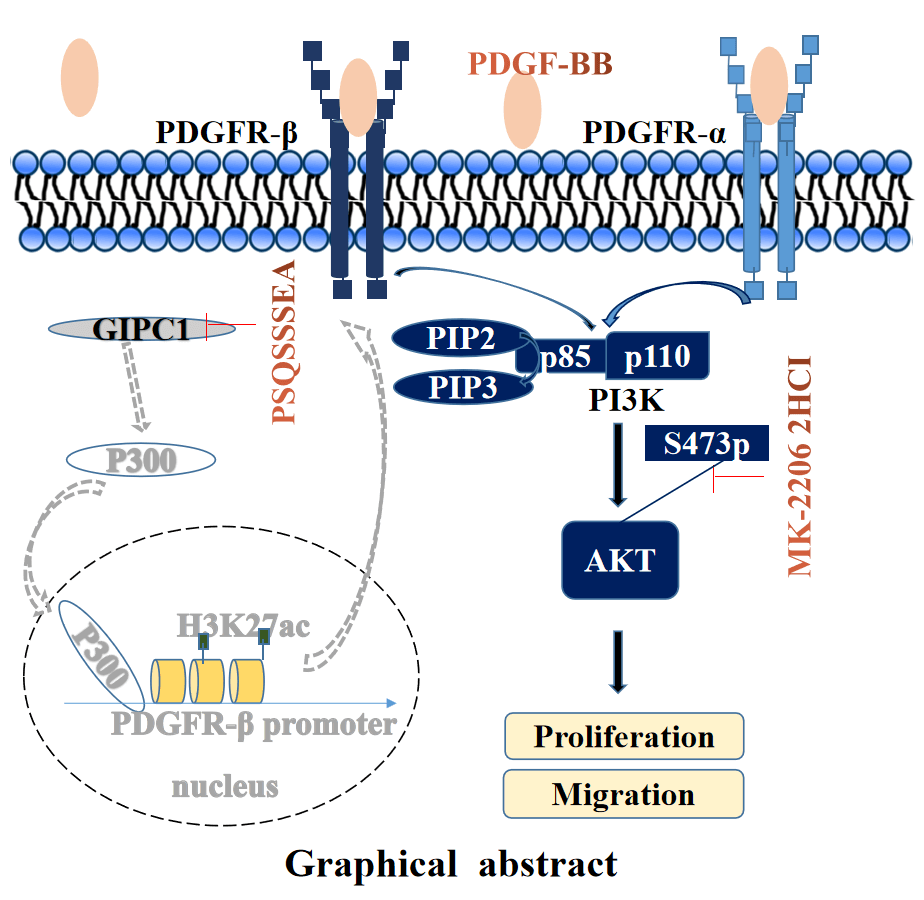
The high mortality rate associated with gastric cancer (GC) has resulted in an urgent need to identify novel therapeutic targets for GC. This study aimed to investigate whether GAIP interacting protein, C terminus 1 (GIPC1) represents a therapeutic target and its regulating mechanism in GC. GIPC1 expression was elevated in GC tissues, liver metastasis tissues, and lymph node metastases. GIPC1 knockdown or GIPC1 blocking peptide blocked the platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and inhibited the proliferation and migration of GC cells. Conversely, GIPC1 overexpression markedly activated the PDGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and promoted GC cell proliferation and migration. Furthermore, platelet-derived growth factor subunit BB (PDGF-BB) cytokines and the AKT inhibitor attenuated the effect of differential GIPC1 expression. Moreover, GIPC1 silencing decreased tumor growth and migration in BALB/c nude mice, while GIPC1 overexpression had contrasting effects. Taken together, our findings suggest that GIPC1 functions as an oncogene in GC and plays a central role in regulating cell proliferation and migration via the PDGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools