 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Combinational therapy with Myc decoy oligodeoxynucleotides encapsulated in nanocarrier and X-irradiation on breast cancer cells
1 Department of Medical Biotechnology, School of Medicine, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran
2 Zanjan Pharmaceutical Biotechnology Research Center, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran
3 Nanotechnology Research Center, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran
4 Department of Radiology Technology, School of Allied Medical Sciences, Zanjan University of Medical Sciences, Zanjan, Iran
* Corresponding Authors: BEHROOZ JOHARI. Email: ,
# Behrooz Johari and Milad Parvinzad Leilan contributed equally to this work and hence are co-first authors
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Signaling Pathway Crosstalk in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics)
Oncology Research 2024, 32(2), 309-323. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.043576
Received 06 July 2023; Accepted 13 October 2023; Issue published 28 December 2023
Abstract
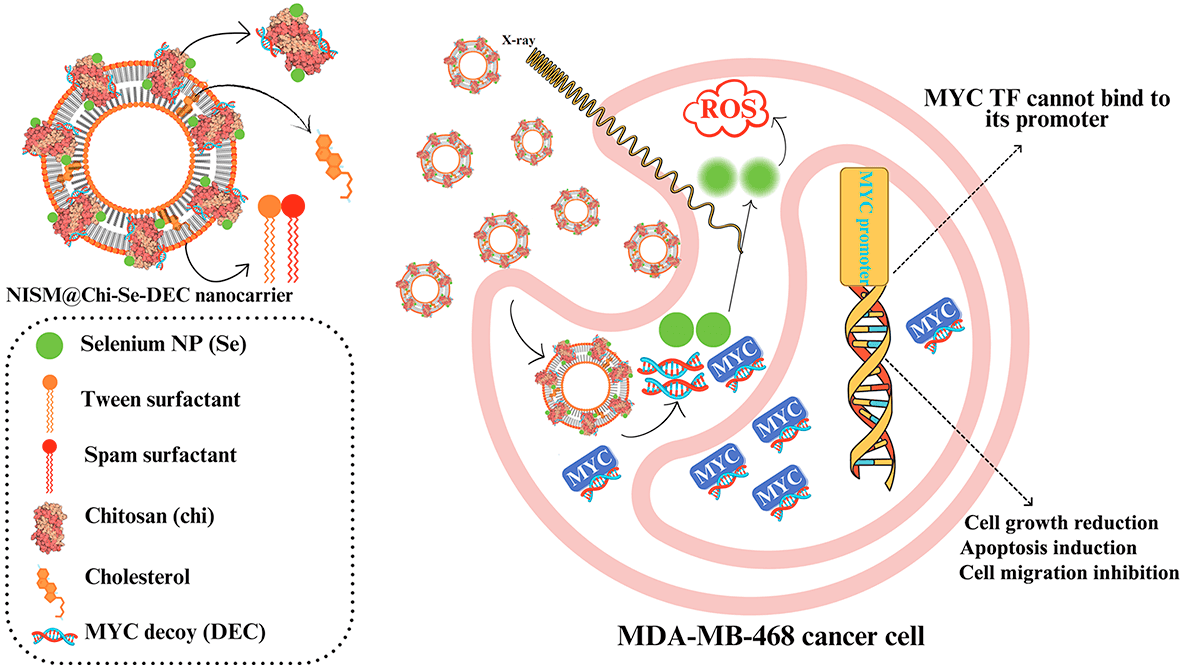
The Myc gene is the essential oncogene in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). This study investigates the synergistic effects of combining Myc decoy oligodeoxynucleotides-encapsulated niosomes-selenium hybrid nanocarriers with X-irradiation exposure on the MDA-MB-468 cell line. Decoy and scramble ODNs for Myc transcription factor were designed and synthesized based on promoter sequences of the Bcl2 gene. The nanocarriers were synthesized by loading Myc ODNs and selenium into chitosan (Chi-Se-DEC), which was then encapsulated in niosome-nanocarriers (NISM@Chi-Se-DEC). FT-IR, DLS, FESEM, and hemolysis tests were applied to confirm its characterization and physicochemical properties. Moreover, cellular uptake, cellular toxicity, apoptosis, cell cycle, and scratch repair assays were performed to evaluate its anticancer effects on cancer cells. All anticancer assessments were repeated under X-ray irradiation conditions (fractionated 2Gy). Physicochemical characteristics of niosomes containing SeNPs and ODNs showed that it is synthesized appropriately. It revealed that the anticancer effect of NISM@Chi-Se-DEC can be significantly improved in combination with X-ray irradiation treatment. It can be concluded that NISM@Chi-Se-DEC nanocarriers have the potential as a therapeutic agent for cancer treatment, particularly in combination with radiation therapy and in-vivo experiments are necessary to confirm the efficacy of this nano-drug.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools