 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Absent in melanoma 2 attenuates proliferation and migration and promotes apoptosis of human colorectal cancer cells by activating P38MAPK signaling pathway
1 Department of General Surgery, Suzhou Ninth People’s Hospital, Suzhou Ninth Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, Suzhou, China
2 Medical College of Nantong University, Nantong, China
3 Department of Gastroenterology, Suzhou Ninth People’s Hospital, Suzhou Ninth Hospital Affiliated to Soochow University, Suzhou, China
4 Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China
5 Department of Oncological Surgery, Kunshan Traditional Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Kunshan, China
* Corresponding Authors: GENHAI SHEN. Email: ; SONGBING HE. Email:
# These authors have contributed equally to this work
Oncology Research 2024, 32(2), 353-360. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.042986
Received 19 June 2023; Accepted 26 September 2023; Issue published 28 December 2023
Abstract
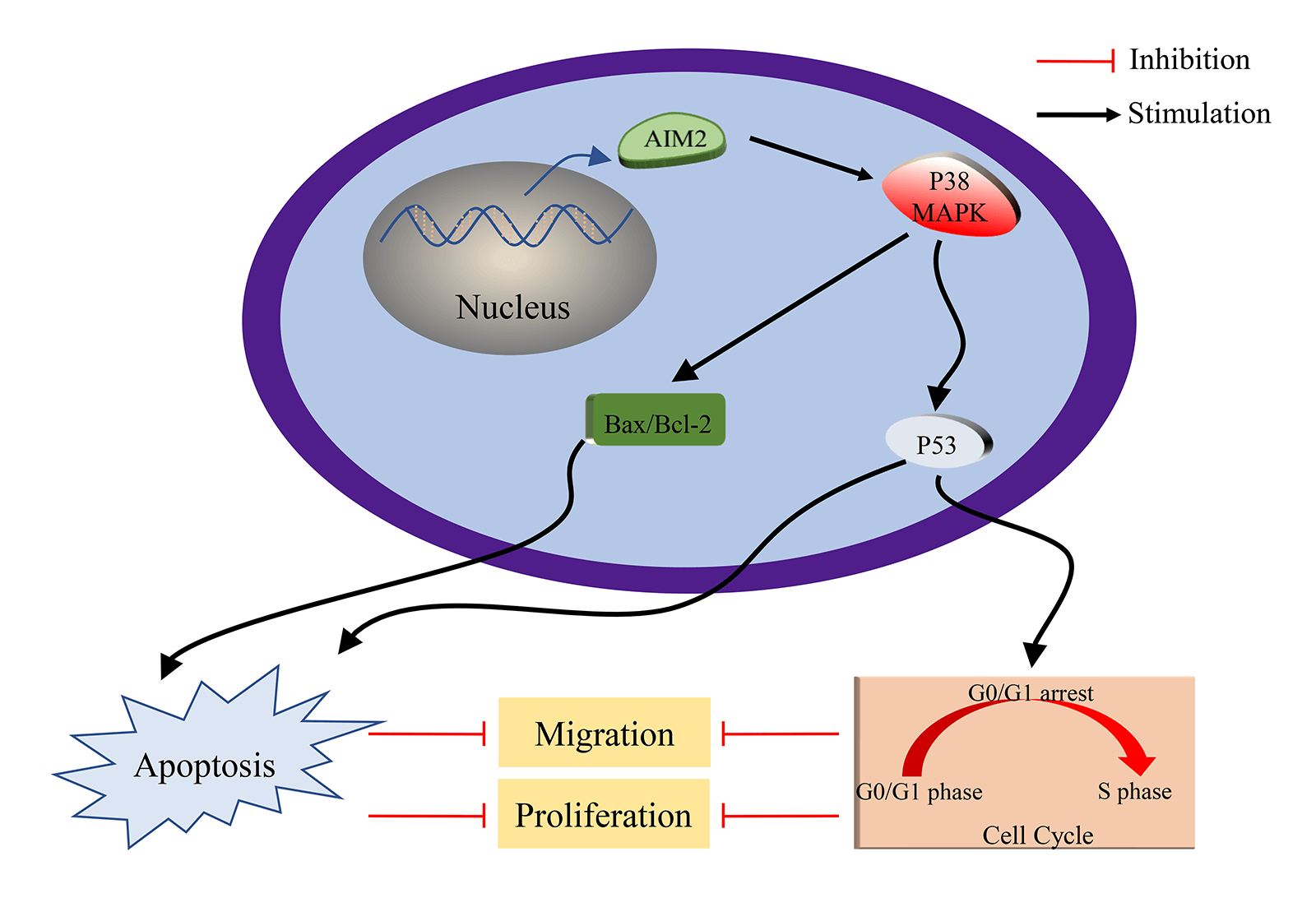
Colorectal cancer (CRC) stands among the top prevalent cancers worldwide and holds a prominent position as a major contributor to cancer-related mortality globally. Absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2), a constituent of the interferon-inducible hematopoietic interferon-inducible nuclear antigens with 200 amino acid repeats protein family, contributes to both cancer progression and inflammasome activation. Despite this understanding, the precise biological functions and molecular mechanisms governed by AIM2 in CRC remain elusive. Consequently, this study endeavors to assess AIM2’s expression levels, explore its potential antitumor effects, elucidate associated cancer-related processes, and decipher the underlying signaling pathways in CRC. Our findings showed a reduced AIM2 expression in most CRC cell lines. Elevation of AIM2 levels suppressed CRC cell proliferation and migration, altered cell cycle by inhibiting G1/S transition, and induced cell apoptosis. Further research uncovered the participation of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (P38MAPK) in AIM2-mediated modulation of CRC cell apoptosis and proliferation. Altogether, our achievements distinctly underscored AIM2’s antitumor role in CRC. AIM2 overexpression inhibited proliferation and migration and induced apoptosis of CRC cells via activating P38MAPK signaling pathway, indicating AIM2 as a prospective and novel therapeutic target for CRC.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools