 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Application of exosomal miRNA mediated macrophage polarization in colorectal cancer: Current progress and challenges
1 Department of Oncology, School of Clinical Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
2 General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
3 School of Basic Medical Sciences, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
4 Department of Surgical Oncology, Tumor Hospital, The General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, China
* Corresponding Author: TAO LI. Email:
# These authors contributed to the work equally and should be regarded as co-first authors
Oncology Research 2024, 32(1), 61-71. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.043481
Received 03 July 2023; Accepted 06 September 2023; Issue published 15 November 2023
Abstract
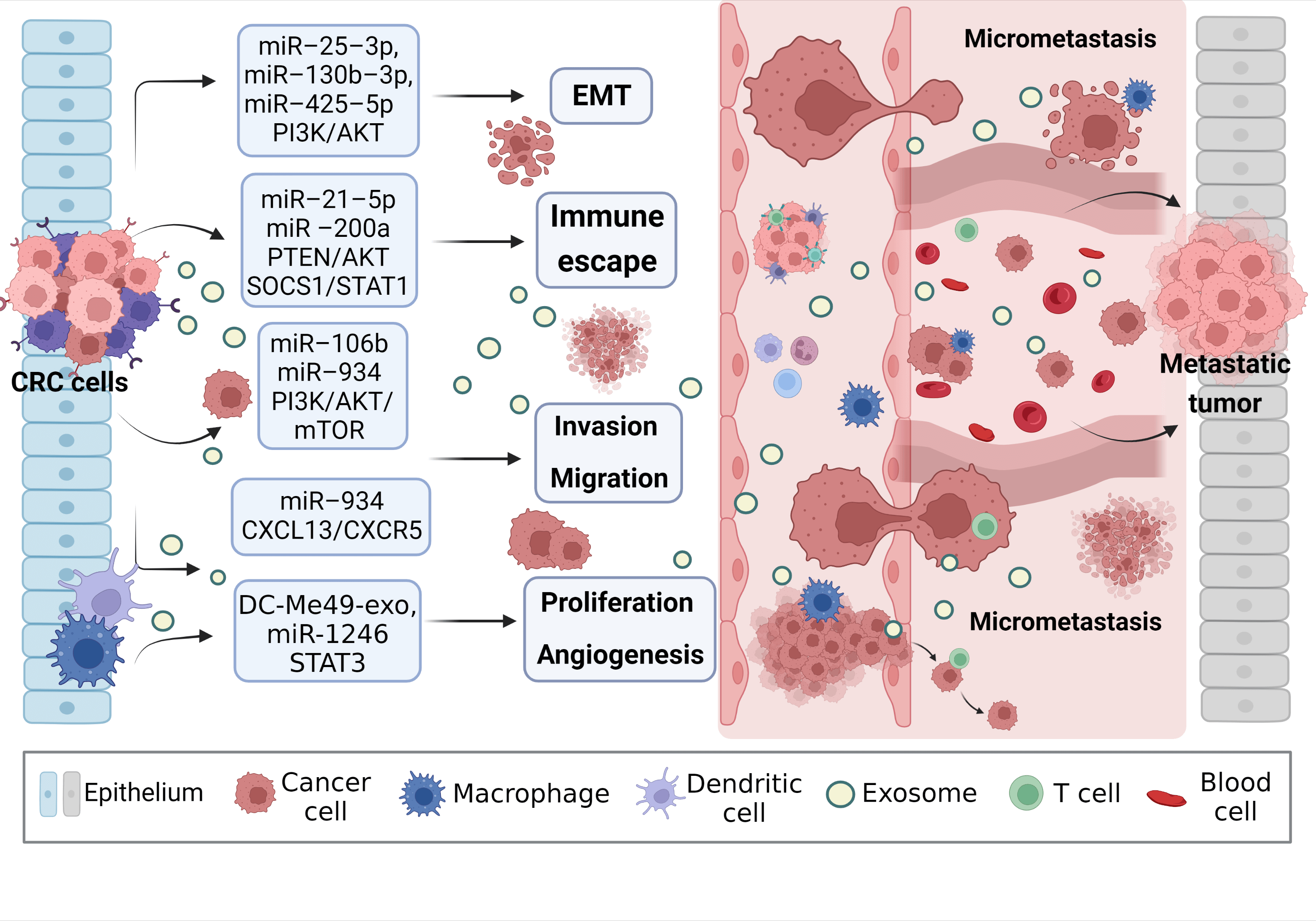
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major global health problem with high morbidity and mortality rates. Surgical resection is the main treatment for early-stage CRC, but detecting it early is challenging. Therefore, effective therapeutic targets for advanced patients are still lacking. Exosomes, tiny vesicles in body fluids, play a crucial role in tumor metastasis, immune regulation, and drug resistance. Interestingly, they can even serve as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Studies have shown that exosomes can carry miRNA, mediate the polarization of M1/M2 macrophages, promote the proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells, and affect the prognosis of CRC. Since the gastrointestinal tract has many macrophages, understanding the mechanism behind exosomal miRNA-mediated macrophage polarization in CRC treatment is crucial. This article summarizes recent advancements in the study of exosomal miRNAs in CRC and their potential as diagnostic and prognostic markers.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools