 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Recent updates on nano-phyto-formulations based therapeutic intervention for cancer treatment
1 Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Delhi Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research University (DPSRU), Pushp Vihar, New Delhi,
110017, India
2 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Gurugram University, Haryana, 122003, India
3 Department of Life Sciences, Sharda School of Basic Sciences and Research, Sharda University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, 201310, India
4 Department of Biotechnology, Graphic Era (Deemed to be University), Dehradun, Uttarakhand, 248002, India
5 Department of Pharmacology, Shobhaben Pratapbhai Patel School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM’s NMIMS, Vile Parle (West), Mumbai,
400056, India
6 Department of Bio-Sciences and Technology, Maharishi Markandeshwar Engineering College, Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed to be University), Mullana,
Ambala, 133207, India
* Corresponding Authors: Madhu Gupta, ; Hardeep Singh Tuli,
Oncology Research 2024, 32(1), 19-47. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.042228
Received 23 May 2023; Accepted 27 July 2023; Issue published 15 November 2023
Abstract
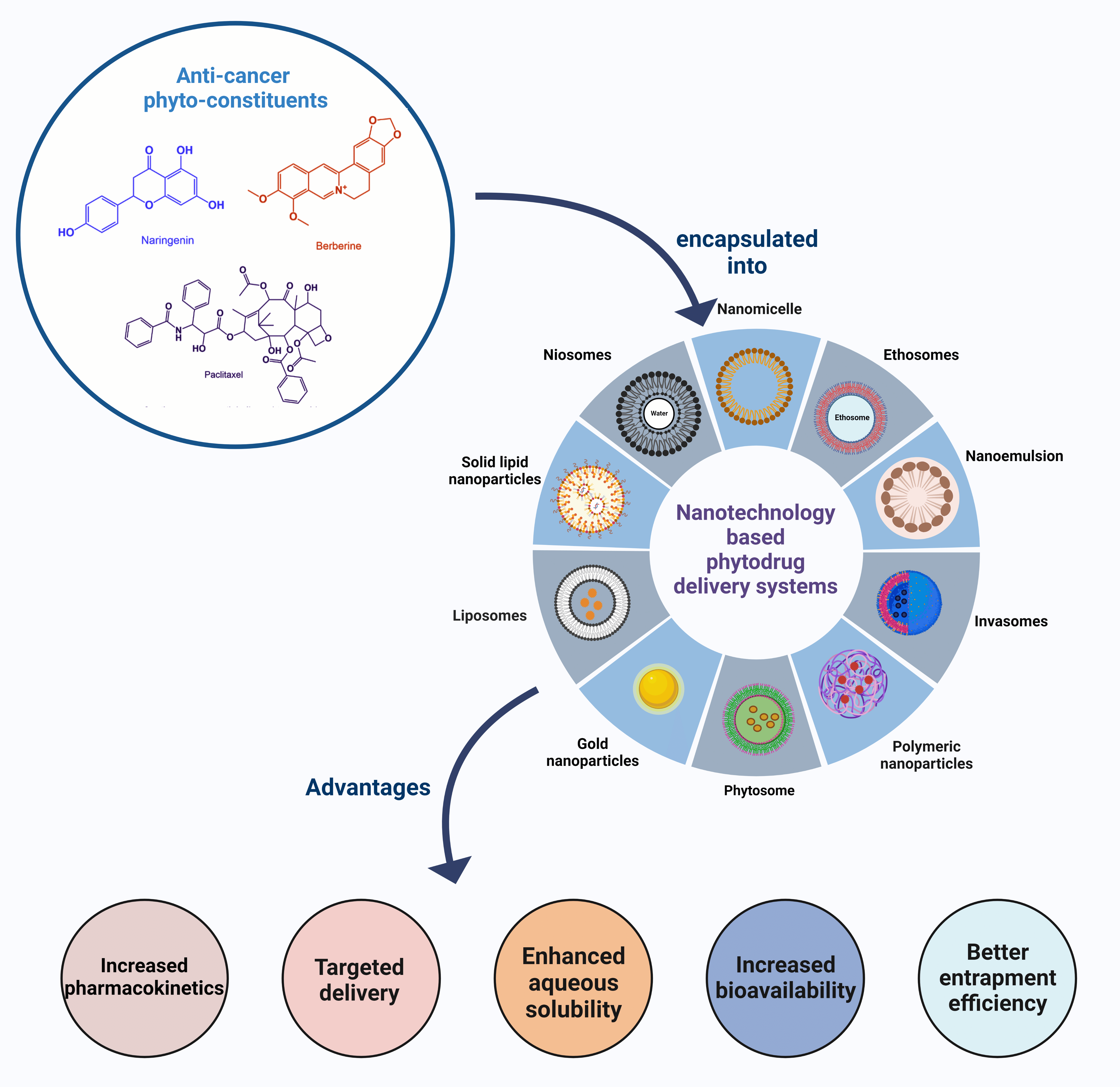
Cancer is a leading cause of death globally, with limited treatment options and several limitations. Chemotherapeutic agents often result in toxicity which long-term conventional treatment. Phytochemicals are natural constituents that are more effective in treating various diseases with less toxicity than the chemotherapeutic agents providing alternative therapeutic approaches to minimize the resistance. These phytoconstituents act in several ways and deliver optimum effectiveness against cancer. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of phyto-formulations in the management of cancers may be constrained due to challenges related to inadequate solubility, bioavailability, and stability. Nanotechnology presents a promising avenue for transforming current cancer treatment methods through the incorporation of phytochemicals into nanosystems, which possess a range of advantageous characteristics such as biocompatibility, targeted and sustained release capabilities, and enhanced protective effects. This holds significant potential for future advancements in cancer management. Herein, this review aims to provide intensive literature on diverse nanocarriers, highlighting their applications as cargos for phytocompounds in cancer. Moreover, it offers an overview of the current advancements in the respective field, emphasizing the characteristics that contribute to favourable outcomes in both in vitro and in vivo settings. Lastly, clinical development and regulatory concerns are also discussed to check on the transformation of the concept as a promising strategy for combination therapy of phytochemicals and chemotherapeutics that could lead to cancer management in the future.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools