 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
System analysis based on the T cell exhaustion‑related genes identifies CD38 as a novel therapy target for ovarian cancer
1 Department of Gynecologic Oncology, The International Peace Maternity and Child Health Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
2 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Embryo Original Diseases, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
* Corresponding Author: MI HAN. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Transcriptome Analysis in Tumor Microenvironment and Tumor Heterogeneity)
Oncology Research 2023, 31(4), 591-604. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2023.029282
Received 10 February 2023; Accepted 21 April 2023; Issue published 25 June 2023
Abstract
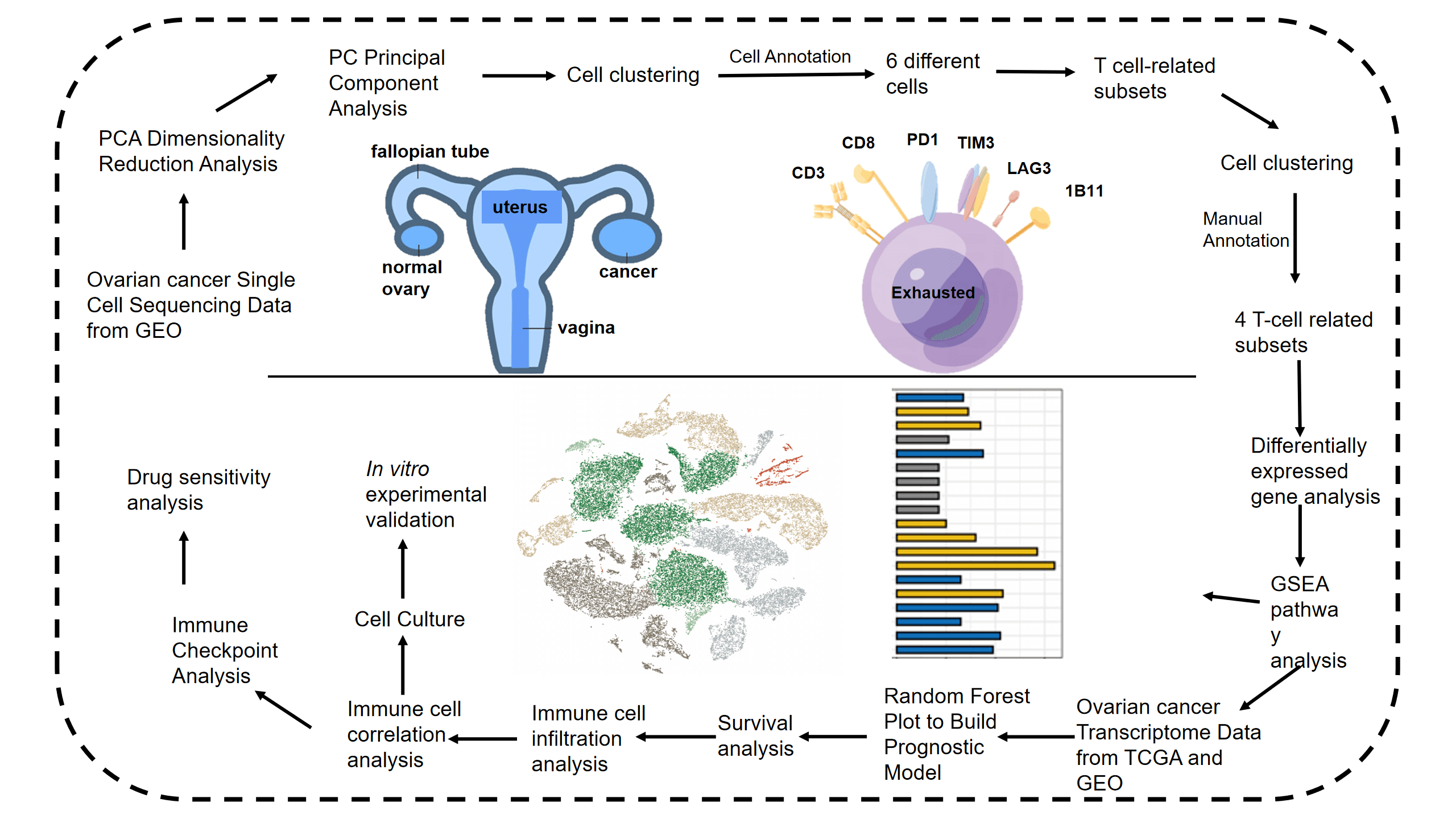
Ovarian cancer (OV) is highly heterogeneous tumor with a very poor prognosis. Studies increasingly show that T cell exhaustion is prognostically relevant in OV. The aim of this study was to dissect the heterogeneity of T cell subclusters in OV through single cell transcriptomic analysis. The single RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) data of five OV patients were analyzed, and six major cell clusters were identified after threshold screening. Further clustering of T cell-associated clusters revealed four subtypes. Pathways related to oxidative phosphorylation, G2M checkpoint, JAK-STAT and MAPK signaling were significantly activated, while the p53 pathway was inhibited in the CD8+ exhausted T cells. The standard marker genes of CD8+ T cell exhaustion were screened to develop a T-cell related gene score (TRS) based on random forest plots in TCGA cohort. The patients with low TRS have better prognosis compared to the patients with high TRS in both TCGA and GEO. In addition, most genes included in the TRS showed significant differences in expression levels between the high- and low-risk groups. Immune cell infiltration was analyzed using the MCPcounter and xCell algorithms, which revealed significant differences between the two risk groups, indicating that the different prognoses may stem from the respective immune landscapes. In addition, CD38 knockdown in OV cell lines increased apoptosis and inhibited invasion in vitro. Finally, we performed a drug sensitivity analysis and identified six potential drug candidates for OV. To summarize, we identified the heterogeneity and clinical significance of T cell exhaustion in OV and built a superior prognostic model based on T cell exhaustion genes, which can contribute to the development of more precise and effective therapies.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools