 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Chitosan oligosaccharide enhances the anti-cancer effects of 5-fluorouracil on SNU-C5 colorectal cancer cells by activating ERK
1 Jeju Research Center for Natural Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, 63243, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, 61452, Republic of Korea
3 Department of Anatomy, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, 61452, Republic of Korea
4 Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Jeju National University, Jeju, 63243, Republic of Korea
* Corresponding Author: SANG-PIL YOON. Email:
Oncology Research 2025, 33(4), 873-884. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.052003
Received 21 March 2024; Accepted 07 June 2024; Issue published 19 March 2025
Abstract
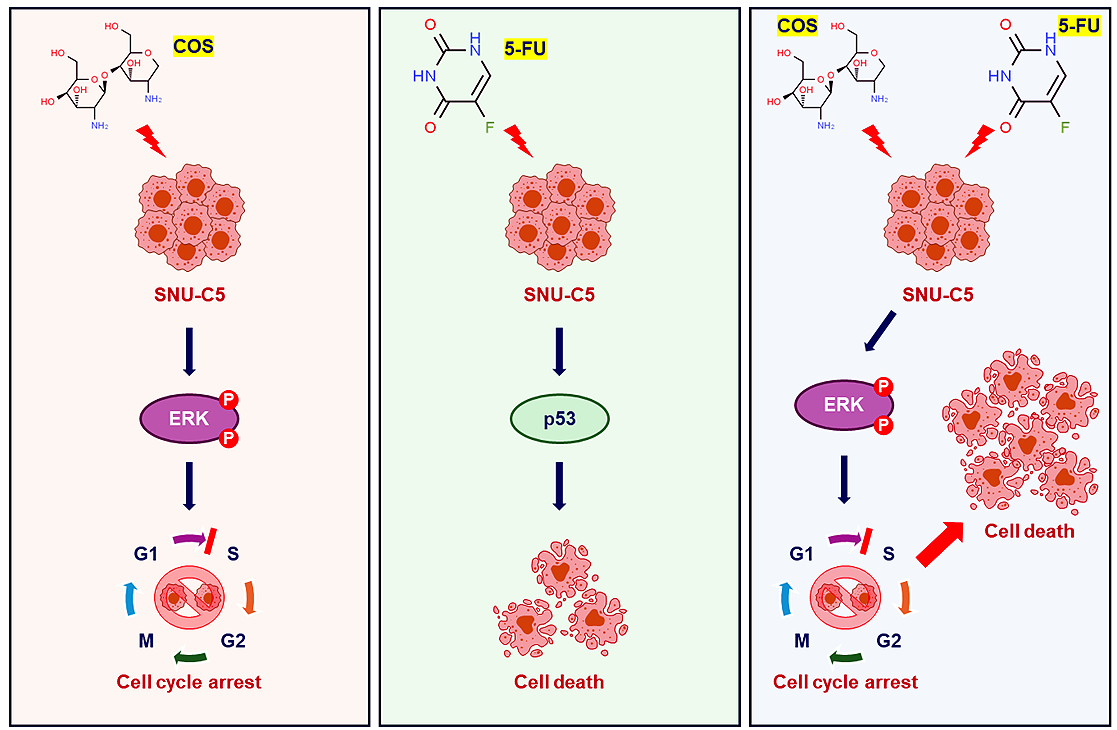
Background: Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS) is the major degradation product of chitosan by enzymatic processes. COS, with complete water solubility, exerts significant biological effects, including anti-cancer activity. We investigated the anti-tumor effects of COS on colorectal cancer as effective therapeutic methods with low side effects are lacking. Methods: COS was obtained from low molecular weight chitosan by an enzymatic method and the anti-cancer effects were measured by cell viability assay, flow cytometry analysis, Western blotting, and xenograft. Results: COS suppressed the proliferation of SNU-C5 cells compared to other colorectal cancer cells, but higher concentrations were required in the xenograft model. Co-treatment with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and COS enhanced the anti-cancer effects of 5-FU in SNU-C5 cells in vitro and in vivo. Flow cytometry revealed that COS induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase without 5-FU or at the S and G2/M phases with 5-FU but did not affect cell death pathways. COS increased extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) activation with or without 5-FU, whereas 5-FU treatment increased p53 activation. A low-dose of an ERK inhibitor suppressed COS-induced ERK activation and resulted in higher proliferation compared with COS. Conclusions: These results suggest that COS might enhance the anti-cancer effects of 5-FU in SNU-C5 colorectal cancer cells by activating ERK.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools