 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Unveiling the therapeutic potential: KBU2046 halts triple-negative breast cancer cell migration by constricting TGF-β1 activation in vitro
1 Research Center, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, 050000, China
2 Key Laboratory of Tumor Gene Diagnosis, Prevention and Therapy, Clinical Oncology Research Center, Shijiazhuang, 050000, China
3 Department of Blood Transfusion, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, 050000, China
4 Breast Center, Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, 050000, China
5 Hebei Provincial Key Laboratory of Tumor Microenvironment and Drug Resistance, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, 050000, China
* Corresponding Authors: YUNJIANG LIU. Email: ; LIANMEI ZHAO. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Cancer Pharmacology)
Oncology Research 2024, 32(11), 1791-1802. https://doi.org/10.32604/or.2024.049348
Received 04 January 2024; Accepted 25 March 2024; Issue published 16 October 2024
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a heterogeneous, recurring cancer characterized by a high rate of metastasis, poor prognosis, and lack of efficient therapies. KBU2046, a small molecule inhibitor, can inhibit cell motility in malignant tumors, including breast cancer. However, the specific targets and the corresponding mechanism of its function remain unclear. Methods: In this study, we employed (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H tetrazolium) (MTS) assay and transwell assay to investigate the impact of KBU2046 on the proliferation and migration of TNBC cells in vitro. RNA-Seq was used to explore the targets of KBU2046 that inhibit the motility of TNBC. Finally, confirmed the predicted important signaling pathways through RT-qPCR and western blotting. Results: In this study, we found that KBU2046 functioned as a novel transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1) inhibitor, effectively suppressing tumor cell motility in vitro. Mechanistically, it directly down-regulated leucine-rich repeat-containing 8 family, member E (LRRC8E), latent TGFβ-binding protein 3 (LTBP3), dynein light chain 1 (DNAL1), and MAF family of bZIP transcription factors (MAFF) genes, along with reduced protein expression of the integrin family. Additionally, KBU2046 decreased phosphorylation levels of Raf and ERK. This deactivation of the ERK signaling pathway impeded cancer invasion and metastasis. Conclusions: In summary, these findings advocate for the utilization of TGF-β1 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and as a therapeutic target in TNBC. Furthermore, our data underscore the potential of KBU2046 as a novel therapeutic strategy for combating cancer metastasis.Graphic Abstract
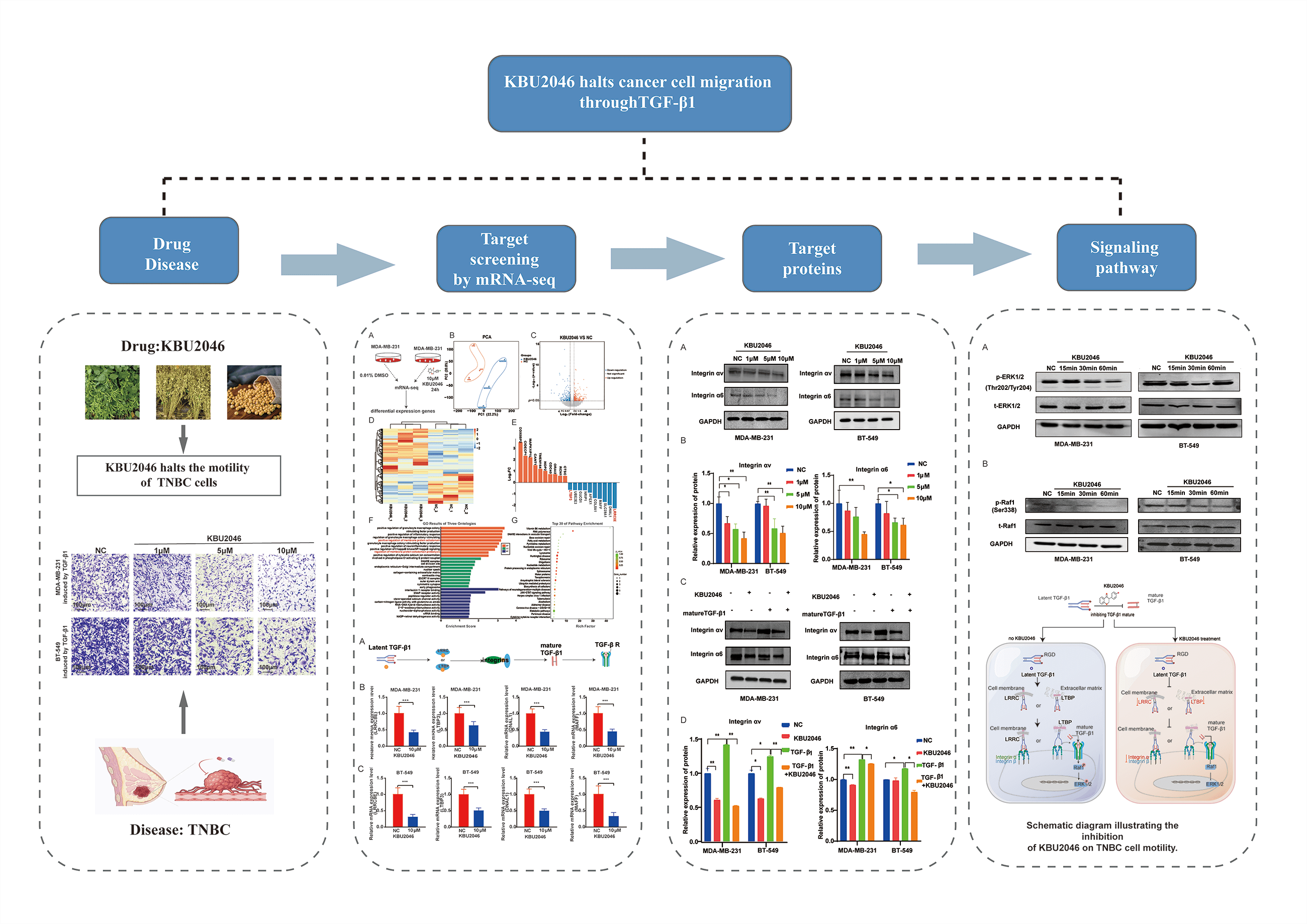
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools