 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Francisco Raúl Borzone1,2,*, María Belén Giorello1, Agustina Freire3, Leandro Marcelo Martinez4, Leonardo Feldman5, Federico Dimase6, Pablo Evelson3, Irene Larripa7, Emilio Batagelj8, Marcela Beatriz González Cid9, Norma Alejandra Chasseing1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074321
Abstract Backgrounds: Breast cancer metastasis remains the leading cause of mortality and frequently targets the bone. Breast cancer cells release soluble factors and extracellular vesicles that disrupt bone marrow (BM)/bone homeostasis, promoting osteoclastogenesis and the accumulation of senescent cells. In line with updated cancer hallmarks, senescent mesenchymal stem/ stromal cells (MSCs), osteoblasts, and osteocytes contribute to remodeling of the BM microenvironment, thereby favoring pre-metastatic niche (PMN) formation and subsequent bone metastasis. We previously demonstrated that untreated stage III-B breast cancer patients (BCPs) exhibit increased oxidative stress and elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, accompanied by senescent… More >
Graphic Abstract
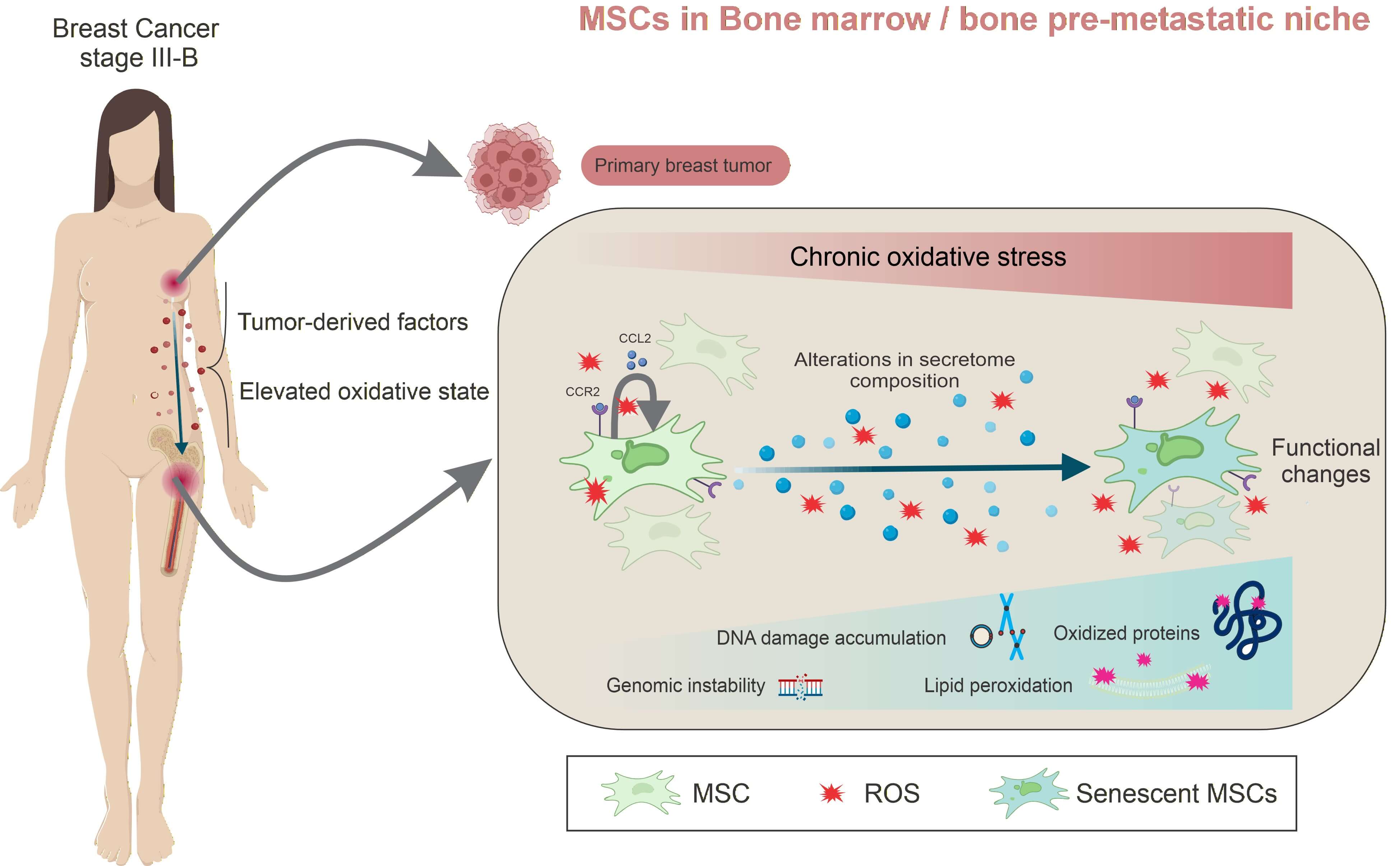
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Awatif Rashed Z. Almotairy1,2, Eman Fayad3, Fatimah Hadadi4, Ahmad F. Alhomodi5, Dalal Nasser Binjawhar6, Hanadi A. Katouah7, Bassma H. Elwakil8,*, Keshav Raj Paudel9,10,*, Mostafa El-Khatib11
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070645
Abstract Objectives: Prostate cancer cells often develop mechanisms to evade conventional therapies. Nanomedicine offers the potential for targeted drug delivery, improved tumor accumulation, and reduced systemic toxicity. This study biosynthesizes silver nanoparticles (NPP/AgONPs) functionalized with propolis, evaluates their antibacterial efficacy against uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), and assesses their cytotoxic effect on cancer cell proliferation using the PC-3, human prostate epithelial cell line. Methods: The synthesized NPP/AgONPs physiochemical parameters were characterized, followed by in vitro assays to evaluate their antibacterial activity against multiple uropathogenic E. coli strains; determining the cytotoxicity against HPrEC and PC-3 cells by measuring cytotoxicity (CC50)… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Abdul Manan1,2, Sidra Ilyas2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074185
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics of Liver Cancer)
Abstract Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a significant global health challenge, with therapeutic efficacy in advanced stages often limited by underlying liver dysfunction and adaptive resistance. In this review, the evolving landscape of molecular targets and combinatorial strategies is critically examined, with a particular focus on the transition from preclinical discovery to clinical application. While traditional molecular heterogeneity is acknowledged, the aim is to elucidate how emerging computational paradigms are redefining target discovery and therapeutic stratification in HCC. The primary purpose is to evaluate the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) as integrative tools… More >
Graphic Abstract
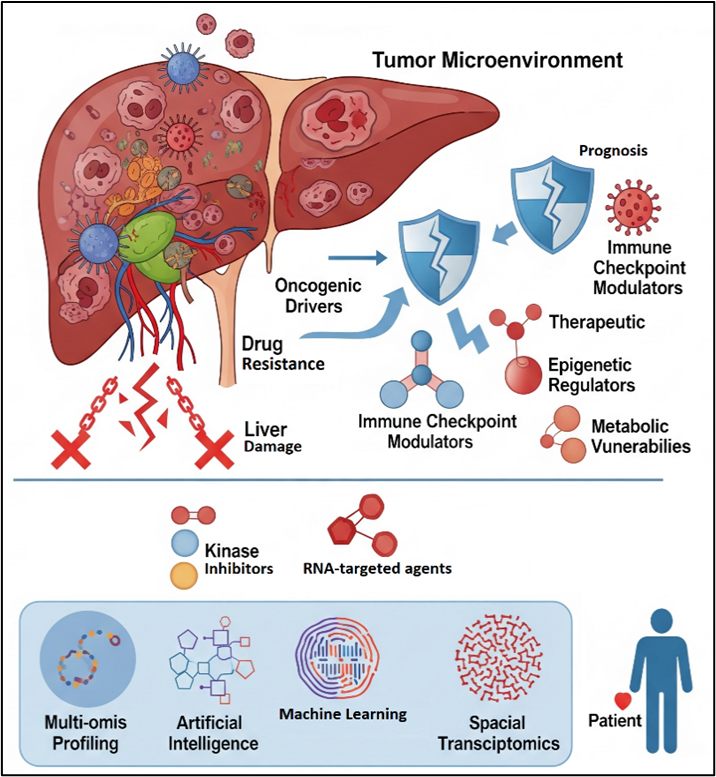
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingzheng Tan1,#, Jiao Xiao2,#, Liyun Tang3,4,#, Jian Wan3,#, Tian Zeng3, Wenchao Zhou3, Xueru Liu3, Xun Chen3,5,*, Yukun Li3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071536
Abstract Background: Lactate, as a critical byproduct of tumor metabolic reprogramming, plays an important role in DNA damage repair and tumor immune infiltration. This work aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which lactate promotes tumor DNA damage repair (DDR) and subsequent immune evasion. Methods: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), and ovarian cancer (OC) cells with cisplatin-induced DNA damage were treated with lactate at a concentration gradient, Endothelial cell-specific molecule 1 (ESM1) shRNA, ESM1 overexpression plasmid, or the Protein Kinase B (AKT) Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 (Akt1) inhibitor LY294002. Proliferation, apoptosis, and DNA damage levels were… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Daniel Burg1, Aryeh Babkoff1, Omer Or2, Noam Olshinka2, Jonathan Abraham Demma3, Mohamad Adila1,3, Marc Wygoda4, Philip Blumenfeld4, Judith Diment5, Masha Galiner6, Yusef Azraq6, Daniela Katz1,7, Petachia Reissman8, Sadie Ostrowicki9, Gabriella Sebbag10, Narmine Elkhateeb1,11, Anat Hershko Moshe1,11, Dania Jaber1,11, Adi Hollander1,11, Limor Rubin1,11, Aviad Zick1,12,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.070233
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Combined Therapy for Soft Tissue Sarcomas)
Abstract Background: —Synovial sarcoma is a rare soft tissue sarcoma. Treatment of synovial sarcoma includes surgery, radiation, pazopanib, and chemotherapy. Targeted therapies, such as B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase (BRAF) inhibitors, are emerging as a potential treatment option. We describe the sixth case of a BRAFV600E synovial sarcoma, the first extra-thoracic case. This case is the first to show a complete pathological response to BRAF & mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors. Case description: —We treated a 22-year-old male with a left groin BRAFV600E synovial sarcoma with doxorubicin, Ifosphamide & Sodium 2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate. When we identified BRAFV600E in the tumor,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Adam Khorasanchi, Merve Hasanov, Richard Wu, Hisham Alsharif, Kari Kendra, Claire Verschraegen*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.069012
Abstract Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (CSCC) is the second most common type of skin cancer and typically involves the head and neck. Systemic therapy is often required for patients with advanced CSCC to achieve optimal disease control. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are now the standard of care for these patients, with a 50%–60% response rate and sustainable remission for at least 30% of patients. Given the activity of ICIs in advanced head and neck CSCC, ICIs are being studied in early-stage disease or neoadjuvant situations. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yiran Dong1, Jingyue Wang1, Jiayang Chen2, Liang Mo2, Yong You1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075191
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Identification of potential targets and biomarkers for cancers and the exploration of novel molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis and metastasis)
Abstract Background: Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), the most prevalent histological subtype of lung cancer, remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality due to late diagnosis, metastasis, and therapy resistance. The aim of the study is to investigate the role of Kinetochore Scaffold 1 (KNL1) in promoting LUAD progression and its underlying molecular regulatory mechanisms. Methods: KNL1 mRNA expression levels across 33 cancer types were analyzed using bioinformatics analysis based on the TCGA database. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to assess KNL1 expression in LUAD and normal tissues. Stable KNL1-knockdown and KNL1-overexpressing LUAD cell lines were established using lentiviral… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yingying Zhao1,2, Jiakang Ma1,3, Rujin Huang1,2, Shuxian Pan1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.070208
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning for Disease Subtyping, from Molecular to Clinical Features)
Abstract Background: Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play critical roles in tumor progression and immunosuppression; however, their contribution to the functional classification and personalized treatment of gastric cancer remains poorly defined. This study aimed to identify effective therapeutic targets to facilitate individualized treatment strategies for patients with gastric cancer. Methods: Single-cell and bulk transcriptomic analyses were integrated to characterize gastric cancer fibroblasts. “Seurat”, “Slingshot”, and “CellChat” were used for dimensionality reduction, trajectory inference, and cell–cell communication analyses, respectively. Key metastasis-associated fibroblast modules were identified using High-dimensional weighted gene co-expression network analysis (hdWGCNA) to construct a prognostic model, which was further… More >
Graphic Abstract
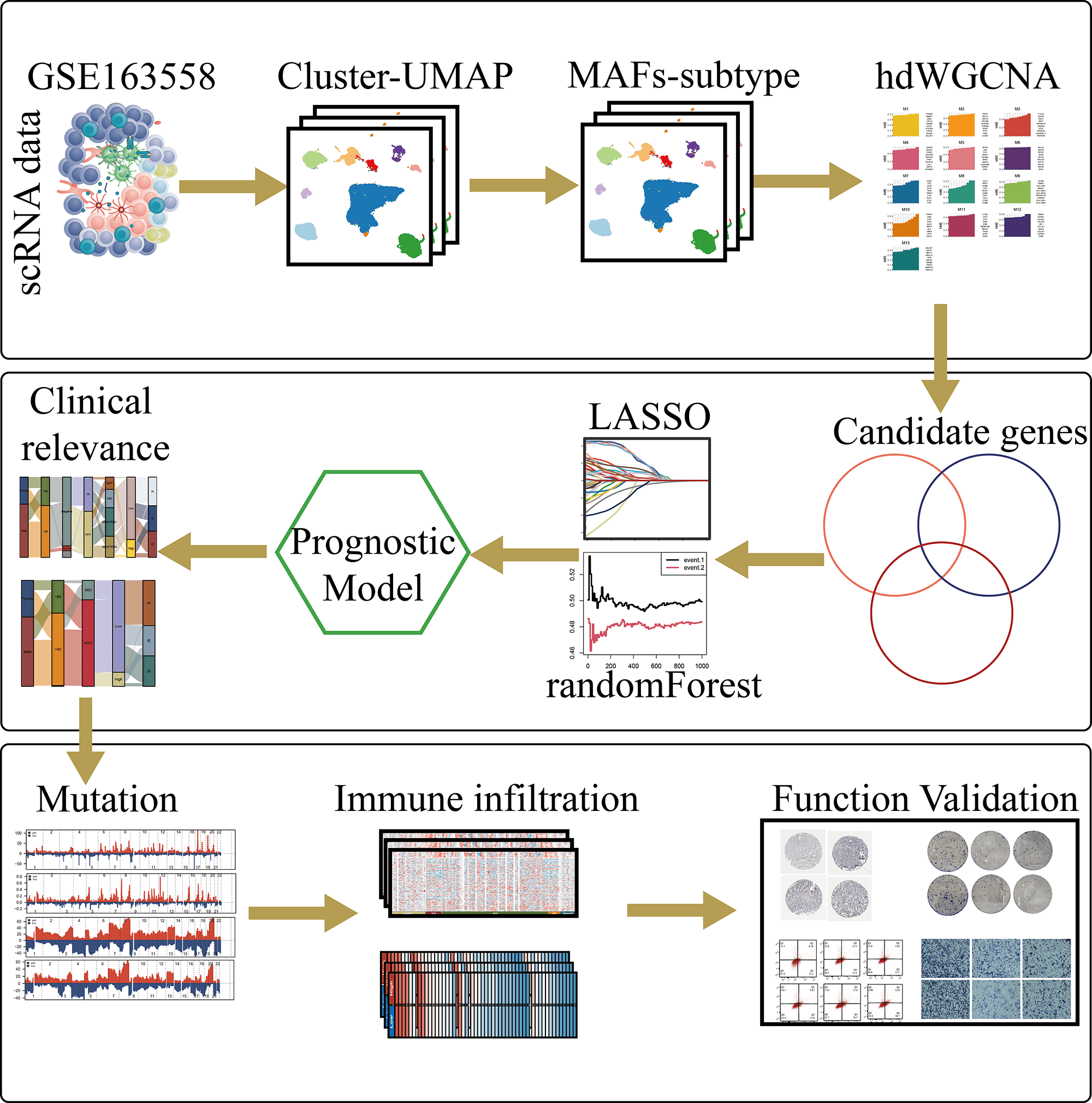
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Aktham Mestareehi1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073745
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Liver Cancer: Novel Therapeutics and Biomarkers for HCC and CCA)
Abstract Objective: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, largely due to late diagnosis, molecular heterogeneity, and limited prognostic biomarkers. Aberrant protein phosphorylation plays a critical role in cancer progression by regulating DNA damage response, cell cycle control, and signaling pathways; however, the prognostic relevance of phosphorylation events in key DNA topology–related proteins remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic significance of phosphorylation of TOP1, TOP2A, TOP2B, and C1orf35 in HCC and to characterize their associated molecular features to identify potential diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers. Methods: Publicly available HCC… More >
Graphic Abstract
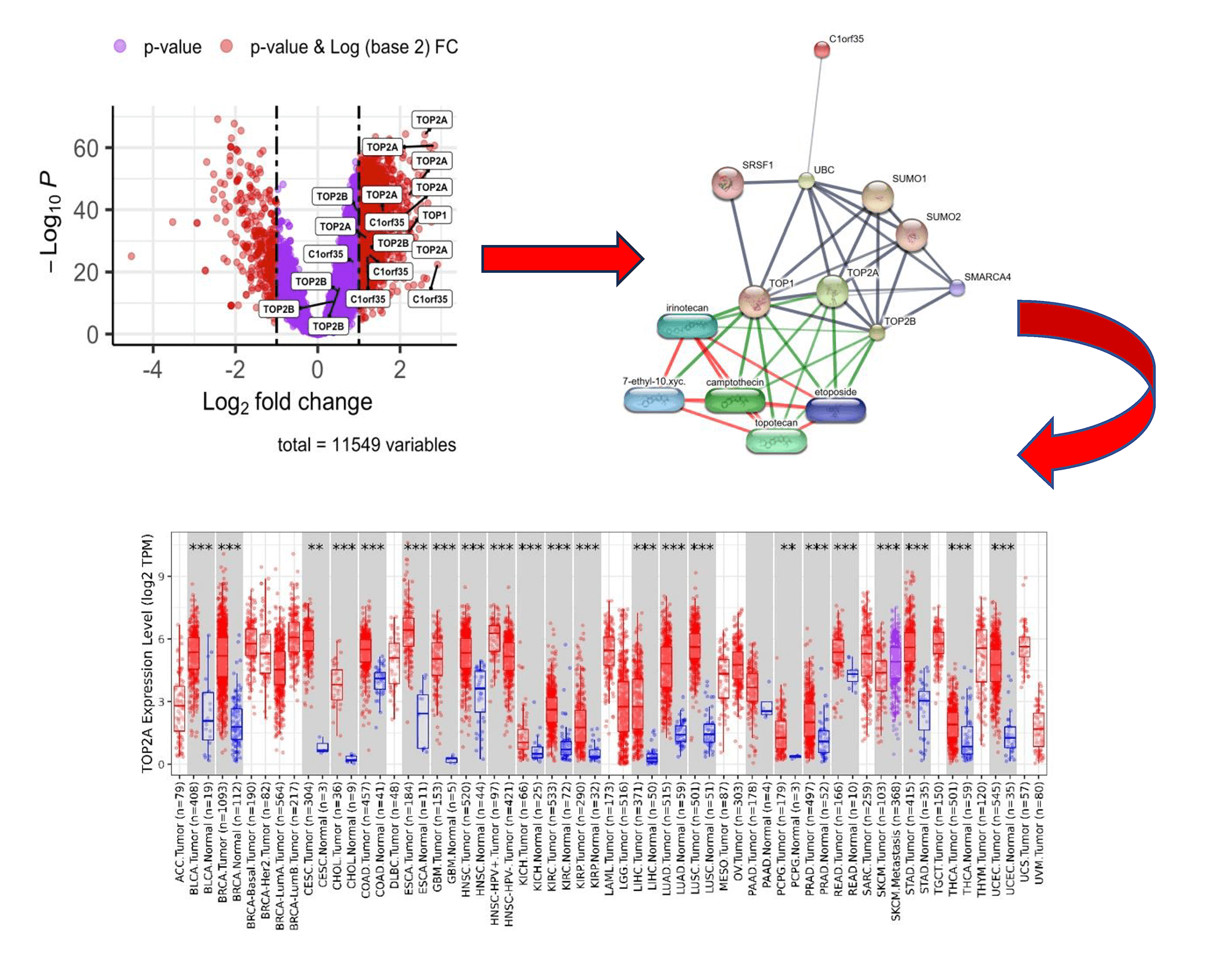
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shanbao Ke, Junya Yan, Xiao Feng, Baiyu Li*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071617
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning for Disease Subtyping, from Molecular to Clinical Features)
Abstract Objectives: Tumor recurrence is a major determinant of poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), yet its cellular and molecular basis remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to identify recurrence-associated genes at single-cell resolution and to develop a prognostic model for predicting survival outcomes and immunotherapy responsiveness in HCC. Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing data from 12 primary and 6 recurrent HCC samples were integrated and analyzed to identify genes characteristic of recurrence. After quality control, principal component analysis, and t-SNE-based clustering were used to identify highly variable genes for cell clustering and annotation. Based on macrophage… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Ye Ri Han1,*, Sang Bong Lee2,3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075923
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract Radiopharmaceuticals deliver diagnostic or therapeutic radionuclides to disease sites with molecular precision. Over the past five years, clinical adoption has accelerated, led by U.S. Food and Drug Administration approvals of 177Lu-DOTA-TATE and 177Lu-PSMA-617 and their complementary Positron Emission Tomography agents (68Ga-DOTA-TATE, 68Ga-PSMA-11), which have established radiotheranostics as a pillar of oncology care. The new generation of agents couples optimized radionuclides (β−, α, and Auger emitters) to antibodies, peptides, and small-molecule vectors that improve tumor uptake, residence time, and clearance profiles, thereby enhancing efficacy and safety. Beyond neuroendocrine tumors and prostate cancer, radiotheranostic strategies are advancing for diverse malignancies… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Maureen Veilleux1,2,#, Anh Nguyen3,#, Charles Cao4,#, Yihui Shi2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072194
Abstract ADP-ribosyltransferases (ARTs) regulate key processes in cancer, including DNA repair, transcription, immune responses, and treatment resistance. The clostridial toxin-like ADP-ribosyltransferase (ARTC) family and the diphtheria toxin-like ADP-ribosyltransferase (ARTD) family play a crucial role in genomic stability by modification of proteins either with mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation (MARylation) or poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PARylation). These ARTs are promising therapeutic targets and could serve as biomarkers in cancer management. This review explores the roles of these enzymes and current knowledge on specific inhibitors. A literature search was conducted in PubMed and Google Scholar to identify studies published between 1992 and 2025 on ADP-ribosyltransferases… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Weiping Yang1,#, Wei Xiao2,#, Wenhao Xu3,#, Lijun Ren1, Xian Li1, Junhua Yu1, Ronghua Wang4,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071122
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning for Disease Subtyping, from Molecular to Clinical Features)
Abstract Background: Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) promote antitumor immunity and predict favorable immunotherapy outcomes in breast cancer. The study aimed to investigate how Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO2)-associated tryptophan metabolism influences TLS maturation and B cell class switching in breast cancer. Methods: Bulk transcriptomic data from The Cancer Genome Atlas-Breast Invasive Carcinoma (TCGA-BRCA, n = 1055) were analyzed using Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA)–based metabolic scoring, immune deconvolution, and TLS quantification. Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq, n = 26) and spatial transcriptomics (n = 1) were applied to map TDO2 expression and TLS spatial organization. Validation was performed by immunohistochemistry (n… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Francesco Chiari1,*, Giovanni Motta2, Daria Maria Filippini3, Claudio Donadio Caporale1, Pierre Guarino1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073086
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Challenges and Controversies in Laryngeal Cancer)
Abstract Objective: Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC) of the larynx is an extremely rare malignancy, accounting for less than 1% of primary laryngeal tumors. The optimal role of adjuvant therapy, particularly radiotherapy (RT), remains unclear due to limited evidence. This systematic review aimed to evaluate oncologic outcomes and the impact of adjuvant treatment in patients with early- and advanced-stage laryngeal MEC. Methods: A systematic literature search was performed according to PRISMA 2020 guidelines in PubMed/Embase, Scopus, and Cochrane for studies published up to 31 July 2025. Results: Twenty-two studies, encompassing 55 patients, were included. Early-stage (T1–T2) patients (n =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
So-Ye Jeon1,#, Zeeshan Ahmad Bhutta1,#, Hong Kyu Lee2, Kyung-Chul Choi1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071328
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Breast Cancer Biomarkers and Drug Targets Discoveries Towards a More Personalized Treatment Setting)
Abstract Objectives: Progesterone (P4) is believed to inhibit breast cancer growth, but its role in counteracting estrogen (E2)-driven progression remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effect of P4 on E2-induced cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in Estrogen receptor (ER)+/progesterone receptor (PR)+ breast cancer cells by examining its regulatory role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Methods: ER and PR-positive MCF-7 clonal variant (MCF-7 CV) breast cancer cells were treated with E2 and co-treated with various concentrations of P4. The effects on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were assessed. The expression of key EMT markers… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Mohsina Patwekar1,2, Faheem Patwekar3, Zulhisyam Abdul Kari1,4,*, Muhammad Rajaei Ahmad Mohd Zain5,*, Arifullah Mohammed6, Rohit Sharma7,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073601
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: The Evolving Landscape of Cancer Treatment: Molecular Insights and Immunotherapeutic Breakthroughs)
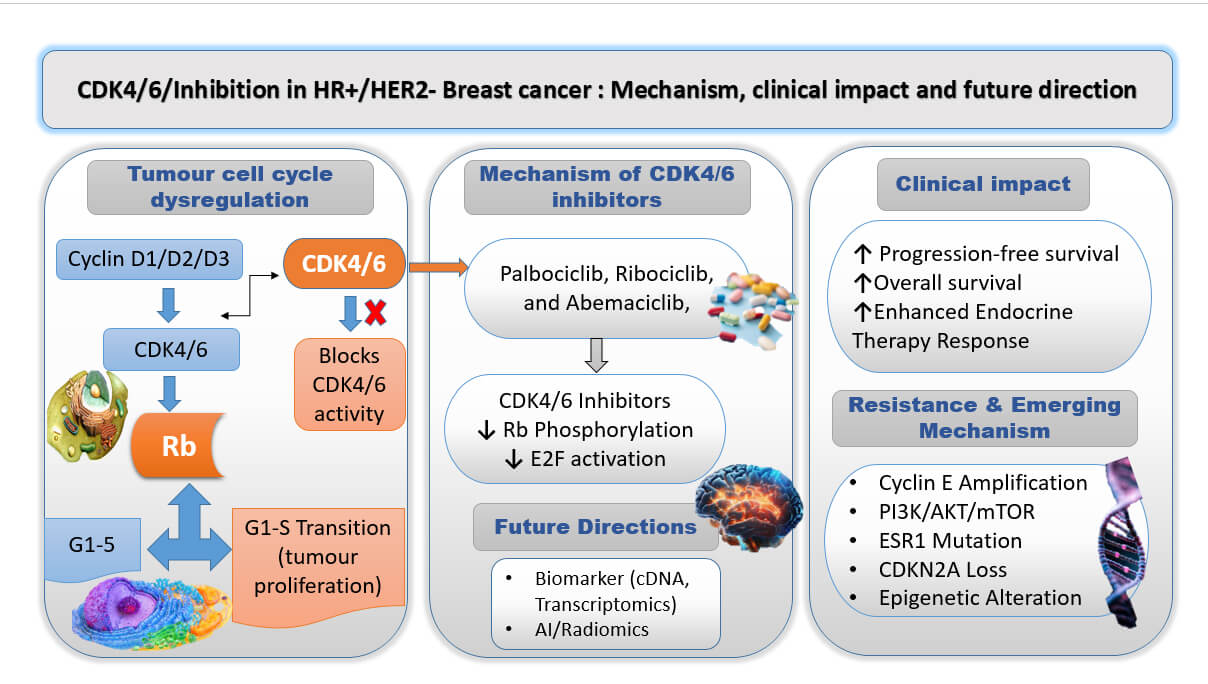
Abstract Breast cancer remains the primary cause of cancer-related mortality for women globally; therefore, further breakthroughs in treatment approaches are crucial. Palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib are among the Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors that have become an innovative family of targeted therapy for hormone receptor-positive, Human Epidermal Growth factor receptor 2 (HR+/HER2−) breast cancer. These inhibitors work by preventing the action of CDK4/6, which are crucial in the regulation of the cell cycle. Leading cancer cells to cell cycle arrest and undergo apoptosis. When these inhibitors are used with endocrine medicines like letrozole and… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Abhishikt David Solomon1,*, Himanshu Kumar Vats2,#, Shivam Chowdhary3,#, Supriya Nandlal Kanoujiya4, Ajit Prakash5, Hina Sultana6, Sabyasachi Mohanty7, Billy W. Day8, Tarun Pant9,10,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.071632
Abstract Tumor survival, genomic stability, and therapy resistance are dictated by the DNA damage response (DDR). Although poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have established the DDR as a therapeutic target, many tumors evade first-generation drugs by rewiring their adaptive repair pathways and imposing microenvironmental constraints. This review synthesizes recent discoveries in key DDR pathways, such as PARP, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related kinase (ATR), ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase (ATM), checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1), WEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase (WEE1), and DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK), and describes the next-generation inhibitors designed to increase selectivity and circumvent resistance. We also… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
COMMENTARY
Leenah Abdulgader1, Abdullah Esmail2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.069227
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targets and Combinatorial Therapeutics of Liver Cancer)
Abstract Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a global challenge, with limited effective treatment options for advanced-stage disease. The HIMALAYA trial (phase III randomized study that evaluated the STRIDE regimen) introduced the Single Tremelimumab Regular Interval Durvalumab (STRIDE) regimen, an immunotherapy-based approach that achieved a median overall survival (OS) of 16.43 months compared to 13.77 months with sorafenib. While statistically significant, this ~2.7 months OS gain warrants scrutiny in light of STRIDE’s increased immune-related toxicity and cost. This commentary evaluates STRIDE’s impact within the broader landscape of first-line systemic therapy for unresectable HCC, alongside other regimens such… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ya-Ling Yang1,#, Ying-Hsien Huang2,#, Hung-Yu Lin3,4,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.075284
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
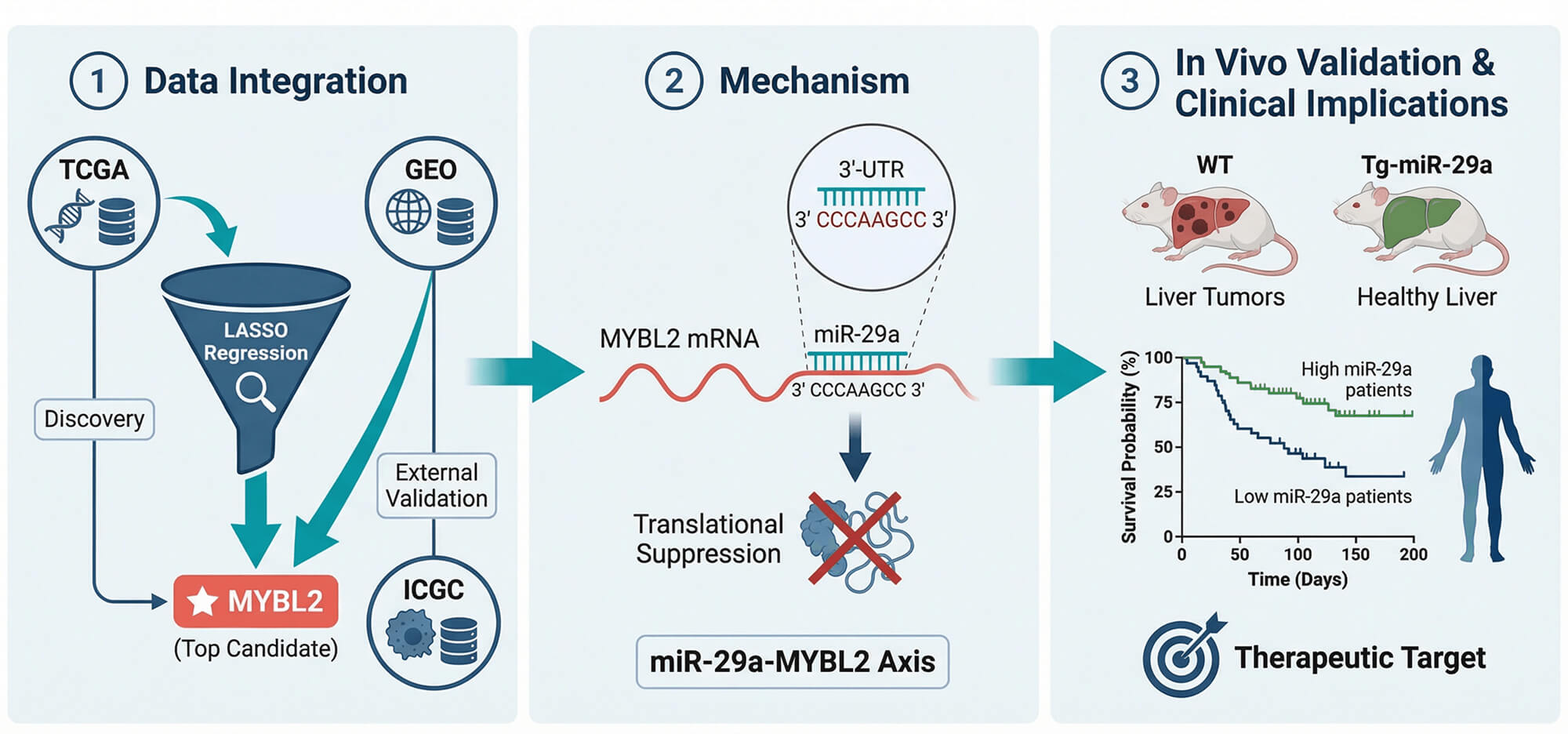
Abstract Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents with poor treatment outcomes, creating an urgent need for novel biomarkers to improve diagnosis, prognosis, and precision medicine. While the MYB family of oncogenes is implicated in cancer, the role and regulatory mechanisms of its member, particularly MYB proto-oncogene like 2 (MYBL2), remain underexplored in HCC. Therefore, this study aimed to systematically validate the clinical significance of MYBL2, elucidate its functional role in tumor progression and drug sensitivity, and identify its upstream regulatory mechanisms using an integrative machine learning and experimental framework. Methods: We applied an integrative pipeline combining LASSO-based… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yanfeng Wang1,2,#, Xinyi Chen1,2,#, Yichen Yin1,2, Tao Li3,*, Jing Chen1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.068695
Abstract Objectives: B-cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) is a transcriptional repressor whose overexpression is closely linked to the progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), making it a promising therapeutic target. This study aims to identify a novel small molecule, synthesized via proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs), capable of degrading BCL6, thereby inhibiting DLBCL growth and providing a foundation for future preclinical studies. Methods: The expression of BCL6 in DLBCL was analyzed using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the Human Protein Atlas. Western blotting assays confirmed BCL6 expression in tumor cell lines, leading to the identification of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jiaxi Li#, Deepak Iyer#, Siming Sui, Zheng Huang, Ryan Wai-Yan Sin, Abraham Tak-Ka Man, Wai-Lun Law, Chi-Chung Foo*, Lui Ng*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074981
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
Abstract Objectives: Piwi-associated RNAs are small non-coding RNAs implicated in cancer, yet few have been characterized in colorectal cancer (CRC). This study aimed to identify a CRC-related piRNA and investigate its clinical relevance, biological function, and biomarker potential. Methods: Candidates were identified by reanalysis of small-RNA sequencing. piR-37524 was quantified by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in colorectal cancer tissues, matched adjacent non-tumor tissues, colorectal adenomas, liver metastases, and serum samples from patients and healthy controls. Clinicopathological correlations and diagnostic performance were evaluated. Functional assays included 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) proliferation, colony formation, and wound-healing migration… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Munro Matthew James1,*, López Vásquez Clara Elena1,2, Wickremesekera Agadha3, Chan Alex Ho Chuen1, Gray Clint Lee1,4,5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074958
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Drug Targets in Oncology: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Innovations)
Abstract Objective: Meningioma is the most common primary brain tumour. Invasion into the brain is a diagnostic feature of grade II meningiomas and is associated with recurrence and poor prognosis. Mebendazole is a microtubule inhibitor typically prescribed as an anthelmintic. However, it has the potential to be repurposed for cancer treatment. Here, we aimed to assess the ability of mebendazole to inhibit meningioma cell invasion. Methods: Primary patient-derived meningioma cell lines were cultured as 3D spheroids and embedded in an extracellular matrix-like matrix as an in vitro model of invasion. Mebendazole-treated and untreated control spheroids were analysed… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Crystal J. Byrd1, Monasia Evans1, Woojung Kim2, Quintera Knight3, Geou-Yarh Liou1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073532
Abstract Objective: The progression of prostate cancer cells to metastasis is supported by their tumor microenvironment. Within this microenvironment, infiltrating immune cells, such as B cells, can be either anti-tumorigenic or pro-tumorigenic. Our preliminary data showed that a higher density of the infiltrating B cells was found near prostate cancer cells in human cancer tissues, as compared to the benign prostate tissue regions, thus suggesting that infiltrating B cells would promote the progression of prostate cancer cells. In this study, we aim to investigate the role of infiltrating B cells in enhancing the migratory ability of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
VIEWPOINT
Paolo Maione1,*, Valentina Palma1,2, Cesare Gridelli1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072992
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract After about 20 years of exciting improvements in treatment efficacy outcomes of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), also combined with a progressively better safety profile, from chemotherapy to new generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) (osimertinib, alectinib, brigatinib), the recent MARIPOSA and CROWN trials have changed this trend. For the first time in the history of EGFR and ALK treatments, we must face the issue of being a step behind in terms of toxicity profile. The combination of amivantamab plus lazertinib in EGFR mutant NSCLC, and… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Vishal Rastogi1,#, Deepak Verma2,#, Saurabh Verma3, Prakash Haloi1, Shruti Kapoor4, Havagiray R. Chitme1, Nethaji Muniraj5,*, Priyanka Saroj1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.072620
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Strategies in the Diagnosis, Prediction, Monitoring, and Treatment of Brain Tumors)
Abstract Metastatic brain tumors undergo profound metabolic–epigenetic reprogramming driven by the unique constraints of the brain microenvironment. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF1α) enhances glycolytic flux, lactate accumulation, and histone lactylation, collectively supporting metastatic colonization and immune evasion. Key metabolites including acetyl-CoA, S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), fumarate, and 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)—directly modify chromatin states by regulating histone acetyltransferases, DNA/histone methyltransferases, and α-KG dependent dioxygenases such as Ten-Eleven Translocation (TET) enzymes and lysine demethylases (KDMs). These metabolic shifts result in aberrant DNA methylation, histone lysine residue at position 27 on Histone H3 (H3K27) trimethylation, and depletion of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), all of… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Liang Zhou, Jia Zhou, Zhengyi Wang*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.069317
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy)
Abstract A clear goal in cold tumor research is to identify strategies for converting them into immunologically ‘hot’ tumors with enhanced immune cell infiltration and activity, thereby improving their responsiveness to immunotherapy. The genesis of cold tumors is exceedingly intricate. In recent times, as the analysis of this phenomenon has been pursued with greater depth, a suite of advanced diagnostic and therapeutic technologies has surfaced. These novel approaches and tactics are anticipated to modulate the tumor immune microenvironment across various dimensions, thereby facilitating the advancement of personalized and precise treatment modalities for cold tumors. The present… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Masanobu Tsubaki*, Taira Matsuo, Rie Komori
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.075217
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Molecular Targeting Therapy for Anticancer Treatment)
Abstract Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematopoietic malignancy originating from hematopoietic stem cells. It is characterized by the Philadelphia chromosome, which arises from a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22. The breakpoint cluster region::Abelson murine leukemia 1 (BCR::ABL1) fusion protein produced from this chromosome is the main factor responsible for disease onset. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have led to significant advances in CML treatment and contributed to improved patient survival rates. Nonetheless, a substantial number of patients develop resistance to TKIs, which remains a major challenge in CML therapy. Currently, two mechanisms are considered More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Eshita Dhar1,2, Muhammad Ashad Kabir3, Divyabharathy Ramesh Nadar4, Li-Jen Kuo5, Jitendra Jonnagaddala6,7, Yaoru Huang1, Mohy Uddin8,*, Shabbir Syed-Abdul1,2,9,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074385
Abstract Objectives: Decisions regarding CT after nCCRT for locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) are challenging due to limited evidence guiding treatment. This study aimed to (i) evaluate the predictive performance of machine learning (ML) models in patients treated with neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (nCCRT) alone vs. those receiving nCCRT plus chemotherapy (CT), (ii) identify features associated with treatment improvement, and (iii) derive ML-based thresholds for treatment response. Methods: This retrospective study included 409 patients with LARC treated at three affiliated hospitals of Taipei Medical University. Patients were categorised into two groups: nCCRT alone followed by surgery (n =… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Sophiette G. Hong1,2, George F. Murphy2, Christine G. Lian2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.073894
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Skin Cancer Management: From Molecular Targets to Innovative Treatments)
Abstract Malignant melanoma (MM) is a highly aggressive skin cancer known for its rapid progression, potential for metastasis, and resistance to treatment. Despite advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapy, the prognosis for metastatic melanoma remains unfavorable. Recent research has shed light on the significance of epigenetic modifications in the pathogenesis of melanoma, revealing critical mechanisms of melanoma development and progression. Epigenetic modifications, including DNA and RNA modifications, histone modifications, chromatin remodeling, and non-coding RNA regulation, disrupt normal gene expression without modifying the DNA sequence, leading to cellular transformation, invasion, immune evasion, and therapeutic resistance. The reversible… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Tiffany Chen1, Grace Kim2, Yekta Rahimi3, Monisha Kamdar4, Eduardo Fernandez-Hernandez4, Karrune Woan4, Eric L. Tam4,*, George Yaghmour4
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072443
Abstract Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains a biologically heterogeneous disease with historically limited targeted therapies and poor outcomes. The development of menin inhibitors represents a promising shift, particularly for patients harboring KMT2A rearrangements (KMT2Ar) and NPM1 mutations (NPM1m). This manuscript reviews the molecular rationale of menin inhibition for aberrant homeobox/myeloid ectopic insertion site 1 (HOX/MEIS1)-driven gene expression and leukemogenesis, clinical trial outcomes, and safety data for menin inhibitors, with a focus on recently FDA-approved revumenib and several other agents in development, ziftomenib (KO-539), bleximenib (JNJ-75276617), and icovamenib (BMF-219). We also focused our discussion on future directions to include More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shuhui Cheng1, Tiana Kordbacheh1, Antonia Banyard2, Anshuman Chaturvedi3, Diego Sanchez Martinez2, Crispin T. Hiley4,5, Maggie Harris3, Clara Chan3, Corinne Faivre-Finn3, Timothy M. Illidge1,3,#, Eleanor J. Cheadle1,#,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072053
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
Abstract Objectives: The PACIFIC trial established the benefit of durvalumab following chemo-radiotherapy for stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the concurrent use of radiotherapy (RT) and durvalumab (PACIFIC-2 trial) showed no additional advantage. The PD-RAD study was set up to understand the immunological effects of RT on the tumor microenvironment (TME) to aid in optimizing sequencing of combination therapies. Methods: The PD-RAD trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03258788) aimed to enroll thirty NSCLC patients receiving radical-intent RT. Tumor biopsies and blood samples were collected pre-RT and at week 2 during RT and analyzed using multiplex… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Vincenzo Montanarella1, Marcelo Guerrero2,3, David Filho2,3, Júlia German-Cortés1, Giacomoluciano Vitelli1, Magalí Sureda1, Carlos Pavón Regaña1, Roser Ferrer1,4, Simó Schwartz1,4, Esteban Durán-Lara2,3, Fernanda Andrade1,5,*, Diana Rafael1,6,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2026.074061
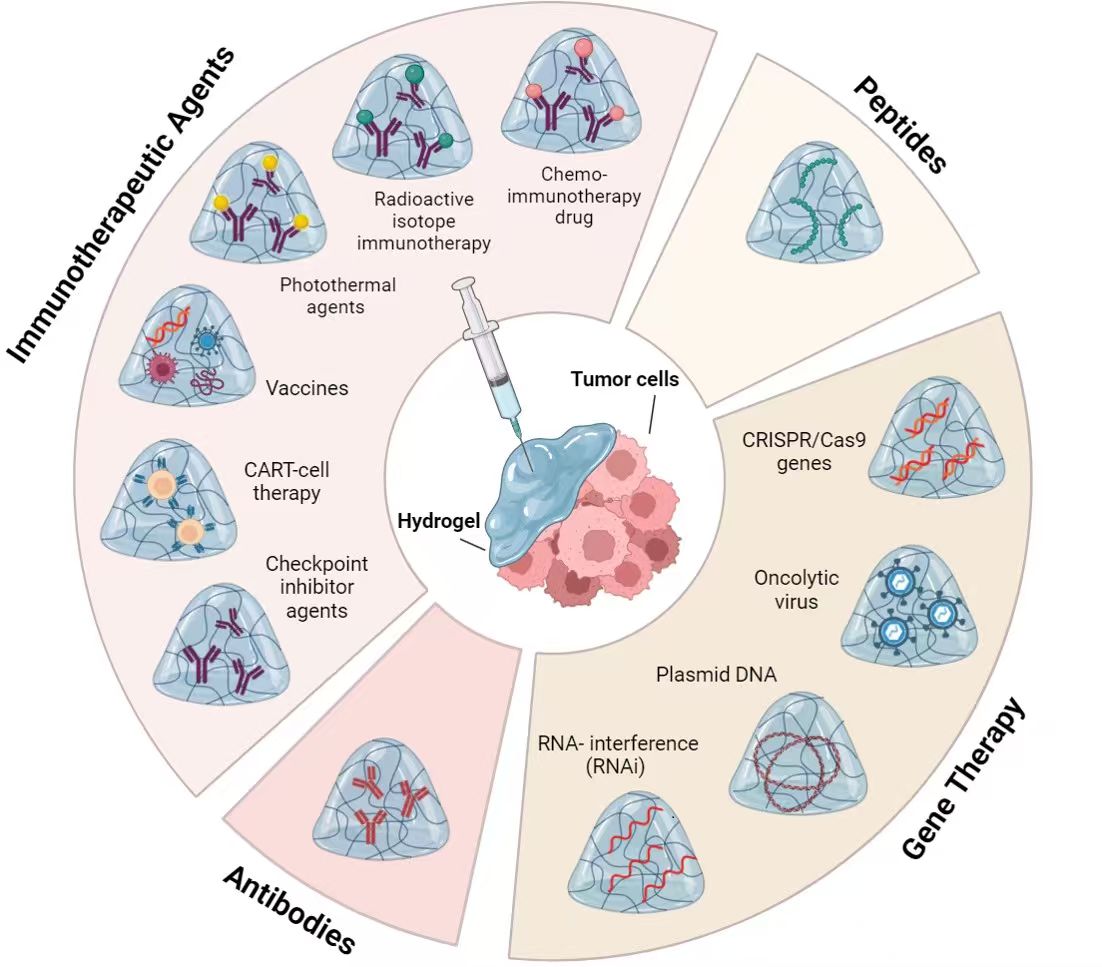
Abstract Despite remarkable advances in nanomedicine, localized delivery of advanced cancer therapeutics remains underexploited. Advanced therapies based on biopharmaceuticals, immunotherapy, or gene therapy have revolutionized oncology. Yet, their systemic administration is often associated with limitations such as poor site-specific accumulation, instability, and systemic toxicity. Hydrogels/macrogels offer the ability to encapsulate, protect, and release biomolecules in situ with sustained and stimulus-responsive profiles, addressing key translational gaps. This review provides a focused synthesis of the last five years of hydrogel-based research for cancer therapy, with emphasis on peptides, antibodies, immunotherapeutic agents, and gene delivery systems. We discuss design principles,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yen-Cheng Chen1,2,3, Tsung-Kun Chang1,2,4, Wei-Chih Su1,2,4, Yung-Sung Yeh4,5,6,7, Po-Jung Chen1,2, Tzu-Chieh Yin2,4,8, Ching-Chun Li2,9, Ching-Wen Huang2,3, Hsiang-Lin Tsai2,3, Jaw-Yuan Wang1,2,3,10,11,12,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.069397
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Innovations in Colorectal Cancer Research and Treatment)
Abstract Background: The long-term outcomes of robotic-assisted surgery and the prognostic significance of the pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) remain uncertain. This study aimed to assess the long-term outcomes of patients with LARC undergoing robotic-assisted surgery and to determine the prognostic value of pretreatment NLR. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 252 patients with LARC who were treated at a single medical center in Taiwan between January 2012 and January 2023. All patients underwent neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CRT) followed by robotic-assisted surgery with total mesorectal excision (TME). Patients were stratified into four groups… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Zheng Qin1,2,#, Yueyao Zhang3,#, Dongze Liu4,#, Xiaokang Zheng5, Kaibin Wang1,2, Xiao Zhu1,2, Yuanhao Zhang1,2, Kexin Xu1,2, Changying Li1,2, Lijuan Kang1,2, Lili Wang1,2, Haitao Wang1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073455
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis (Ⅱ))
Abstract Objective: Prostate cancer is the second most common fatal cancer in men. Identifying new biological therapeutic targets is crucial to effectively improve the prognosis of prostate cancer patients. Ovarian tumor family deubiquitinase 4 (OTUD4) is a member of the ovarian tumor-associated protease domain (OTUDs) family. Although previous studies have shown that the expression and function of OTUD4 vary across different tumors, its role in prostate cancer remains unknown. The aim of this study is to explore new therapeutic targets and diagnostic markers for prostate cancer and investigate their mechanisms of action. Methods: Cell culture, Cell… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shuwen Sun1,2,3,4,#, Jingcheng Zhang1,2,3,#, Zongtai Zheng5,#, Yajuan Hao1,3, Tianyuan Xu1,2,3, Ji Liu1,3, Liang Sun2, Aimin Wang2, Yadong Guo1,3, Shiyu Mao1,3, Xu Zhang6, Yunfei Xu1,3,*, Yifan Chen1,2,3,*, Yang Yan1,2,3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072373
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment: Emerging Insights into Cancer Progression and Therapeutics)
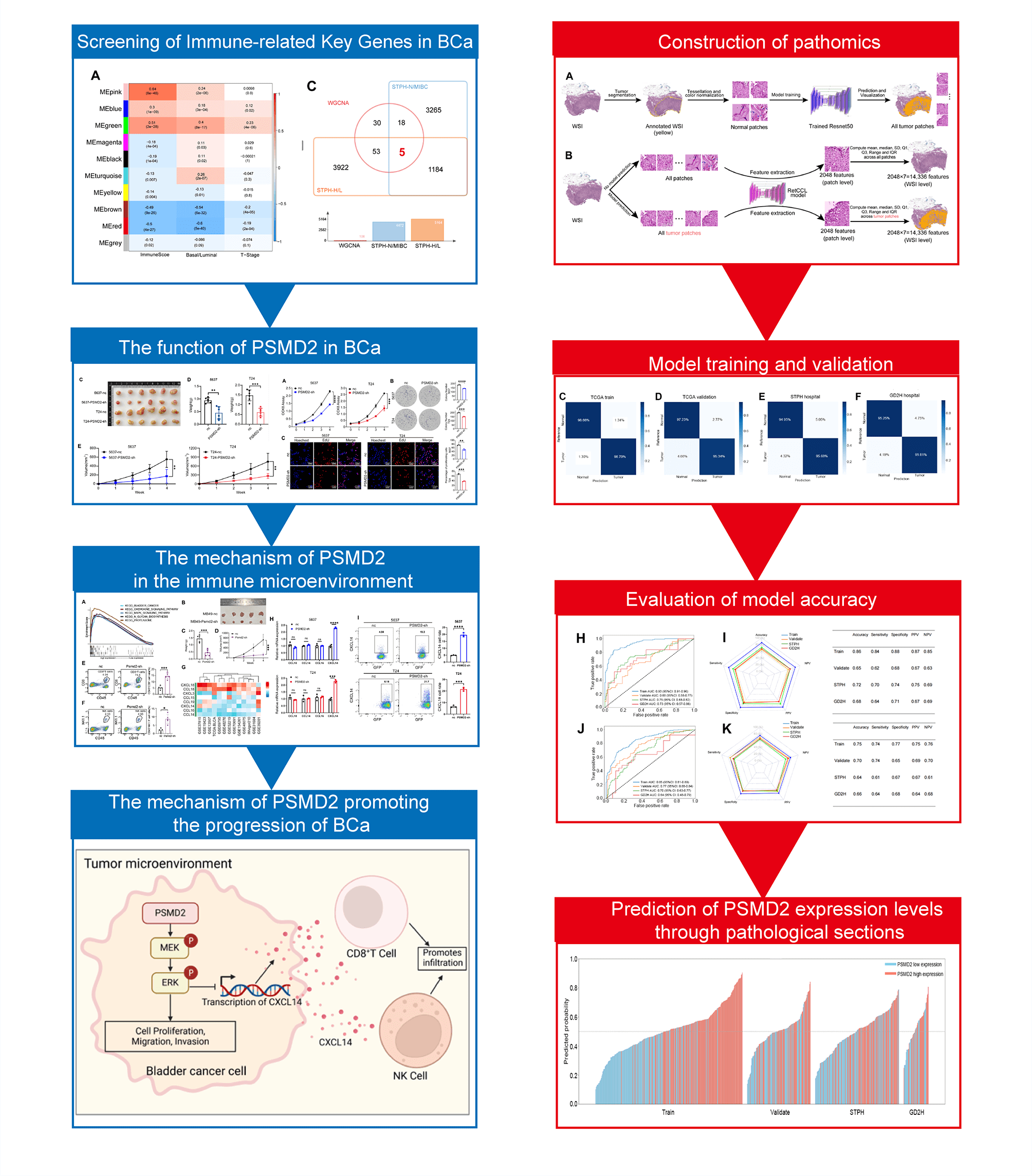
Abstract Objectives: Bladder cancer (BCa) progression is closely linked to the immune microenvironment. However, the key molecules that regulate this microenvironment and their specific mechanisms remain poorly understood. This study aims to identify a key molecule and elucidate its mechanisms, providing a theoretical basis for identifying novel therapeutic targets. Methods: Immune microenvironment-related genes in BCa were identified using The Cancer Genome Atlas and Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital datasets. Proteasome 26S subunit non-ATPase 2 (PSMD2) expression was validated via quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), Western blot (WB) analysis, and immunofluorescence (IF). In vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed the… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Ina Shehaj1,2,*, Slavomir Krajnak1, Katrin Almstedt1, Yaman Degirmenci1, Roxana Schwab1, Kathrin Stewen1, Walburgis Brenner1, Annette Hasenburg1, Marcus Schmidt1,#, Anne-Sophie Heimes1,#
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072222
Abstract This article has no abstract. More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Pauline Gousseau#, Laurie Genest, Guillaume Froget, Tristan Rupp§,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072141
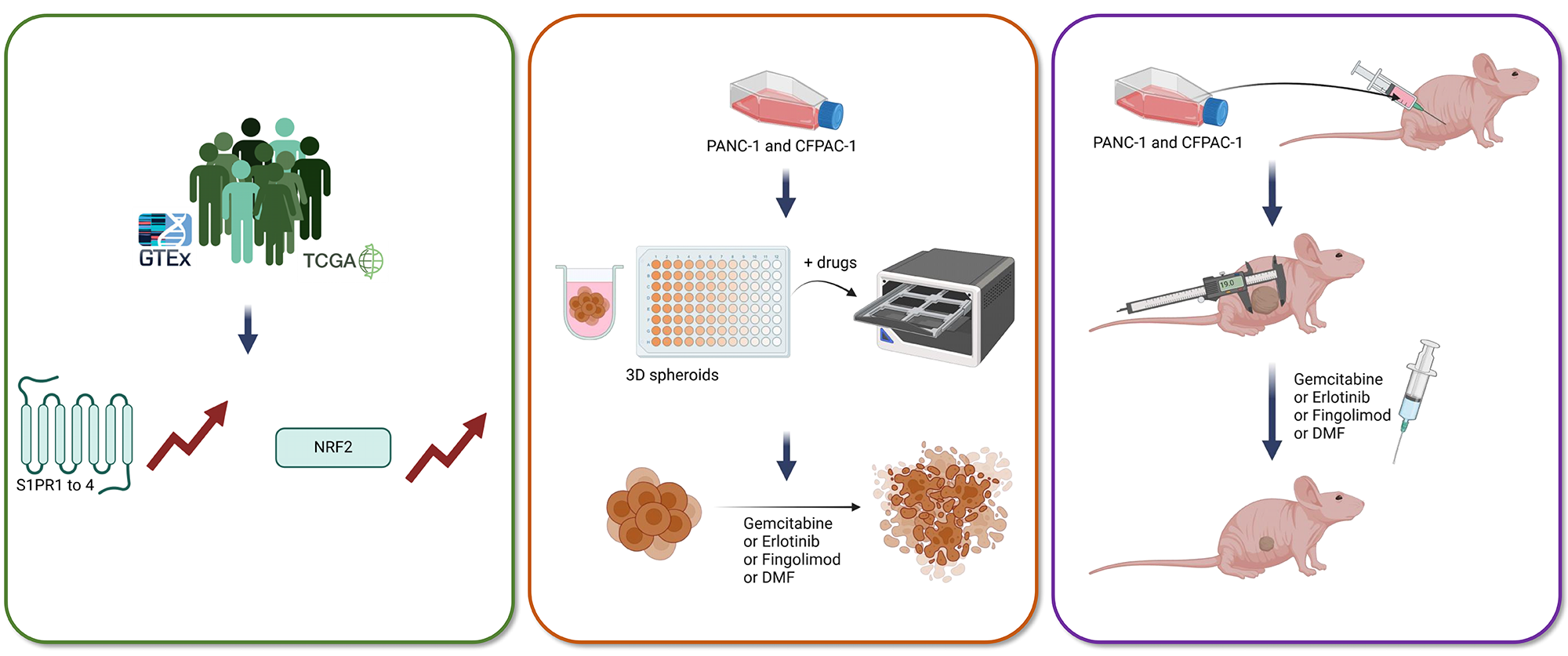
Abstract Objectives: The five-year survival rate for pancreatic cancer is notably low, posing a significant challenge to patient health. The primary treatments are radiotherapy and chemotherapy, sometimes combined with targeted therapy; however, their clinical benefits are limited. Therefore, developing new models to evaluate the therapeutic potential of novel molecules is essential. Fingolimod and Dimethyl Fumarate (DMF), currently used to treat multiple sclerosis, have recently been shown to have anti-cancer effects in several preclinical tumor models. This study aims to evaluate the therapeutic potential of Fingolimod and DMF in pancreatic cancer by investigating their respective in vitro cytotoxicity… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Frank Traub1,#, Muhammad A. Panezai1,#, Michaela Moisch1, Julia Melke1, Leonard Schöbel1, Tilmann Busse1, Fei Xing2, Jiachen Sun2, Ulrike Ritz1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071919
Abstract Objectives: Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a minimally invasive method used in the treatment of various cancers and skin diseases, but it is not widely used in bone cancer, where the current therapy is often not effective and accompanied by side effects. Alternative and more effective therapies like PDT are needed. In this in-vitro study, the effect of the photosensitizer (PS) chlorin e6 (Ce6) on cancerous bone tumor cells using PDT was examined. Methods: A total of 27 tissue specimens from patients with primary bone cancers or bone metastases of different origins were genetically characterized and treated… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Shulong Zhang1,#, Yijun Zhao2,#, Li Geng2, Feihong Song2, Li Feng3, Jun Jiang3, Qianqian Cai4,*, Fei Fan2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071739
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly lethal malignancy driven by both intrinsic oncogenic pathways and immune microenvironmental regulation. Emerging evidence suggests that DNASE1L3 may influence tumor biology and immune responses; however, its specific roles in HCC progression and macrophage-mediated regulation remain unclear. This study aimed to elucidate the biological functions of DNASE1L3 in HCC and to determine how it modulates tumor behavior and immune interactions. Methods: Bioinformatics analyses of the GSE41804 and Cancer Genome Atlas-Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (TCGA-LIHC) datasets were used to identify hub genes. Functional assays assessed the impact of DNASE1L3 on HCC cell proliferation,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Guojian Zhou1,2,#, Rui Zhang1,#, Lei Nie1,#, Yi Si1, Ting Liu1, Jing Wang1, Shuangshuang Han1, Mingda Xuan1, Jia Wang3,*, Weifang Yu1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070333
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Identification of potential targets and biomarkers for cancers and the exploration of novel molecular mechanisms of tumorigenesis and metastasis)
Abstract Objectives: Gastric cancer (GC) is among the most prevalent malignancies worldwide, ranking as the fifth most common cancer and the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality. This study intends to investigate how Inhibin subunit beta A (INHBA) promotes the progression of GC by activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway via targeting Integrin alpha-6 (ITGA6). Methods: Quantitative reverse transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) were utilised to validate the expression levels of INHBA in GC, which were subsequently correlated with the clinicopathological factors and outcomes. Cellular and animal studies were conducted to ascertain… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
VIEWPOINT
Guido Carloni, Monica Rinaldi*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071847
Abstract Hepatitis C virus (HCV) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are increasingly recognized as significant etiological factors in the pathogenesis of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (B-NHLs). Epidemiological and molecular studies have demonstrated a consistent association between chronic viral infection and B-NHLs. Multiple pathogenic mechanisms have been implicated in lymphomagenesis, both direct and indirect, including chronic antigenic stimulation, direct infection of B cells, and viral protein–mediated oncogenic signaling, It is likely that a combination of several pathogenic conditions is required to eventually lead to the development of lymphoma. The prevalence of B-cell lymphomas among individuals with chronic… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Yuanxin Miao1,2, Fengyun Hao3,*, Sae Hwi Ki1,4,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.071034
Abstract Objectives: The eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF4F) translation initiation complex inhibitors (eIF4Fi) were recently found to hyperactivate extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) signals, which contribute to acquired resistance to BRAF (B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase) inhibitors in melanoma. This present study aims to elucidate how to overcome the resistance of the eIF4Fi in BRAFV600E mutant melanoma cells and explore the underlying mechanisms. Methods: Melanoma A375 (vemurafenib [VEM]-sensitive) and A375R (VEM-resistant) cells were exposed to eIF4Fi RocA at varying doses and durations in vitro. We investigated the impact of RocA on the activity of ERK1/2, AKT serine/threonine kinase 1… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Iara Santos1, Joana Liberal1,2, Paulo Teixeira1,3,4, Diana Martins1,2,5,6, Fernando Mendes1,2,5,6,7,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070281
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Innovations in Colorectal Cancer Research and Treatment)
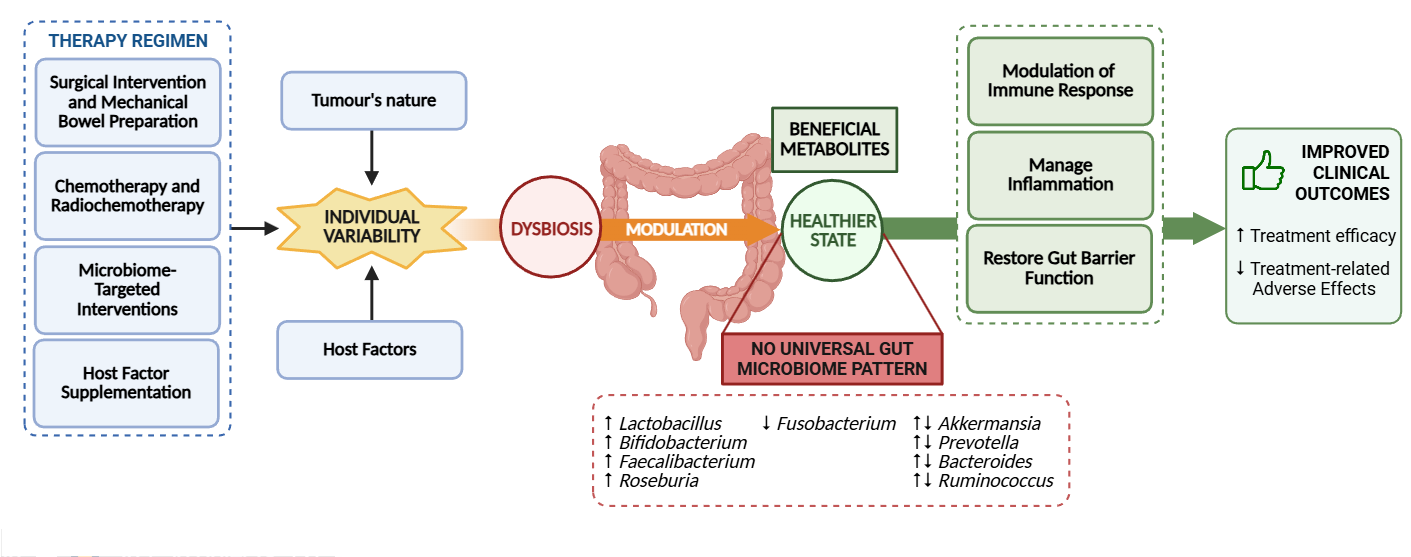
Abstract Background: The Colorectal Cancer (CRC) pathogenesis and therapeutic efficacy are influenced by the gut microbiome, making it a promising biomarker for predicting treatment responses and adverse effects. This systematic review aims to outline the gut microbiome composition in individuals with CRC undergoing the same therapeutic regimen and evaluate interindividual microbiome profile variations to better understand how these differences may influence therapeutic outcomes. Methods: Key studies investigating the microbiome’s role in therapeutic approaches for CRC were searched in both PubMed and Cochrane databases on 12 and 22 March 2025, respectively. Eligible studies included free full-text English-language… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Pingping Hu1,2,#, Zhenhao Fei1,2,#, Jianhua Bai1,2, Zhiwen Wang1,2, Yun Jin1,2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.070207
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Cancer Therapeutics)
Abstract Objectives: Pancreatic cancer (PC) is characterized by poor prognosis due to its limited treatment choices and delayed detection. S100A14 has been implicated in tumor progression, yet its regulatory hierarchy and functional interplay in PC remain unclear. This study aimed to define the role of S100A14 in PC progression. Methods: Integrated bioinformatic analyses of TCGA-PAAD and GSE22780 datasets identified candidate hub genes. Prognostic relevance was assessed via Kaplan-Meier and ROC analyses. Functional experiments were performed in PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells, including qRT-PCR, CCK-8 assay, Western blotting, Transwell assay, and apoptosis assay. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) was used to verify… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Candela Cives-Losada1,2, Cristiana Soldani2, Michela Anna Polidoro2, Barbara Franceschini2, Ana Lleo3,4, Marcello Di Martino1,5, Matteo Donadon1,5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.074093
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment: Emerging Insights into Cancer Progression and Therapeutics)
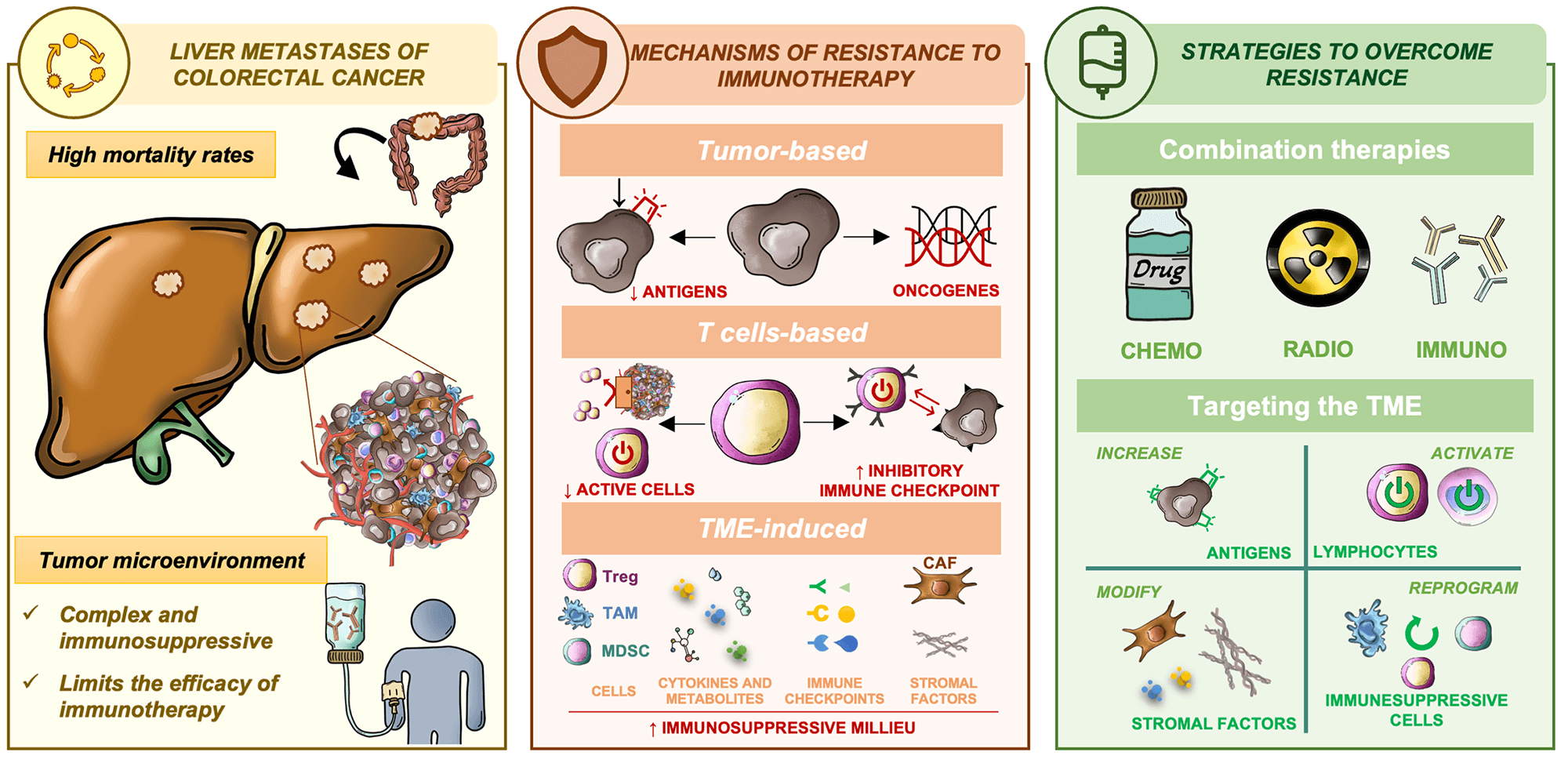
Abstract Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second deadliest cancer worldwide, being the presence of metastasis, mainly in the liver, a major contributor to high mortality rates in affected patients. The tumor microenvironment (TME)—comprised of interacting endothelial, stromal, and immune cells—plays a critical role in creating a supportive niche for tumor cell colonization and immune evasion and, thus, the establishment of metastases. The liver’s intrinsic nature further facilitates the development of immune tolerance, mediated by regulatory T cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and soluble factors such as anti-inflammatory cytokines, which together dampen antitumor immune responses. This immunosuppressive milieu More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Donatella Coradduzza1,#, Anna La Salvia2,#, Giuseppe Fanciulli3, Maria Rosaria De Miglio3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073045
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Tumor Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Targeted Therapy)
Abstract Background: An increasing number of studies have shown that ferroptosis is related to the initiation and development of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). The systematic review aimed to summarize the characteristics of ferroptosis from its pathogenetic role to translational therapeutic implications in SCLC. Methods: This systematic review, registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251090058), followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines. Comprehensive research of PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science was performed for studies published between January 2010 and July 2025 investigating ferroptosis mechanisms, genetic or pharmacological modulation, or molecular profiling in SCLC. Two reviewers independently performed data extraction and quality… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Gwan Hee Han1,2,#, Hee Yun3,#, Joon-Yong Chung4, Jae-Hoon Kim3,5,6, Hanbyoul Cho3,5,6,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072105
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis (Ⅱ))
Abstract Objectives: Phosphodiesterase 1A (PDE1A) regulates intracellular cyclic nucleotide signaling and has been implicated in tumor progression, but its clinical relevance and functional role in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), particularly in relation to the response to platinum remain unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical significance of PDE1A in EOG and to clarify its functional role in tumor progression and response to platinum-based chemotherapy. Methods: PDE1A mRNA and protein levels were analyzed using public databases, RNA sequencing, and immunohistochemistry. Correlations between PDE1A expression, clinicopathological features, and prognosis were assessed. Functional roles were investigated in ovarian… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Fangyuan Zhang1,#, Xi Wang2,#, Xinxin Shen3, Pei Xiong3, Yan Yang4,*, Jincheng Wang5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.074893
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Transcriptome Analysis in Tumor Microenvironment and Tumor Heterogeneity)
Abstract Accumulating evidence indicates that the neuro-immune axis is central to gastric cancer pathogenesis. Dynamic, bidirectional signaling between neural circuits and immune cells promotes tumor progression, shapes an immunosuppressive microenvironment, and contributes to therapeutic resistance. We synthesize current knowledge on how autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and sensory innervation regulate gastric cancer biology. These circuits act through neurotransmitters (catecholamines, acetylcholine) and neuropeptides (substance P [SP], calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]) to foster tumor growth and angiogenesis, facilitate perineural invasion, and enable immune evasion by recruiting suppressive myeloid and lymphoid populations and by inducing checkpoint molecule expression. We also… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Jo-Yu Lin1,#, Tien-Huang Lin2,3,#, Ya-Jing Jiang4, Liang-Wei Lin4, Kuan-Ying Lai5, Yi-Chin Fong6,7,8, Chih-Chuang Liaw5,9,*, Chih-Hsin Tang1,4,10,11,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.074202
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advancements in Molecular Therapeutics for Prostate Cancer)
Abstract Background: Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most prevalent malignancy in men and often correlates with distant metastasis in its advanced stages. The study aimed to investigate the effects of Ugonin J, a natural compound isolated from Helminthostachys zeylanica, on PCa metastasis. Methods: The effects of Ugonin J on cell motility were assessed using migration and invasion assays. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and Western blotting were used to evaluate the impact of Ugonin J on mRNA and protein expression. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis was performed to investigate candidate mechanisms. Differential gene expression analysis in PCa patients… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Saad Alobid1,#, Hussam Albassam1,#, Tebyan O. Mirgany2, Faris Almutairi1, Mohammed Mufadhe Alanazi1, Ahmed H. Bakheit2, Hanadi H. Asiri2, Eram Eltahir3, Gamaleldin I. Harisa3,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073371
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Pharmacological Bases of Anticancer Drug Therapies in Precision Oncology)
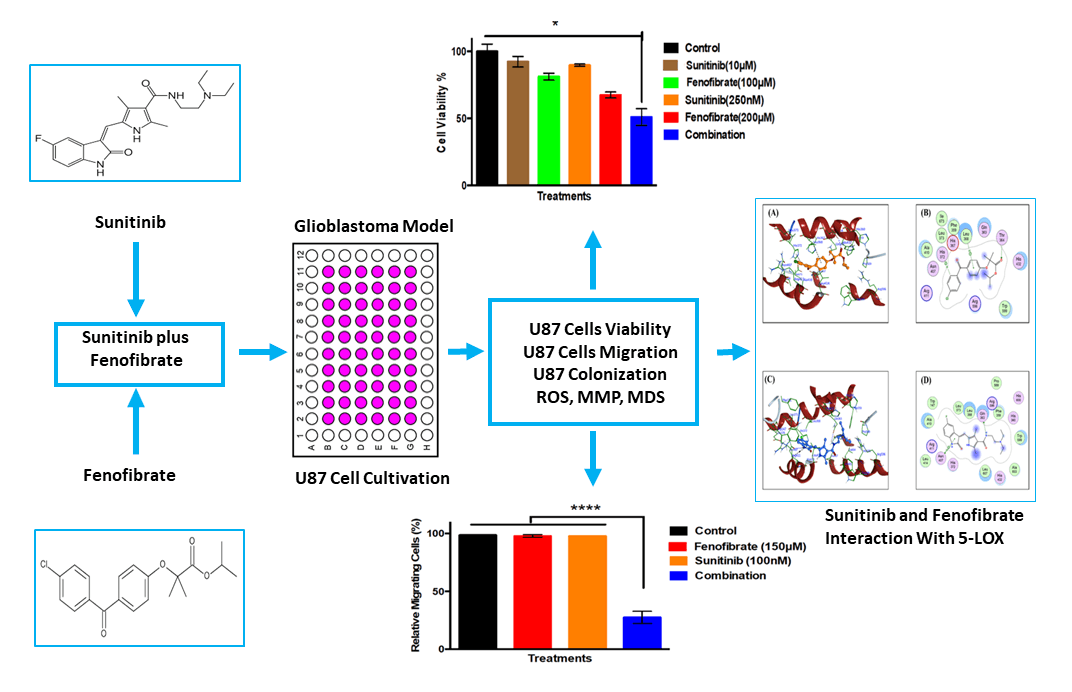
Abstract Objective: Glioblastoma (GB) therapy is challenged by tumor heterogeneity and multidrug resistance (MDR), highlighting the need for effective therapies. This study aimed to explore the combined anticancer effects of Sunitinib (SNB) and Fenofibrate (FEN) on U87 cells. Methods: U87 cells were exposed to SNB, FEN, or their combination for 24 h, followed by evaluations of cell viability, migration, and clonogenic survival using MTT, scratch, and colony formation assays. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were quantified via the 2′, 7′-dichlorofluorescein assay, while mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) was assessed using JC-1 red/green fluorescence. Molecular docking was performed to… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Norbert Nass1,2,*, Atanas Ignatov3, Thomas Kalinski1
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072793
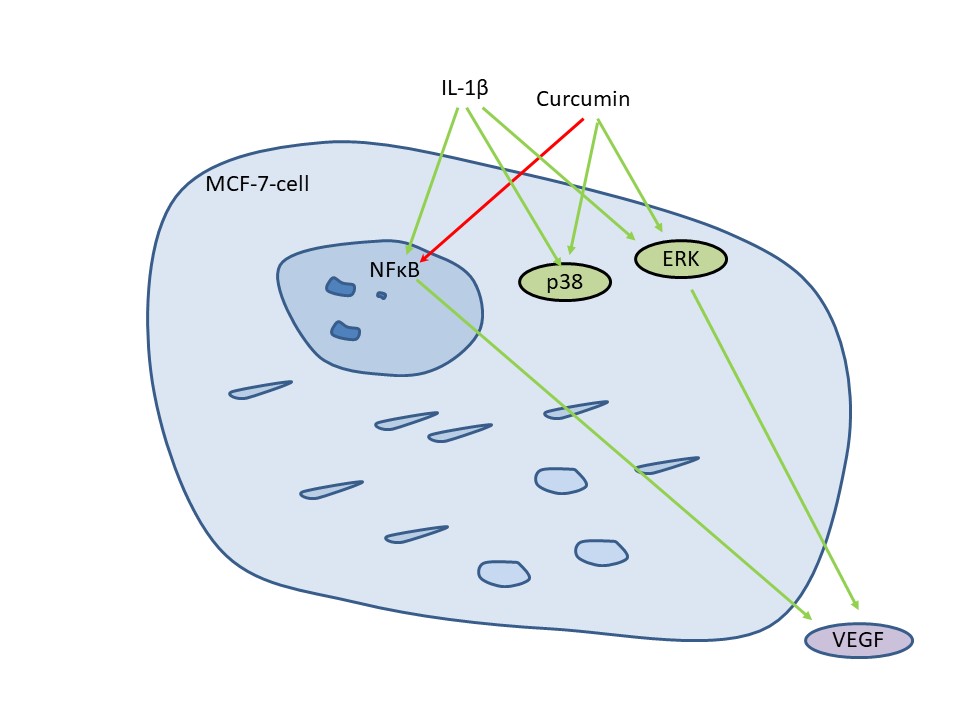
Abstract Objectives: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) regulates tumor vascularization in response to hypoxia and inflammatory signals. The polyphenol curcumin is supposed to interfere with inflammation-induced VEGF secretion and might therefore support anti-VEGF-based treatments. We aimed to investigate the interaction between curcumin and the inflammatory cytokine Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) for VEGF secretion in breast cancer cell lines representing major breast cancer subtypes. Methods: VEGF in cell cultures was detected by Western blot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Kinase phosphorylation was investigated by Western blotting. Gene expressions were analyzed by correlation tests. VEGF was evaluated in a retrospective… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Yuriy Mayasin1,*, Maria Osinnikova2, Daria Osadchaya1, Victoria Dmitrienko1, Anna Gorodilova1, Chulpan Kharisova1, Kristina Kitaeva1, Valeria Solovyeva1, Albert Rizvanov1,3
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073008
Abstract Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is characterized by rare Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (HRS) tumor cells that uniformly express cluster of differentiation (CD)30 molecules and orchestrate an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, making CD30 an attractive and selective therapeutic target. We summarize the biological rationale for CD30 as a therapeutic target and the preclinical and clinical evidence across major platforms: antibody-drug conjugates (brentuximab vedotin), monoclonal antibodies (including acimtamig and its combinations with Natural Killer cells), second- and third-generation chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells, and alternative modalities. Particular attention is given to standardized response assessment (IWG, Lugano, RECIL criteria), which enables appropriate… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Amy J. Petty*, Drew A. Emge, Adela R. Cardones
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073383
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Shaping the Future: The Next Evolution of Cancer Immunotherapy)
Abstract Skin cancer remains the most commonly diagnosed malignancy worldwide, with basal cell carcinoma (BCC), cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC), and melanoma representing the most clinically significant types. While traditional treatments are effective for early-stage disease, advanced or metastatic cases often pose significant therapeutic challenges. Patients with high-risk or recurrent disease face limited options and poor prognoses. The emergence of immunotherapy has dramatically transformed the treatment landscape across multiple cancer types, including cutaneous malignancies. This review highlights recent advancements in immunotherapeutic strategies for BCC, cSCC, and melanoma, underscoring their growing importance in dermatologic oncology. We synthesize More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Amal F. Gharib1, Ohud Alsalmi1, Hayaa M. Alhuthali1, Afaf Alharthi1, Saud Ayed Alharthi2, Shaimaa A. Alharthi3, Rasha L. Etewa4, Wael H. Elsawy5,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.073051
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Novel Biomarkers and Treatment Strategies in Solid Tumor Diagnosis, Progression, and Prognosis (Ⅱ))
Abstract Background: Locally advanced laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LA-LSCC) presents clinical challenges due to the lack of reliable non-invasive biomarkers. This study aimed to evaluate miR-449a as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in LA-LSCC. Methods: miR-449a expression was analyzed in tumor tissues, adjacent normal tissues, and serum from 81 LA-LSCC patients and 50 controls using quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). We assessed the diagnostic accuracy by Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (ROC curves), clinicopathological associations, survival outcomes (Kaplan-Meier), and treatment response dynamics. Results: miR-449a was significantly downregulated in LA-LSCC tissues (p < 0.0001) and serum (p <… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Myeong Ryeo Kim1,*, Jae Rim Lee1, Xiaohan Zhang2, Kwang Won Jeong1,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072592
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Discover Biomarkers for Personalized Oncology)
Abstract Objectives: Tamoxifen is a key drug that provides endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor (ER)
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Marcia Eduarda Viana Luna1,2, Gustavo Jacob Lourenço2, Juliana Carron2,*
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072133
Abstract This literature review explores the complex interaction between p53 and microRNAs (miRNAs) in the occurrence and progression of breast cancer (BC), the most common and lethal tumor type among women. BC is a multifactorial disease resulting from a combination of genetic and epigenetic alterations in cell DNA, influencing proliferation, differentiation, and migration. TP53 gene, which codifies p53 protein, is a known tumor suppressor, and it plays an important role in cell maintenance as DNA repair, cell proliferation control, and apoptosis activation. TP53 expression can be modulated by several miRNAs, as miR-30c, miR-34a, and the miR-200 family, More >
 Open Access
Open Access
CASE REPORT
Tena Šimunjak1,*, Bernardica Jurić2, Andro Košec3,4, Vladimir Bedeković3,4
Oncology Research, DOI:10.32604/or.2025.072100
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances and Innovations in Head and Neck Cancer: Cutting-Edge Treatments and Future Directions)
Abstract Background: Collision medullary and papillary thyroid carcinoma (MTC/PTC) is a rare entity, constituting less than 1% of all thyroid malignancies. The concurrent presence of these malignancies in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease, such as Graves’ disease, is even more uncommon. Calcitonin (Ctn) is considered one of the key MTC biomarkers. Mixed tumors may alter this relationship. Case Description: We report the case of a 55-year-old female with a history of Graves’ disease, who underwent total thyroidectomy for persistent dysthyroid orbitopathy. Histopathological analysis revealed a 9-mm collision MTC/PTC tumor in the left thyroid lobe, confirmed through More >