 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plectranthus Amboinicus Leaf Extract for Preparation of CMC/PVA Nanocomposite Film
1 Nong Lam University Ho Chi Minh City, Ho Chi Minh City, 700000, Vietnam
2 Industrial University of Ho Chi Minh City, Ho Chi Minh City, 700000, Vietnam
3 University of Science, Viet Nam National University Ho Chi Minh City, Ho Chi Minh City, 700000, Vietnam
* Corresponding Author: Nguyen Thi Thanh Thuy. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Food Packaging Materials Based on Renewable Resources)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2021, 9(8), 1393-1411. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2021.015772
Received 12 January 2021; Accepted 13 February 2021; Issue published 08 April 2021
Abstract
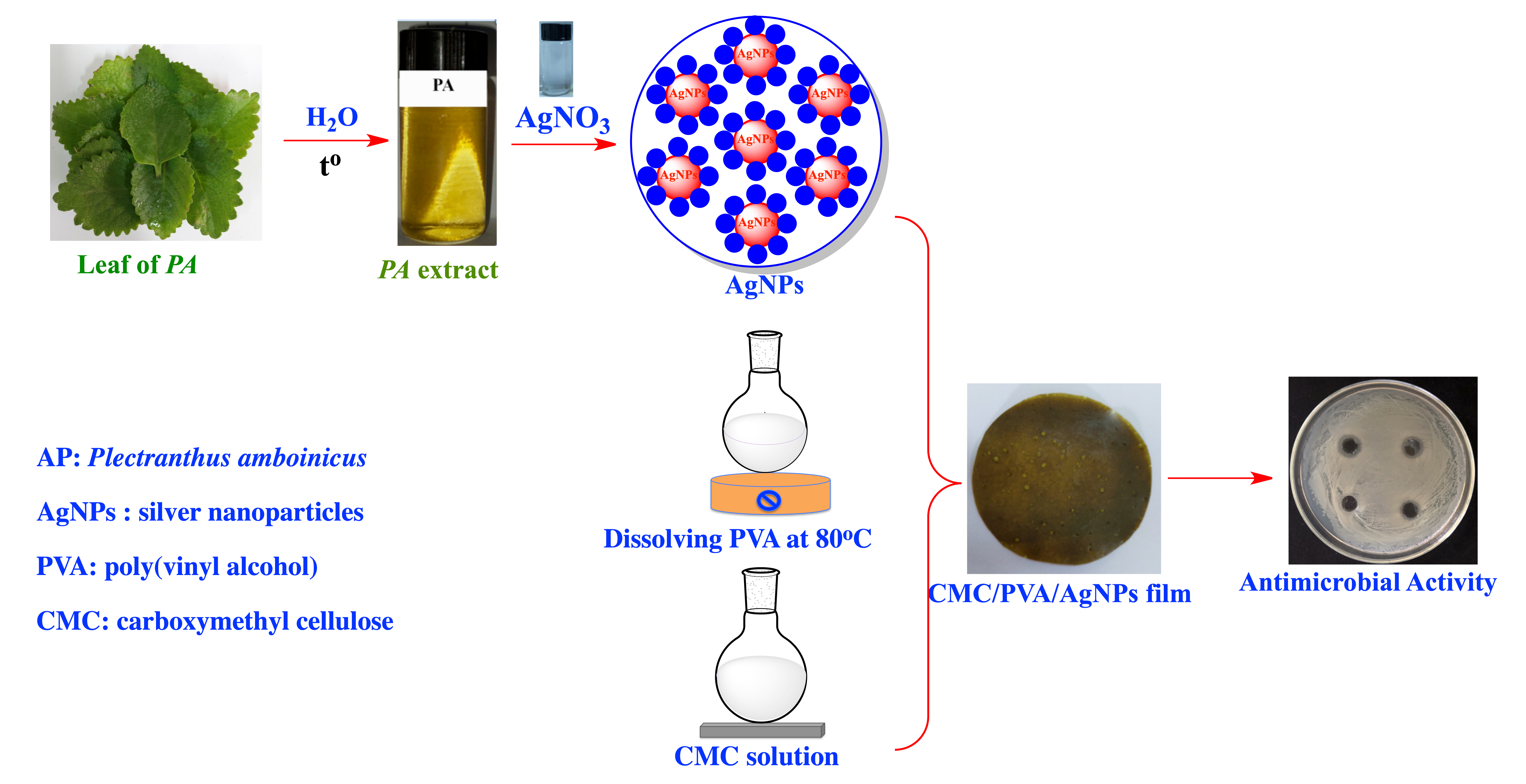
In the present study, the biogenic silver nanoparticles have been synthesized using aqueous leaf extract of Plectranthus amboinicus (PA), which acted as both reducing and stabilizing agents. The PA synthesized silver nanoparticles were blended with carboxymethyl cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol (CMC/PVA) biocomposite. The prepared AgNPs as well as the biogenic AgNPs incorporated CMC/PVA films were investigated using UV-visible spectrophotometry, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), dynamic light scattering (DLS), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and X–ray diffraction (XRD). The DLS results showed that biogenic AgNPs had the average particle size of 65.70 nm with polydispersity index of 0.44. The surface plasmon resonance of AgNPs, which was determined by UV-vis spectrophotometry, showed the value of 410.00 nm. These results therefore confirmed the reduction Ag+ into Ag° and the formation of AgNPs in the medium. The SEM imaging showed that AgNPs was quasi-spherical and monodisperse. The XRD peaks at 33.07°, 44.19°, 64.58° and 77.47° confirmed the crystalline nature and presence of AgNPs. The CMC/PVA films that incorporated with AgNPs displayed best mechanical strength and morphological properties than the pure CMC/PVA film. The film of CMC/PVA-AgNPs exhibited significant antibacterial activities against Bacillus spizizenii, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhi and Escherichia Coli.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools