 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fiber Loading of Date Palm and Kenaf Reinforced Epoxy Composites: Tensile, Impact and Morphological Properties
1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Acharya Nagarjuna University-College of Engineering and Technology, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, RVR & JC College of Engineering and Technology, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India
* Corresponding Author: Syed Waheedullah Ghori. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Material from Agricultural Waste and By-Product and Its Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2021, 9(7), 1283-1292. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2021.014987
Received 14 November 2020; Accepted 23 January 2021; Issue published 18 March 2021
Abstract
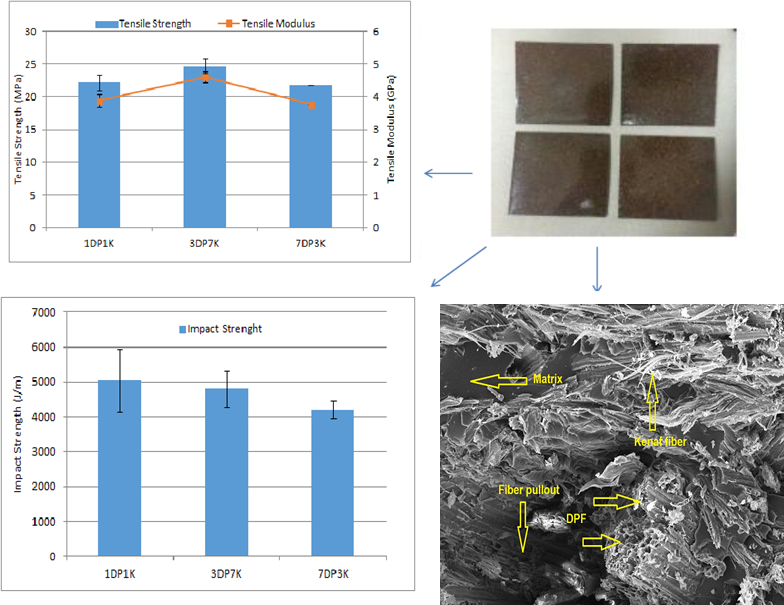
Date palm fiber (DPF) and kenaf fiber were reinforced in epoxy having various fiber loading 40%, 50%, and 60% by weight. These hybrid samples were manufactured by hot press technique and then characterized for tensile, impact, and morphological behavior to evaluate the ratio of fibers in the hybrid composites; the addition of kenaf improved the tensile properties, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) revealed the interfacial bonding of fiber/matrix, and dispersion and void content in composites. Impact test studies reflected the effect of natural fiber with epoxy, level of stress transfer from matrix to reinforced material, and reinforced material’s role in absorbing the impacts. It showed that 50% of DPF had the best shock-absorbing capacity. The obtained results indicated that 30% DPF in hybrid composite showed improved tensile properties and homogeneous distribution of fiber without void content; however, 50% DPF loading in hybrid composites had the best impact properties.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools