 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Experimental Investigation on Hydrophobic Behavior of Carbon Spheres Coated Surface Made from Microplastics
State Key Laboratory of Multiphase Flow in Power Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, 710049, China
* Corresponding Author: Hui Jin. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Plastic waste management towards a sustainable future)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2021, 9(12), 2159-2174. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2021.016166
Received 13 February 2021; Accepted 31 March 2021; Issue published 22 June 2021
Abstract
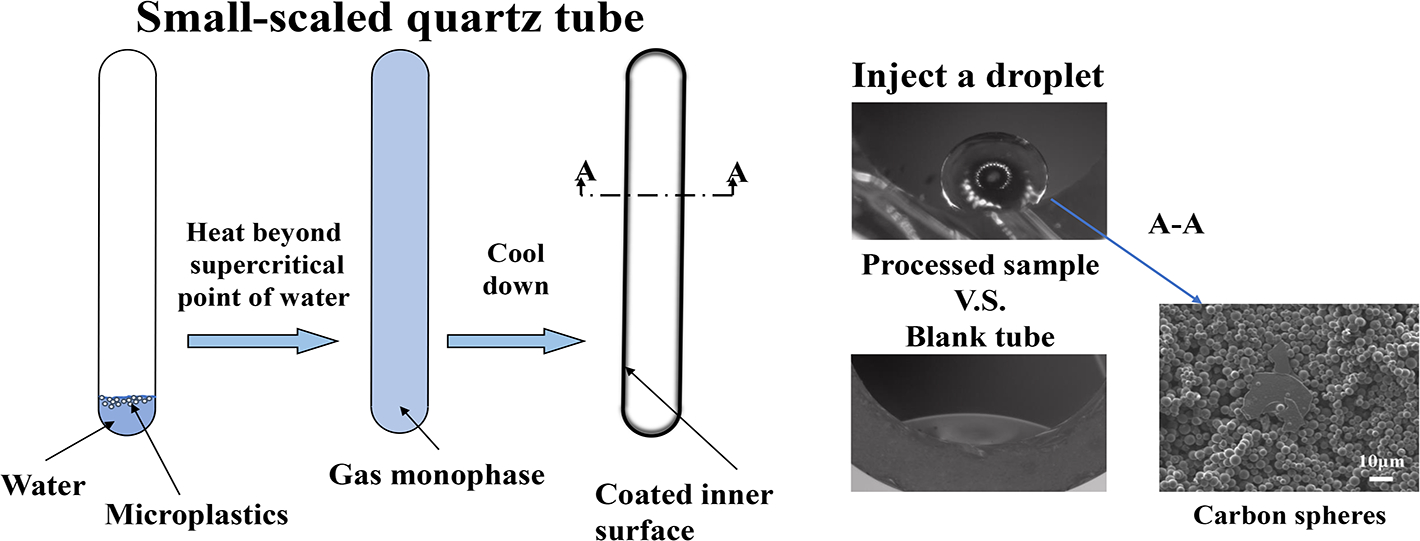
In this paper, a simple method to plate a hydrophobic coating on the inner surface of a small-scaled tube was proposed, where the coating consisted of carbon microspheres. Three common plastics polystyrene, polycarbonate and polyethylene were used as the feedstocks to be processed in supercritical water in a quartz tubular reactor. After reaction, the contact angle of droplet on the inner surface of the quartz tube was turned out to be over 100°, significantly larger than that of the blank tube 54°. When processing polystyrene in the 750C supercritical water for 10 min, the largest contact angle was obtained, up to 145°. Besides, in this sample, the size of carbon spheres was smallest, about 2.09 μm diameter on average. When comparing among different types of plastics under the same condition, the contact angle of surface made from PC took the dominant position over that of PS and PE, 124°, 100° and 90°, respectively. In the sample made from PC, carbon spheres adhered into a mountainlike shape, producing a binary geometric structure. Furthermore, this research could be helpful in the discussion of plastic waste management and carbon spheres fabrication with low cost.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools