 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
The Spatial and Electronic Effects of Substituent Groups on the Thermal Curing of Bio-Based Benzoxazines
1
Laboratory of Specially Functional Polymeric Materials and Related Technology (ECUST), Ministry of Education, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, 200237, China
2
The 806th Institute of the Eighth Academy of CASC, Huzhou, 313000, China
* Corresponding Author: Xiaoyun Liu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable and Biosourced Adhesives)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2021, 9(12), 2093-2117. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2021.015827
Received 17 January 2021; Accepted 05 March 2021; Issue published 22 June 2021
Abstract
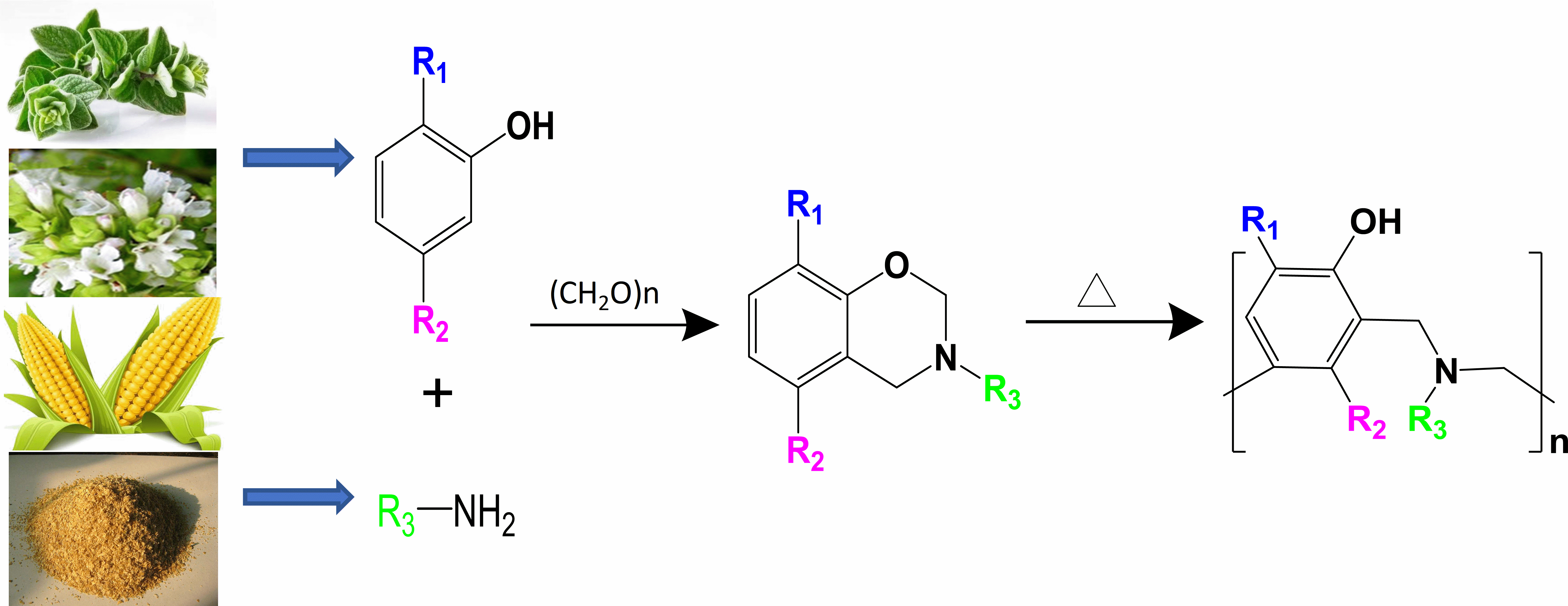
To explore the influence of substituent groups on thermally induced curing, eight new bio-based benzoxazines containing different substituent groups with different electron negativity and volumes were synthesized. The thermal curing of these bio-based benzoxazines was studied in detail. Combined with the curing reaction kinetics, simulation and calculation of Highest Occupied Molecular and Lowest Unoccupied Molecular values, the spatial and electronic effects of different substituent groups on the curing of benzoxazine was explored. It was found that when the substituent was located at the position directly connected to the N atom, the steric hindrance effect of the group was dominant. When the substituent group was located on the benzene ring connected to the O atom, both the electronic effect and the spatial effect influenced the curing of benzoxazine. When an electron-withdrawing group was connected ortho position to the O atom, the curing reaction was promoted due to the decreased electron cloud density of O- on the oxazine ring, making the C-O bond easier to break. When an electron-donating group was connected to the meta position of the O atom it also promoted the curing reaction, possibly because it increased the electron cloud density of the + CH2 reaction site and thereby facilitated electrophilic substitution via attack of + CH2 on the cross linking reaction centre. This work provides a deeper understanding of how spatial and electronic effects of substituents affect the curing of benzoxazine.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
Citations
 Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF

 Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools