 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Biobased Biodegradable Polybutylene Succinate Polymers and Composites: Synthesis, Structure Properties and Applications—A Review
1 Centre for Nanostructures and Advanced Materials (CeNAM), Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Pretoria, 0001, South Africa
2 Department of Chemistry, University of the Western Cape, Bag X17, Robert Sobukwe Drive, Bellville, 7535, South Africa
3 Department of Chemistry, Nelson Mandela University, Port Elizabeth, 6001, South Africa
4 Department of Chemical Sciences, University of Johannesburg, Doornfontein, 2018, South Africa
5 Department of Engineering Metallurgy, Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, 2028, South Africa
* Corresponding Authors: Peter Ramashadi Makgwane. Email: ; Sudhakar Muniyasamy. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Bio-based/Degradable Materials towards A Sustainable Future)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2025, 13(3), 449-495. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2025.027523
Received 02 November 2022; Accepted 24 January 2025; Issue published 20 March 2025
Abstract
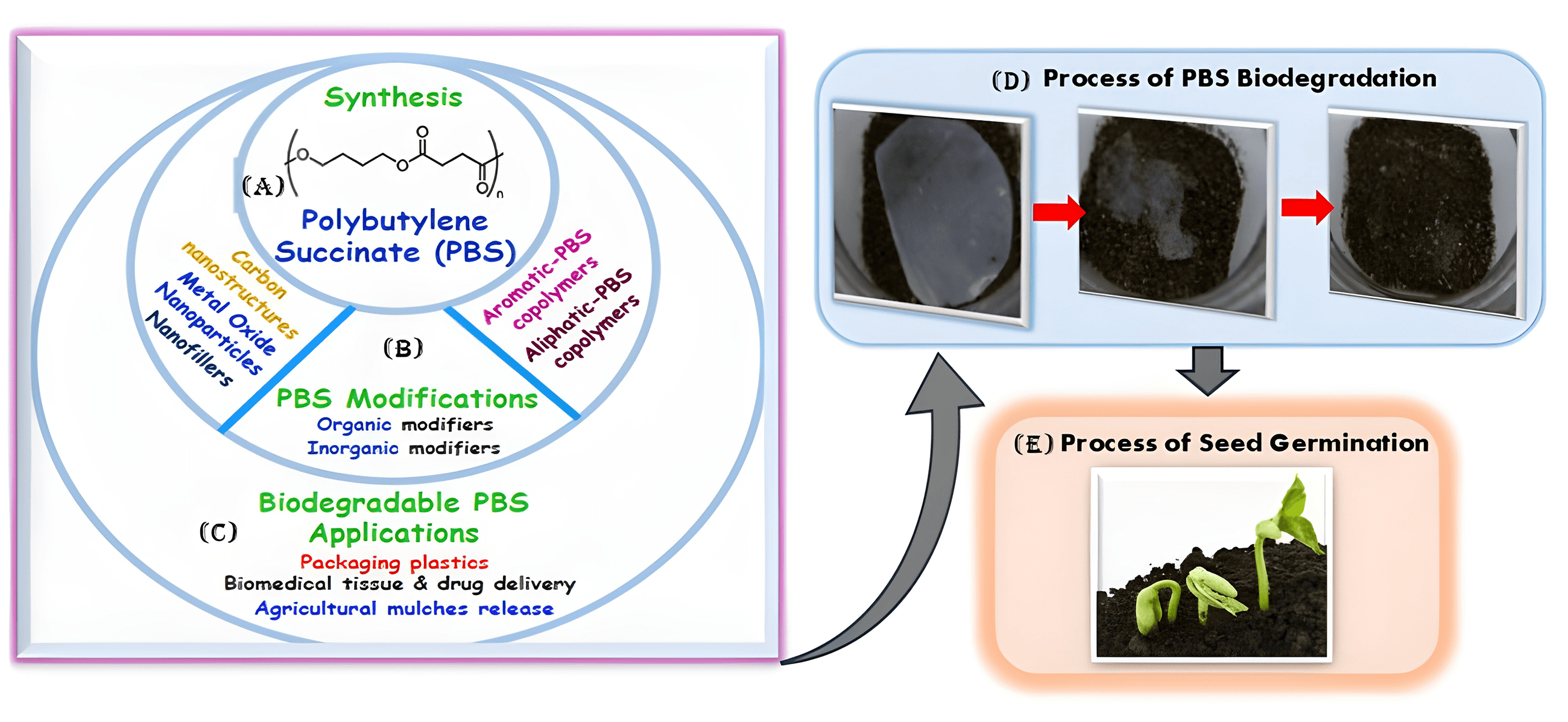
The materialization of polybutylene succinate (PBS) belongs to the family of polyesters which are degradable and biodegradable, their biodegradability properties have attracted enormous interest for product development towards different polymer-based applications. Besides its biodegradability, PBS can be derived from petroleum and biobased monomers. At the same time, the latter is the driving factor for its growing interest in bioplastics for fully green and sustainable biobased-derived polymer products. The processes and techniques presented herein, are based on the production of biobased succinic acid monomer to PBS. However, the counterpart biobased monomer 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BDO) production has not been commercially demonstrated. This review discusses the progress in state-of-the-art developments in the synthesis strategies of PBS, its copolymers, and composites with the view to improve molecular weight, thermal, and mechanical properties. It further analyzes the different strategies to synthesize modified PBS polymer composites from organic and inorganic nanofillers to enhance their chemical, thermal, stability and mechanical structural properties. Importantly, the review highlights the progress in the applications of PBS copolymers and composites with tailored structure-designed properties for specific sectors such as packaging films, biomedical and drug release, fire retardants, and agricultural products. The structure-functional performance characteristics of these developments in the PBS, copolymers, and composites are highlighted to provide baseline insights for future developments in engineering the specific applications, and structural interface PBS composites with enhanced structure-functional performance properties.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools