 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Properties of Activated Carbons from Sugarcane Leaves and Rice Straw Derived Charcoals by Activation at Low Temperature via KMnO4 Pre-Oxidation-Hydrolysis
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok, 65000, Thailand
* Corresponding Author: Sumrit Mopoung. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances in Biochar and Carbon-Based Materials Characteristics and Environment Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(8), 1433-1454. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.052925
Received 19 April 2024; Accepted 30 May 2024; Issue published 06 September 2024
Abstract
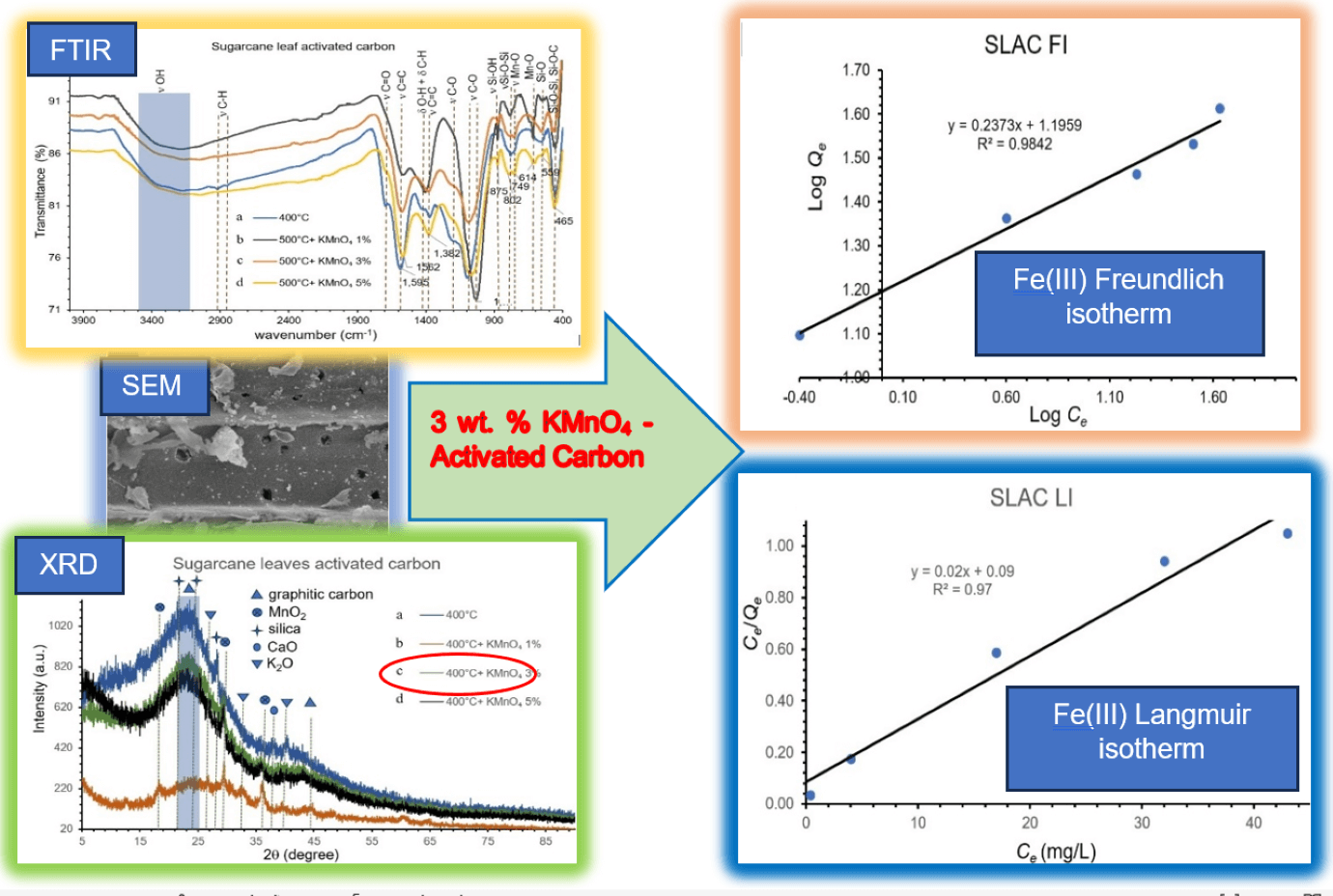
Activated carbon preparation from sugarcane leaves and rice straw by carbonization (250°C–400°C) and activation at 500°C were studied. The effects of pre-oxidation, hydrolysis of derived charcoals by boiled KMnO4 aqueous solution were evaluated. The derived charcoals products were pretreated using oxidation-hydrolysis with 1–5 wt.% KMnO4 at 100°C and then activated at 500°C. The derived charcoal and activated carbon products were characterized by FTIR, XRD, SEM-EDS and BET. Iodine number and methylene blue number of derived products were also used for the analysis of the products. It was found that fabricated charcoal materials made at 350°C–400°C possess good characteristics with low content of surface functional groups and high carbon content. After pre-oxidation-hydrolysis and activation at 500°C, the resulting derived activated carbon materials from charcoals with 400°C carbonization temperature have high content of oxygen containing surface functional groups such as Mn-O, Si-O, Si-O-Si, C-O, or O-H. In addition, MnO2 accumulated on the surface of the derived activated carbon products. The surface area and pore volume of the activated carbon products have also increased with increasing of KMnO4 concentration from 1 to 3 wt.% and then decreased with 5 wt.% used during activation. Therefore, activated carbon products made by pre-oxidation-hydrolysis with 3 wt.% KMnO4 were used for Fe(III) adsorption experiments. It was found that Fe(III) adsorption on the activated carbon materials can be fitted with both the Freundlich and the Langmuir models. The calculated maximum Fe(III) adsorption capacities of sugarcane leaves derived activated carbon and rice straw derived activated carbon products were 50.00 and 39.37 mg/g, respectively. It was shown that the effect of pre-oxidation-hydrolysis by KMnO4 and activation at 500°C are beneficial for activated carbon preparation with environmentally friendly and low-cost simplified operation.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools