 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Thermo-Mechanical, Physico-Chemical, Morphological, and Fire Characteristics of Eco-Friendly Particleboard Manufactured with Phosphorylated Lignin Addition
1 Department of Forest Products, Faculty of Forestry, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Kampus USU Padang Bulan, Medan, North Sumatra, 20155, Indonesia
2 Department of Chemistry, Lahore College for Women University, Lahore, 4444, Pakistan
3 Department of Wood Industry, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Cawangan Pahang Kampus Jengka, Shah Alam, 26400, Malaysia
4 Faculty of Forest Industry, University of Forestry, Sofia, 1797, Bulgaria
5 Department of Forest Product, Faculty of Forestry and Environment, IPB University, Bogor, 16680, Indonesia
6 Research Center for Biomass and Bioproducts, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Cibinong, 16911, Indonesia
7 Department of Forest Engineering, Faculty of Security Engineering, University of Zilina, Zilina, 01001, Slovakia
8 Materials Technology Research Group (MaTReC), School of Chemical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Minden, Penang, 11800, Malaysia
9 Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Engineering and Sciences, SRM University-AP, Amaravati, Andhra Pradesh, 522240, India
10 Department of Bio and Natural Resources, Faculty of Bioengineering and Technology, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Jeli, Kelantan, 17600, Malaysia
11 Department of Forest Biomaterials Engineering, College of Forest and Environmental Sciences, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, 24341, Republic of Korea
* Corresponding Author: Apri Heri Iswanto. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Eco-friendly Wood-Based Composites: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and Applications – Ⅱ)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(7), 1311-1341. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.052172
Received 25 March 2024; Accepted 28 June 2024; Issue published 21 August 2024
Abstract
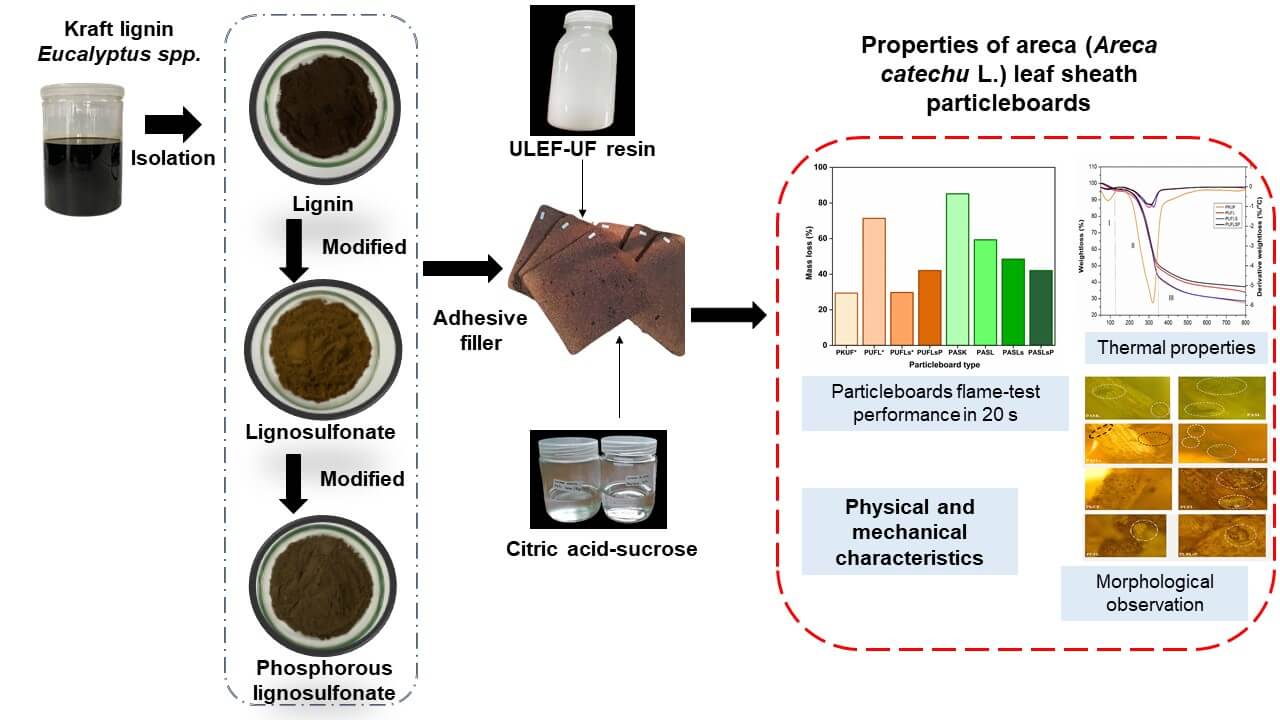
Lignin, lignosulfonate, and synthesized phosphorylated lignosulfonate were introduced as green fillers in citric acid-sucrose adhesives for bonding particleboard fabricated from areca leaf sheath (ALS). The characteristics of particleboards were compared to that of ultralow emitting formaldehyde (ULEF-UF). The fillers derived from Eucalyptus spp. kraft-lignin were added for flame retardancy enhancement. 10% of each lignin and modified lignin was added into the ULEF-UF and citric acid-sucrose bonded particleboards. Analyses applied to particleboards included thermal characteristics, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), morphological properties, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), as well as physical, mechanical, and fire resistance characteristics of the laboratory-fabricated particleboards. Lignin and modified lignin resulted in improved thermal stability of the composites bonded with ULEF-UF while the improvement in the particleboard bonded with citric acid-sucrose was not significant. The introduction of filler exerted a higher influence on the UF-bonded particleboards compared to composites fabricated with citric acid-sucrose. Generally, the presence of lignin, lignosulfonate, and phosphorylated lignosulfonate enhanced the mechanical strength of the ULEF-bonded particleboards, although their dimensional stability has deteriorated. Markedly, the use of lignin and lignosulfonate enhanced the fire resistance of the particleboards produced with lower observed weight loss. All laboratory particleboards exhibited satisfactory fire resistance, attaining a V-0 rating in according to the UL-94 standard.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools