 Open Access
Open Access
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Preparation of Regenerated Silk Fibroin Hybrid Fibers with Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing Properties by Wet Spinning
1 College of Biotechnology, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, 212100, China
2 College of Agriculture, Anshun University, Anshun, 561000, China
* Corresponding Author: Guohua Wu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(6), 1043-1055. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.051767
Received 14 March 2024; Accepted 18 April 2024; Issue published 02 August 2024
Abstract
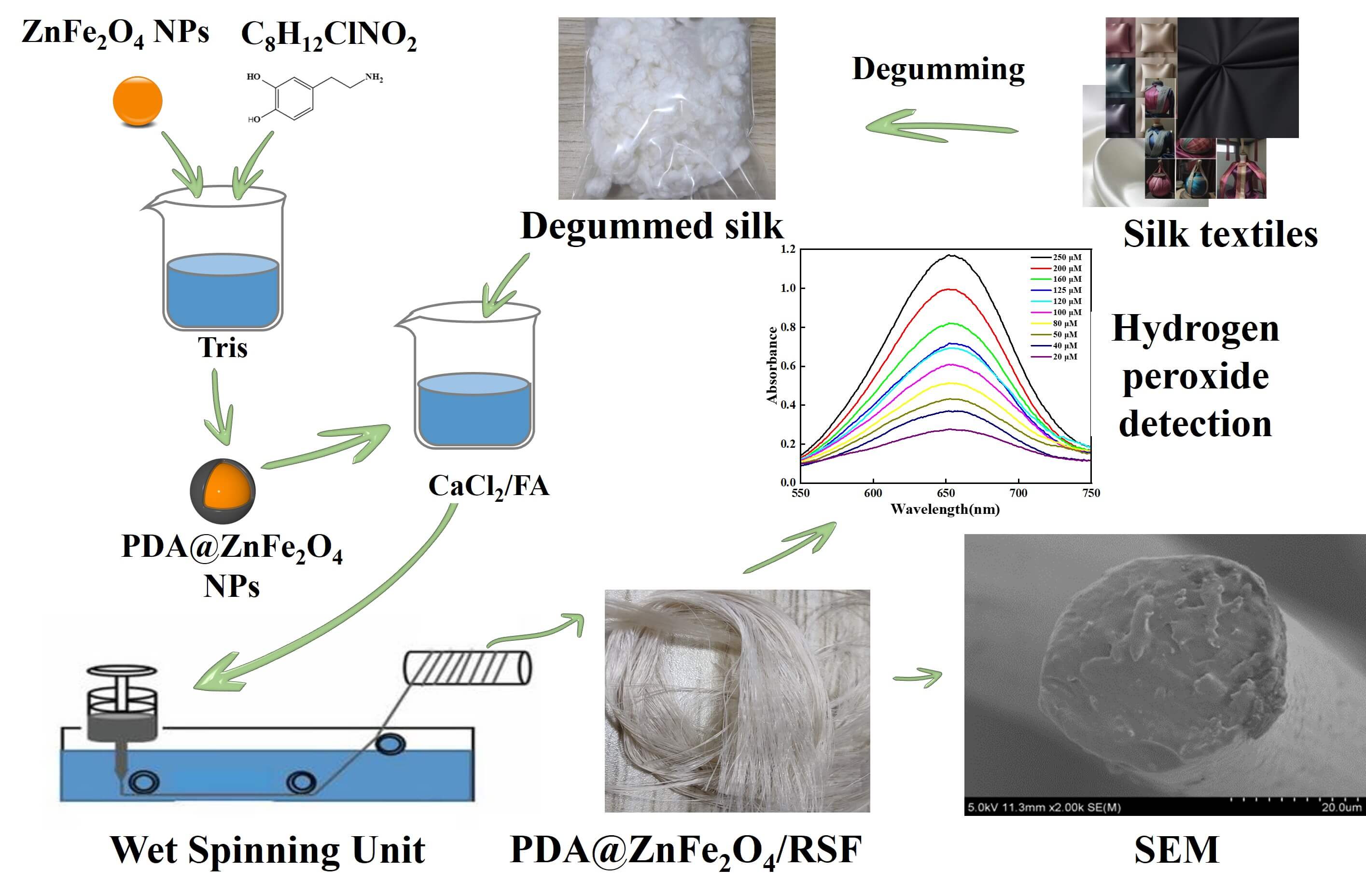
Silk is widely used in the production of high-quality textiles. At the same time, the amount of silk textiles no longer in use and discarded is increasing, resulting in significant waste and pollution. This issue is of great concern in many countries where silk is used. Hydrogen peroxide as a naturally occurring compound is an important indicator of detection in both biology and the environment. This study aims to develop a composite fiber with hydrogen peroxide-sensing properties using discarded silk materials. To achieve this goal, firstly, polydopamine (PDA) was used to encapsulate the ZnFeO NPs to achieve the improvement of dispersion, and then regenerated silk fibroin (RSF) and PDA@ZnFeO/RSF hybrid fibers are prepared by wet spinning. Research has shown that PDA@ZnFeO/RSF demonstrates exceptional sensitivity, selectivity, and stability in detecting hydrogen peroxide, while maintaining high mechanical strength. Furthermore, the complete hybridization of PDA@ZnFeO with silk fibroin not only results in the combination of the durability of silk fibroin and PDA@ZnFeO’s rigidity, ensuring a reliable service life, but also makes PDA@ZnFeO/RSF exhibit excellent catalytic activity and biocompatibility. Therefore, the composite fiber exhibits exceptional mechanical properties and reliable hydrogen peroxide sensing capabilities, making it a promising material for biological and medical applications.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools