 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Isolation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofiber (CNF) from Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) Bast through the Chemo-Mechanical Process
1 School of Life Sciences and Technology, Institut Teknologi Bandung, Bandung, 40132, Indonesia
2 Research Center for Biomass and Bioproducts, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Cibinong, 16911, Indonesia
* Corresponding Authors: Rudi Dungani. Email: ; Widya Fatriasari. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Special Issue in Celebration of JRM 10 Years)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(6), 1057-1069. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.049342
Received 03 January 2024; Accepted 07 March 2024; Issue published 02 August 2024
Abstract
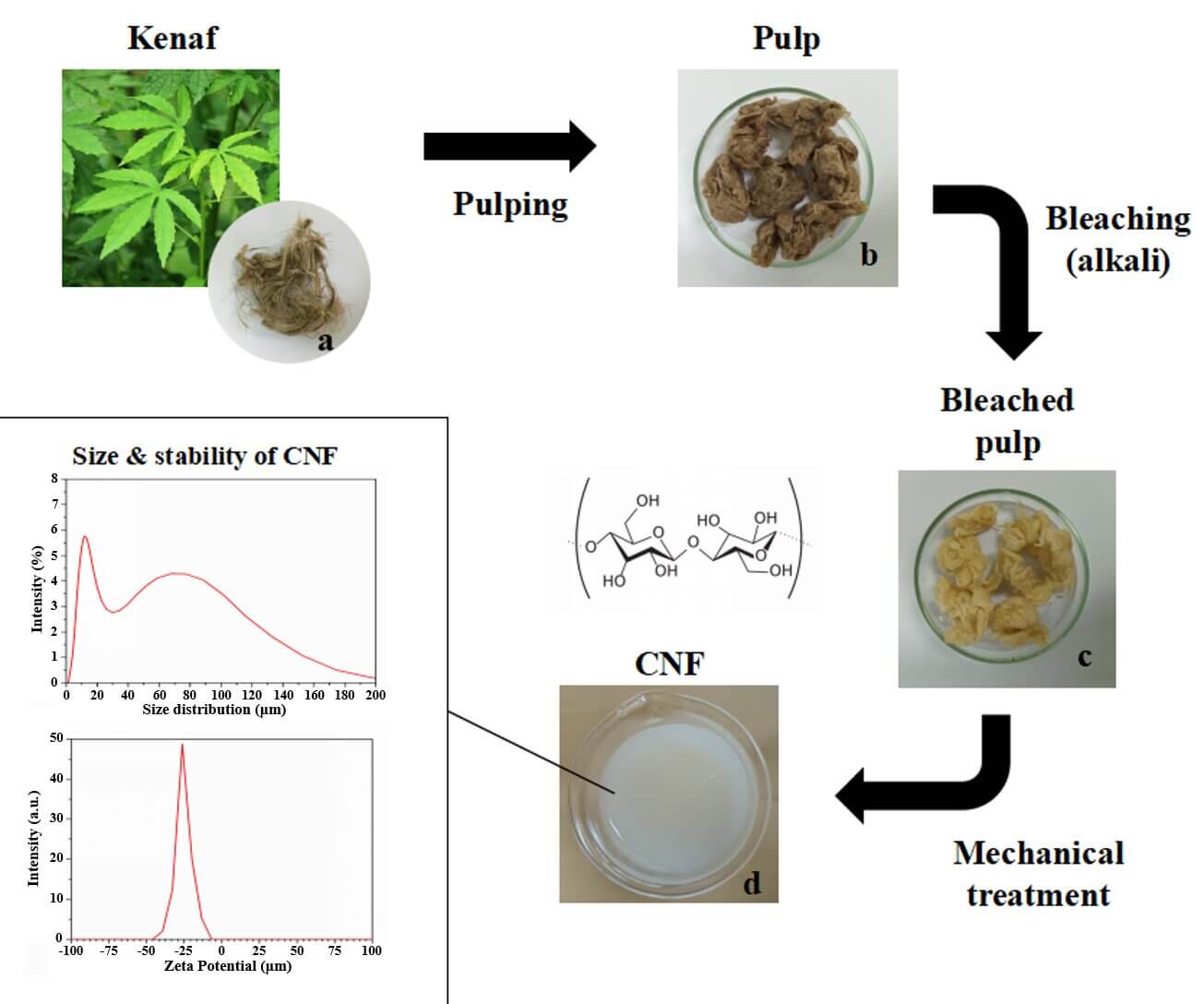
The present work emphasizes the isolation of cellulose nanofiber (CNF) from the kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) bast through a chemo-mechanical process. In order to develop high CNF yield with superior properties of CNF for improving compatibility in varied applications this method is proposed. The fiber purification involved pulping and bleaching treatments, whereas mechanical treatment was performed by grinding and high-pressure treatments. The kraft pulping as a delignification method followed by bleaching has successfully removed almost 99% lignin in the fiber with high pulp yield and delignification selectivity. The morphology of the fibers was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, which showed a smooth surface, fiber bundles, gel-shaped nanofiber, and an average size of 94.05 nm with 69% of CNF in 34–100 nm size. The chemo-mechanical process exhibited a more crystalline nature in CNF than pulp kenaf. The low zeta potential values exhibit the distribution of fibrils and colloidal suspension stability without any further agglomeration. A lower concentration of CNF is less stable exhibiting the product agglomeration. Therefore, the chemo-mechanical process for the isolation of CNF (Hibiscus cannabinus) from kenaf involves sustainable, low-cost, non-toxic, and cheap alternatives than other traditional methods.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools