 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
One-Step to Prepare Lignin Based Fluorescent Nanoparticles with Excellent Radical Scavenging Activity
1 The Key Laboratory of Synthetic and Biological Colloids, Ministry of Education, School of Chemical and Material Engineering, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, 214122, China
2 Environmental Health and Safety Program, College of Health Sciences, Abu Dhabi University, P.O. Box 59911, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
3 Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, Materials Engineering Center, Perugia University, UdR INSTM, Terni, 05100, Italy
* Corresponding Author: Weijun Yang. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(5), 895-908. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.049810
Received 18 January 2024; Accepted 06 March 2024; Issue published 17 July 2024
Abstract
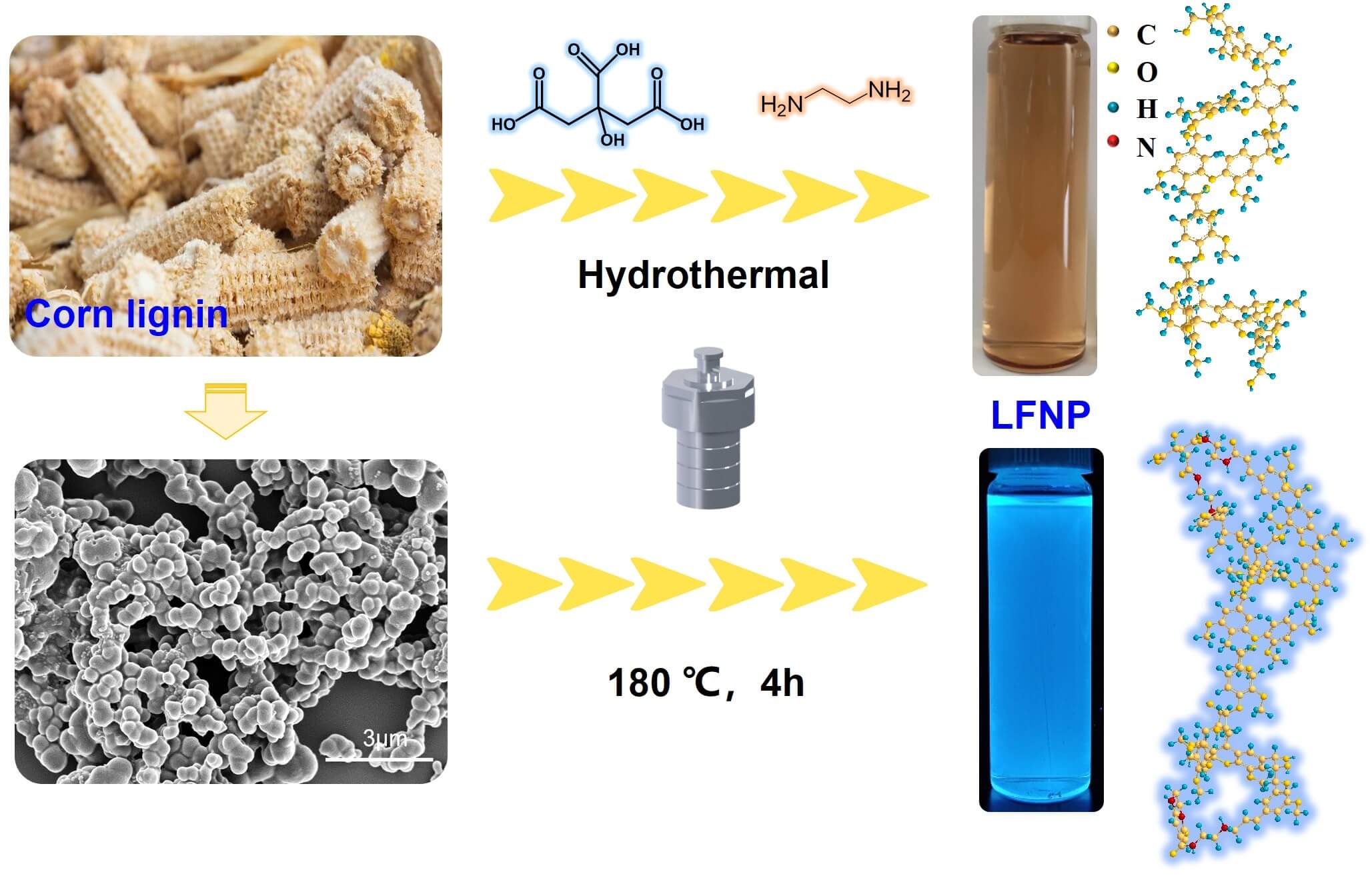
Fluorescent nanomaterials have attracted much attention, due to their unique luminescent properties and promising applications in biomedical areas. In this study, lignin based fluorescent nanoparticles (LFNP) with high yield (up to 32.4%) were prepared from lignin nanoparticles (LNP) by one-pot hydrothermal method with ethylenediamine (EDA) and citric acid. Morphology and chemical structure of LFNP were investigated by SEM, FT-IR, and zeta potential, and it was found that the structure of LFNP changed with the increase of citric acid addition. LFNP showed the highest fluorescence intensity under UV excitation at wavelengths of 375–385 nm, with emission wavelengths between 454–465 nm, and exhibited strong photoluminescence behavior. Meanwhile, with the increase of citric acid content, the energy gap (ΔE) gradually decreased from 3.87 to 3.14 eV, which corresponds to the gradual enhancement of fluorescence performance. LFNP also exhibited excellent antioxidant activity, with DPPH free radical scavenging rate increased from 80.8% for LNP up to 96.7% for LFNP, confirming the great potential of these materials for application in biomedicine and cosmetic health care.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools