 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Fabrication of Core-Shell Hydrogel Bead Based on Sodium Alginate and Chitosan for Methylene Blue Adsorption
School of Material Engineering, Jinling Institute of Technology, Nanjing, 211169, China
* Corresponding Author: Xiaoyu Chen. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(4), 815-826. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.048470
Received 08 December 2023; Accepted 18 February 2024; Issue published 12 June 2024
Abstract
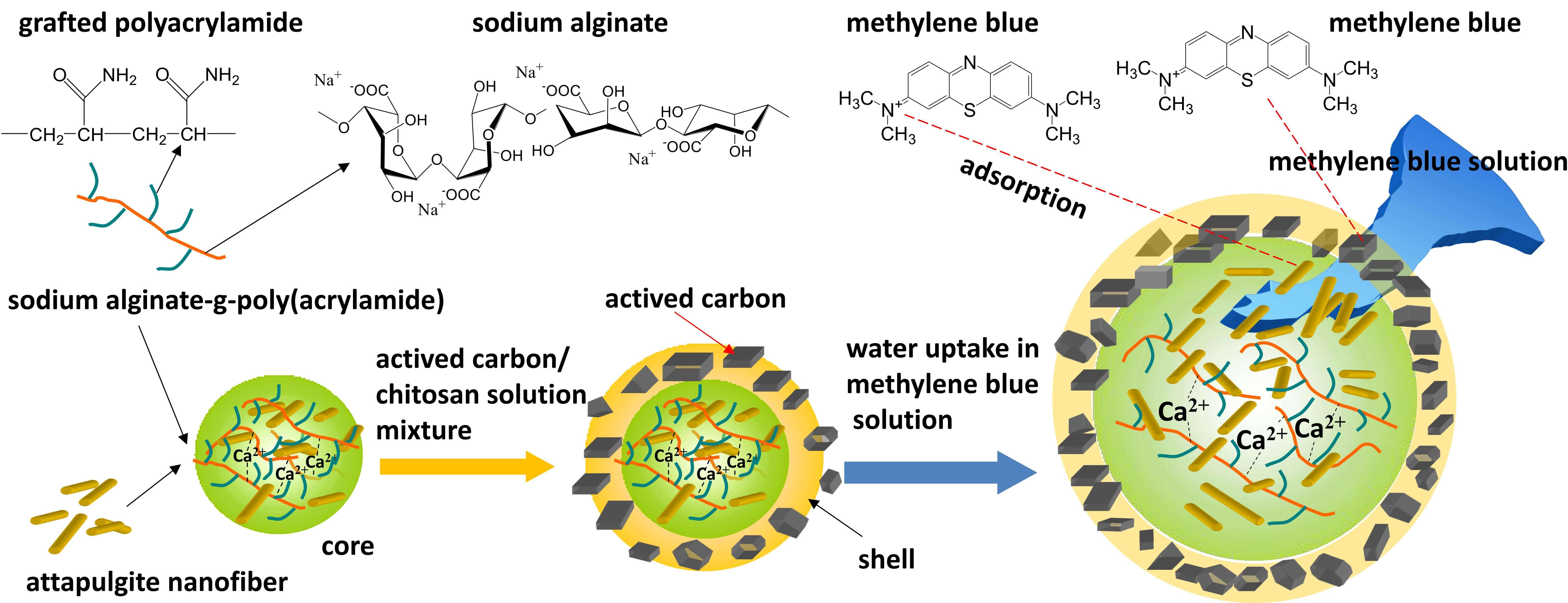
A novel core-shell hydrogel bead was fabricated for effective removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions. The core, made of sodium alginate-g-polyacrylamide and attapulgite nanofibers, was cross-linked by Calcium ions (Ca). The shell, composed of a chitosan/activated carbon mixture, was then coated onto the core. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy confirmed the grafting polymerization of acrylamide onto sodium alginate. Scanning electron microscopy images showed the core-shell structure. The core exhibited a high water uptake ratio, facilitating the diffusion of methylene blue into the core. During the diffusion process, the methylene blue was first adsorbed by the shell and then further adsorbed by the core. Adsorption tests showed that the core-shell structure had a larger adsorption capacity than the core alone. The shell effectively enhanced the adsorption capacity to methylene blue compared to the single core. Methylene blue was adsorbed by activated carbon and chitosan in the shell, and the residual methylene blue diffused into the core and was further adsorbed.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools