 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Novel Sustainable Cellulose Acetate Based Biosensor for Glucose Detection
1 Chemical and Petrochemical Engineering Department, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El-Arab, Alexandria, Egypt
2 Fabrication Technology Research Department, Advanced Technology and New Materials Research Institute, City of Scientific Research and Technological Applications (SRTA-City), New Borg El-Arab, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt
3 Department of Public Works Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Mansoura University, Mansoura, 35516, Egypt
4 Environmental Engineering Department, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology, New Borg El-Arab, Alexandria, Egypt
5 Electronic Materials Research Department, Advanced Technology and New Materials Research Institute, City of Scientific Research and Technological Applications (SRTA-City), New Borg El-Arab, Alexandria, 21934, Egypt
* Corresponding Author: M. F. Elkady. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Eco-Friendly Waste-Base Materials for Pollution Control Sustainable Technologies)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(2), 369-380. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.046585
Received 08 October 2023; Accepted 14 December 2023; Issue published 11 March 2024
Abstract
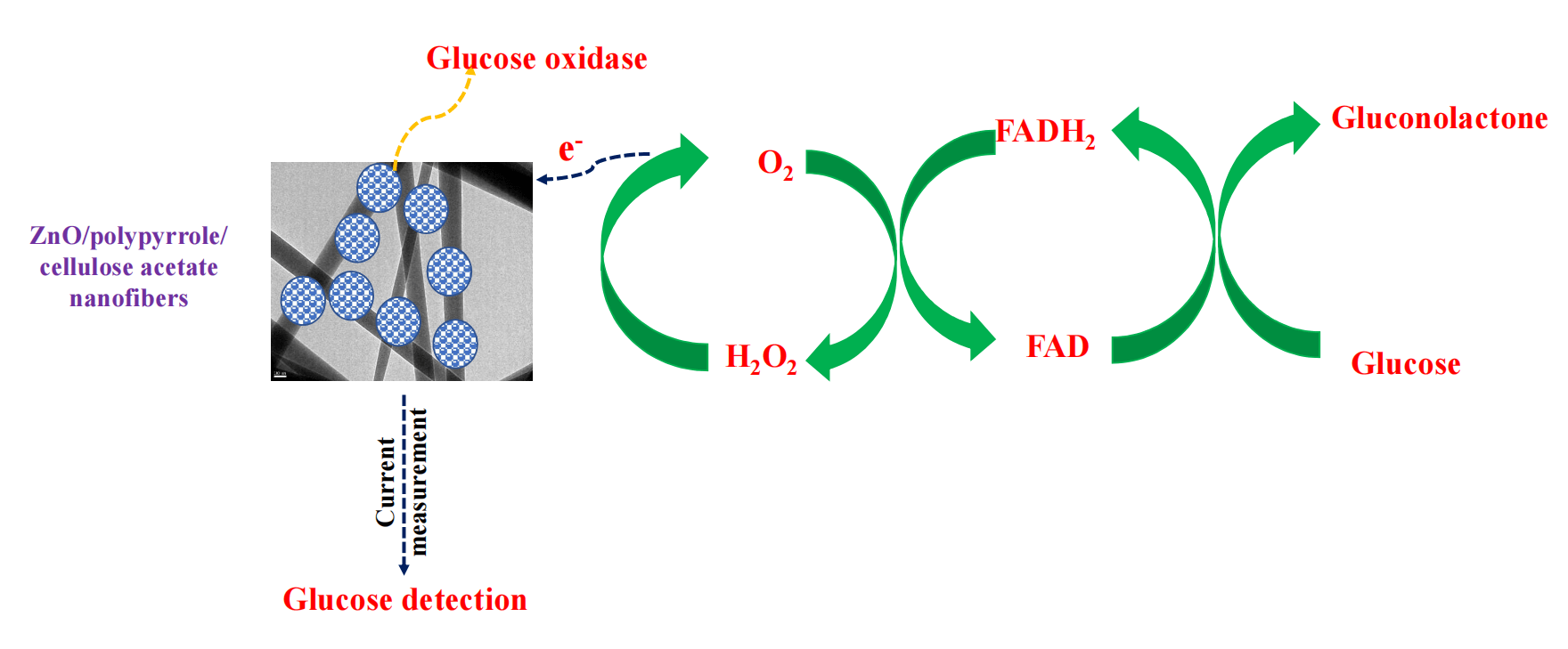
In this study, green zinc oxide (ZnO)/polypyrrole (Ppy)/cellulose acetate (CA) film has been synthesized via solvent casting. This film was used as supporting material for glucose oxidase (GOx) to sensitize a glucose biosensor. ZnO nanoparticles have been prepared via the green route using olive leaves extract as a reductant. ZnO/Ppy nanocomposite has been synthesized by a simple in-situ chemical oxidative polymerization of pyrrole (Py) monomer using ferric chloride (FeCl3) as an oxidizing agent. The produced materials and the composite films were characterized using X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Glucose oxidase was successfully immobilized on the surface of the prepared film and then ZnO/Ppy/CA/GOx composite was sputtered with platinum electrode for the current determination at different initial concentrations of glucose. Current measurements proved the suitability and the high sensitivity of the constructed biosensor for the detection of glucose levels in different samples. The performance of the prepared biosensor has been assessed by measuring and comparing glucose concentrations up to 800 ppm. The results affirmed the reliability of the developed biosensor towards real samples which suggests the wide-scale application of the proposed biosensor.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools