 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Greener, Safer Packaging: Carbon Nanotubes/Gelatin-Enhanced Recycled Paper for Fire Retardation with DFT Calculations
Cellulose and Paper Department, National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, P.O. Box 12622, Egypt
* Corresponding Author: Hebat-Allah S. Tohamy. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Recent Advances on Renewable Materials)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(12), 1963-1983. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2024.054977
Received 13 June 2024; Accepted 14 October 2024; Issue published 20 December 2024
Abstract
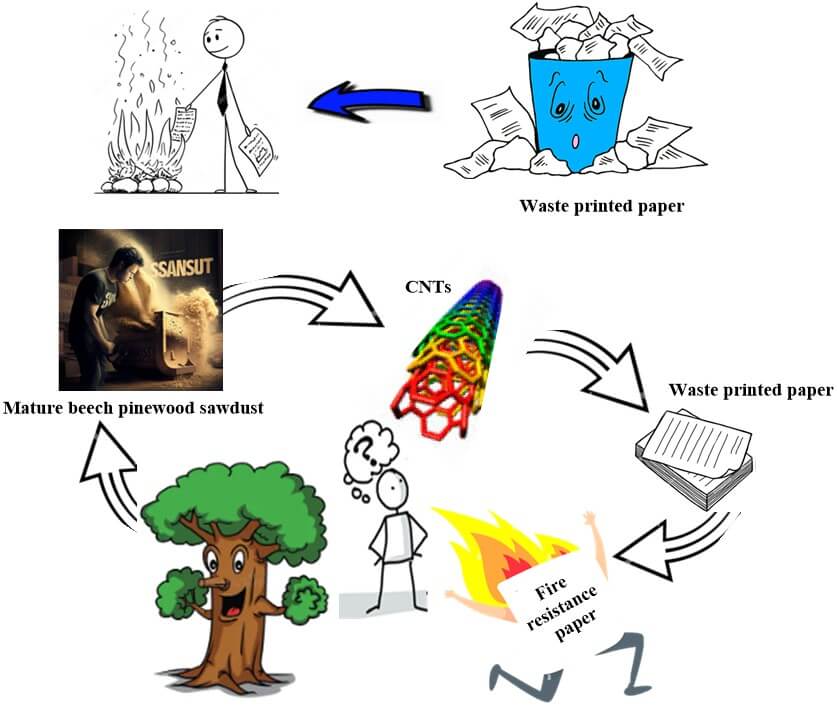
Fire retardant CNTs/WPP/Gel composite papers were fabricated by incorporating bio-based carbon nanotubes (CNTs) recycled from mature beech pinewood sawdust (MB) and cellulosic waste printed paper (WPP) into a gelatin solution (Gel) and allowing the mixture to dry at room temperature. The CNTs within the WPP matrix formed a network, enhancing the mechanical and thermal properties of the resulting CNTs paper sheet. In comparison to pure WPP/Gel, CNTs/WPP/Gel exhibited superior flexibility, mechanical toughness, and notable flame retardancy characteristics. This study provides a unique and practical method for producing flame-retardant CNTs/WPP/Gel sheets, suitable for diverse industrial applications, especially packaging, where used paper materials pose a significant fire risk. Bio-CNT-based fire-resistant packaging offers enhanced safety during transportation and storage. The sheets demonstrated increased strength and stiffness, with optimal mechanical properties achieved at a 20% CNTs loading. Additionally, thermal stability was improved, as confirmed by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential thermogravimetry (DTG). Flame retardancy tests revealed a rise in LOI (Limiting Oxygen Index) values with increasing CNTs content, indicating the CNTs’ effectiveness in inhibiting combustion. The compatibility of recycled paper, CNTs, and Gel suggests potential applications in industrial fields, capitalizing on the biocompatible and biodegradable nature of cellulose. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations using the B3LYP with the 6-31G(d) basis set were employed to optimize the stability of these compounds and elucidate their chemical interactions.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools