 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
High-Value-Added Utilization of Turpentine: Screening of Anti-Influenza Virus Agents from β-Pinene Derivatives
1 East China Woody Fragrance and Flavor Engineering Research Center of National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Camphor Engineering Research Center of National Forestry and Grassland Administration, College of Forestry, Jiangxi Agricultural University, Nanchang, 330045, China
2 Institute of Chemical Industry of Forestry Products, China Academy of Forestry, National Engineering Laboratory for Biomass Chemical Utilization, Key and Open Laboratory of Forest Chemical Engineering, State Forestry Administration, Key Laboratory of Biomass Energy and Material, Jiangsu Province, Nanjing, 210042, China
3 College of Chemical Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, 361021, China
* Corresponding Authors: Zongde Wang. Email: ; Shengliang Liao. Email:
# These authors contributed equally to this work
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Material from Agricultural Waste and By-Product and Its Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2024, 12(1), 45-56. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.031089
Received 13 May 2023; Accepted 28 July 2023; Issue published 23 January 2024
Abstract
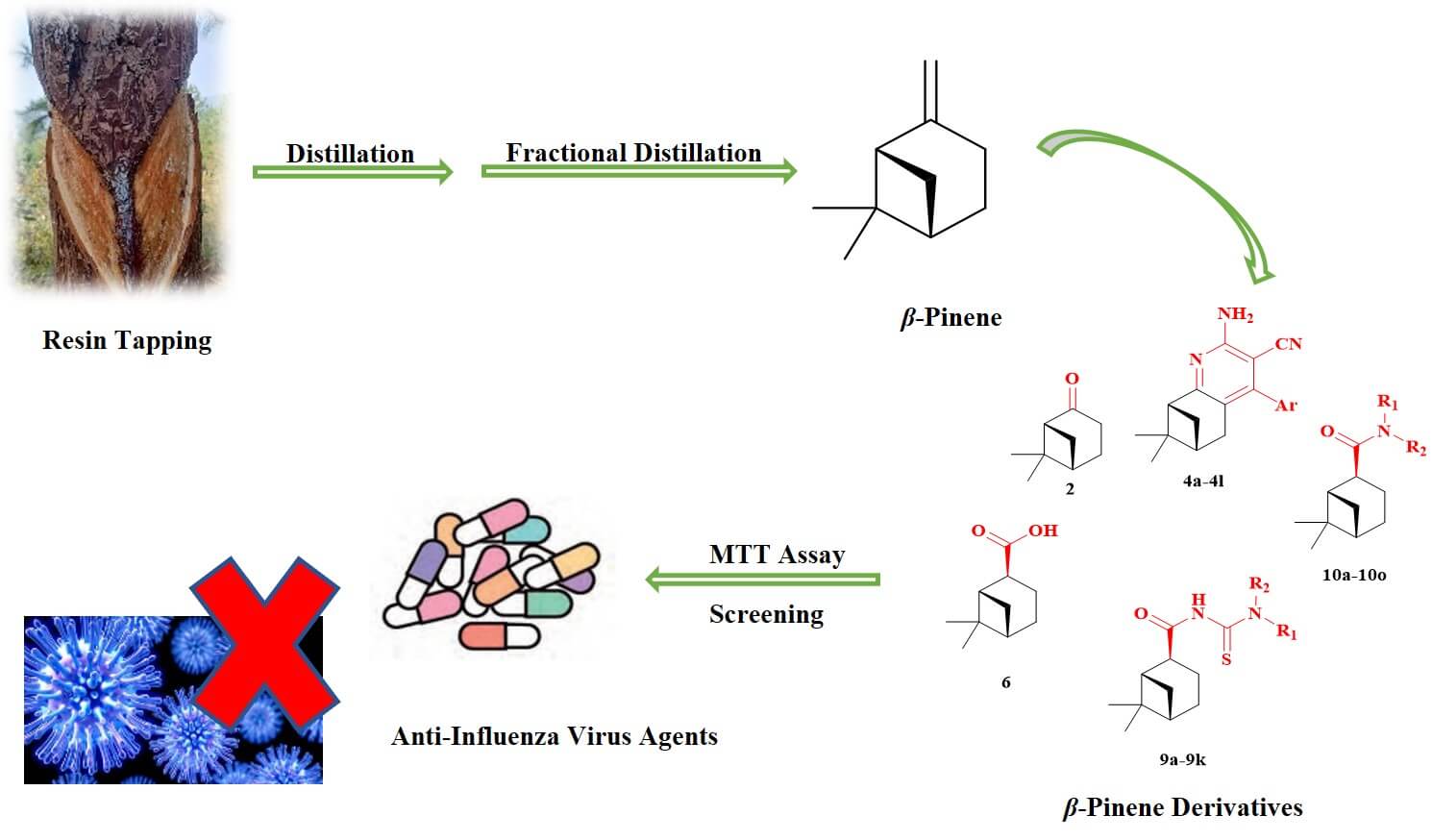
Turpentine is a renewable and resourceful forest product. The deep processing and utilization of turpentine, particularly its primary component β-pinene, has garnered widespread attention. This study aimed to synthesize 40 derivatives of β-pinene, including nopinone, 3-cyanopyridines of nopinone, myrtanyl acid, myrtanyl acylthioureas, and myrtanyl amides. We assessed the antiviral activities of these β-pinene derivatives against influenza virus A/Puerto Rico/8/34 (H1N1) using the 3-(4,5-dimetylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide method. The β-pinene derivatives were used before and after cellular infection with the influenza virus to evaluate their preventive and therapeutic effects against the H1N1 virus. The results showed that only compound 10o exhibited a preventive effect against the H1N1 virus with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 47.6 μmol/L. Among the compounds, 4e, 4i, and 4l demonstrated therapeutic effects against cellular infection, with compound 4e displaying the most potent therapeutic effect (IC50 = 17.5 μmol/L), comparable to the positive control ribavirin. These findings indicated that certain β-pinene derivatives exhibited in vitro antiviral activity against the H1N1 influenza A virus, warranting further investigation as potential anti-influenza agents.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material FileCite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools