 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Research of Microstructure, Phase, and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum-Dross-Based Porous Ceramics
1 Key Laboratory of New Processing Technology for Nonferrous Metals & Materials, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, 541004, China
2 Guangxi Scientific Experiment Center of Mining, Metallurgy and Environment, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, 541004, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center for Exploration of Nonferrous Metal Deposits and Efficient Utilization of Resources, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin, 541004, China
4 Hebei Technology Innovation Center for Intelligent Development and Control of Underground Built Environment, School of Exploration Technology and Engineering, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang, 050031, China
* Corresponding Authors: Xiuling Cao. Email: ; Yanli Jiang. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(7), 3057-3072. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.025732
Received 27 July 2022; Accepted 13 September 2022; Issue published 05 June 2023
Abstract
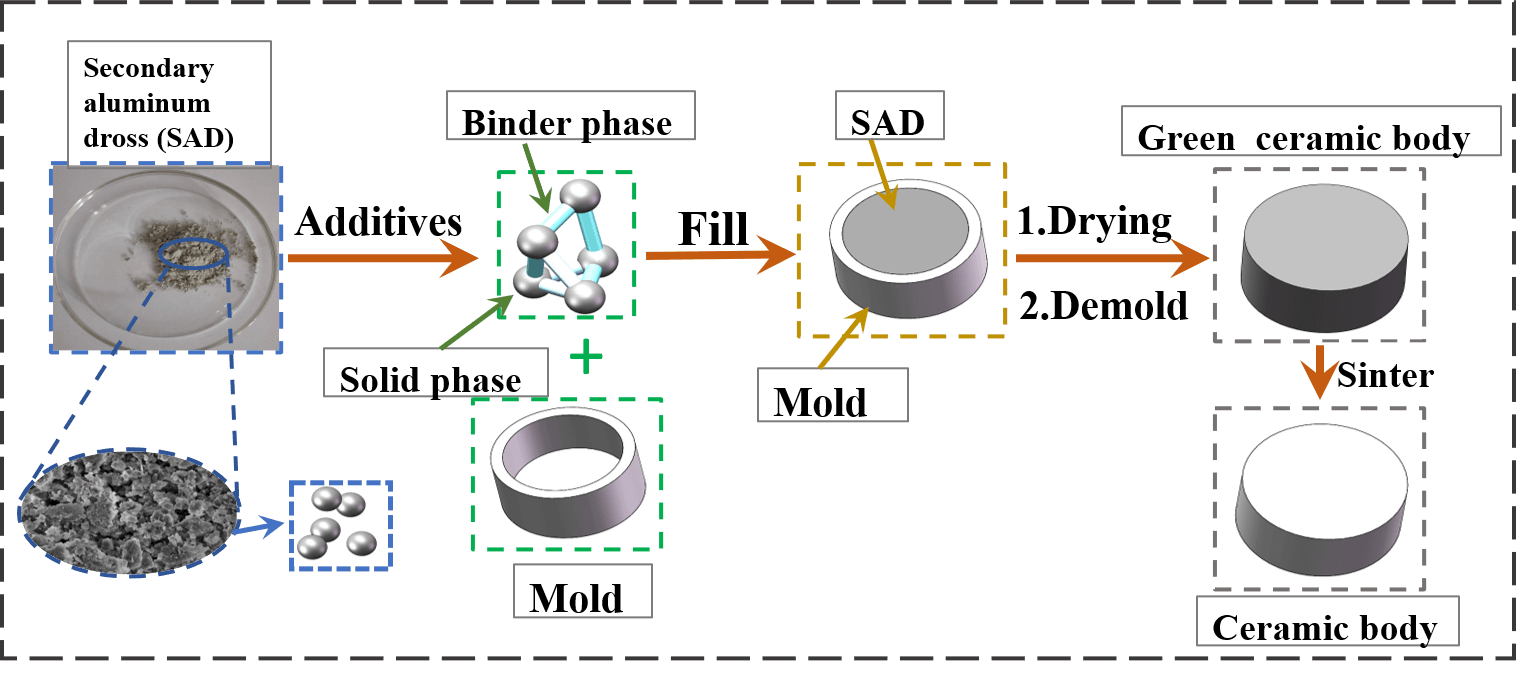
In this study, the effect of sintering temperature and the addition of kaolin, a sintering agent, on the microscopic, phase, and mechanical properties of ceramics were investigated using secondary aluminum dross (SAD) as the main component in the manufacturing of ceramics. The basic phases of the ceramics were Al2O3, MgAl2O4, NaAl11O17, and SiO2 without the addition of kaolin. The diffraction peaks of MgAl2O4, NaAl11O17, and SiO2 kept decreasing while those of Al2O3 kept increasing with an increase in temperature. In addition, the increase in temperature promoted the growth of the grains. The grains were uniform in size and regular in distribution, with a shrinkage of 2.2%, porosity of 72.5%, bulk density of 1.076 g/cm3, and compressive strength of 1.12 MPa. When the sintering temperature was 1450°C, the basic phases of the ceramic after the addition of kaolin were Al2O3, MgAl2O4, NaAl11O17, and SiO2. With the increase of kaolin, the diffraction peaks of NaAl11O17 and SiO2 decreased until they disappeared, while the diffraction peaks of Al2O3 increased significantly. When kaolin was added at 30 wt.%, the ceramics obtained had shrinkage of 18%, a porosity of 47.26%, a bulk density of 1.965 g/cm3, and compressive strength of 31.9 MPa. Cracks existed inside the ceramics without the addition of kaolin, while the addition of kaolin significantly changed this defect. It is shown that SAD can obtain porous ceramics with good properties at a sintering temperature of 1450°C and a kaolin addition of 30 wt.%.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools