 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Effect of PEG Incorporation on Physicochemical and in vitro Degradation of PLLA/PDLLA Blends: Application in Biodegradable Implants
1
Department of Metallurgical and Material Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Indonesia, Depok City, 16424,
Indonesia
2
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Indonesia, Depok City, 16424, Indonesia
* Corresponding Author: Mochamad Chalid. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(7), 3043-3056. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.026788
Received 25 September 2022; Accepted 06 February 2023; Issue published 05 June 2023
Abstract
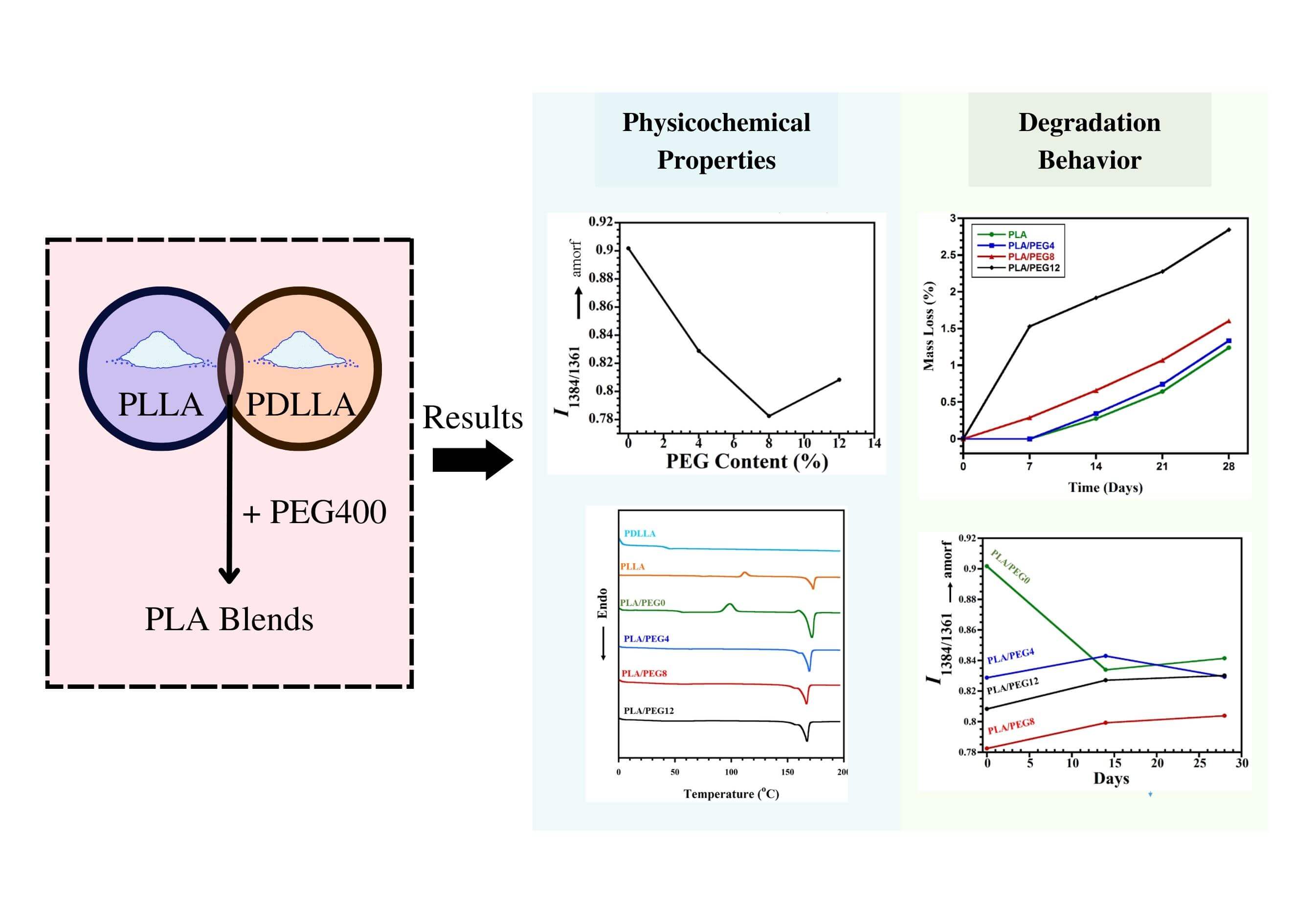
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) was added at different concentrations to the blend of poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) and poly(D,L-lactic acid)(PDLLA) to tailor the properties. The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurement showed that all blends were miscible due to shifting a single glass transition temperature into a lower temperature for increasing PEG content. The DSC, FTIR, and XRD results implied the crystallinity enhancement for PEG content until 8 wt%, then decreased at 12 wt% PEG. The XRD result indicated the homo crystalline phase formation in all blends and no stereocomplex crystal. The in vitro degradation study indicated that PEG content is proportional to the degradation rate. The highest weight loss after 28 days was achieved at 12 wt% PEG. The FTIR analysis showed a structural evolution overview during hydrolytic degradation, viz. increasing and decreasing crystallinity during 14 days for the blend without and with PEG, respectively. In conclusion, the PEG addition increased crystallinity and degradation rate of the PLLA/PDLLA mixture, but PEG higher amounts led to a decrease in crystallinity, and the weight loss was intensified. This can be useful for tuning PLA-based biomaterials with the desired physicochemical properties and appropriate degradation rates for applications in drug delivery/ tissue engineering.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools