 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Comprehensive Assessment of the Safety of Eucommia ulmoides Leaf Extract for Consumption as a Traditional Chinese Health Food
1
School of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, Hunan Institute of Technology, Hengyang, 421002, China
2
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Chemical Measurement and Emergency Test Technology, Guangdong Provincial
Engineering Research Center for Ambient Mass Spectrometry, Institute of Analysis, Guangdong Academy of Sciences (China
National Analytical Center, Guangzhou), Guangzhou, 510070, China
* Corresponding Authors: Jiali Fang. Email: ; Xuesong Wang. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable Biomass as a Platform for Preparing Green Chemistry)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(7), 3091-3114. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.026689
Received 20 September 2022; Accepted 07 November 2022; Issue published 05 June 2023
Abstract
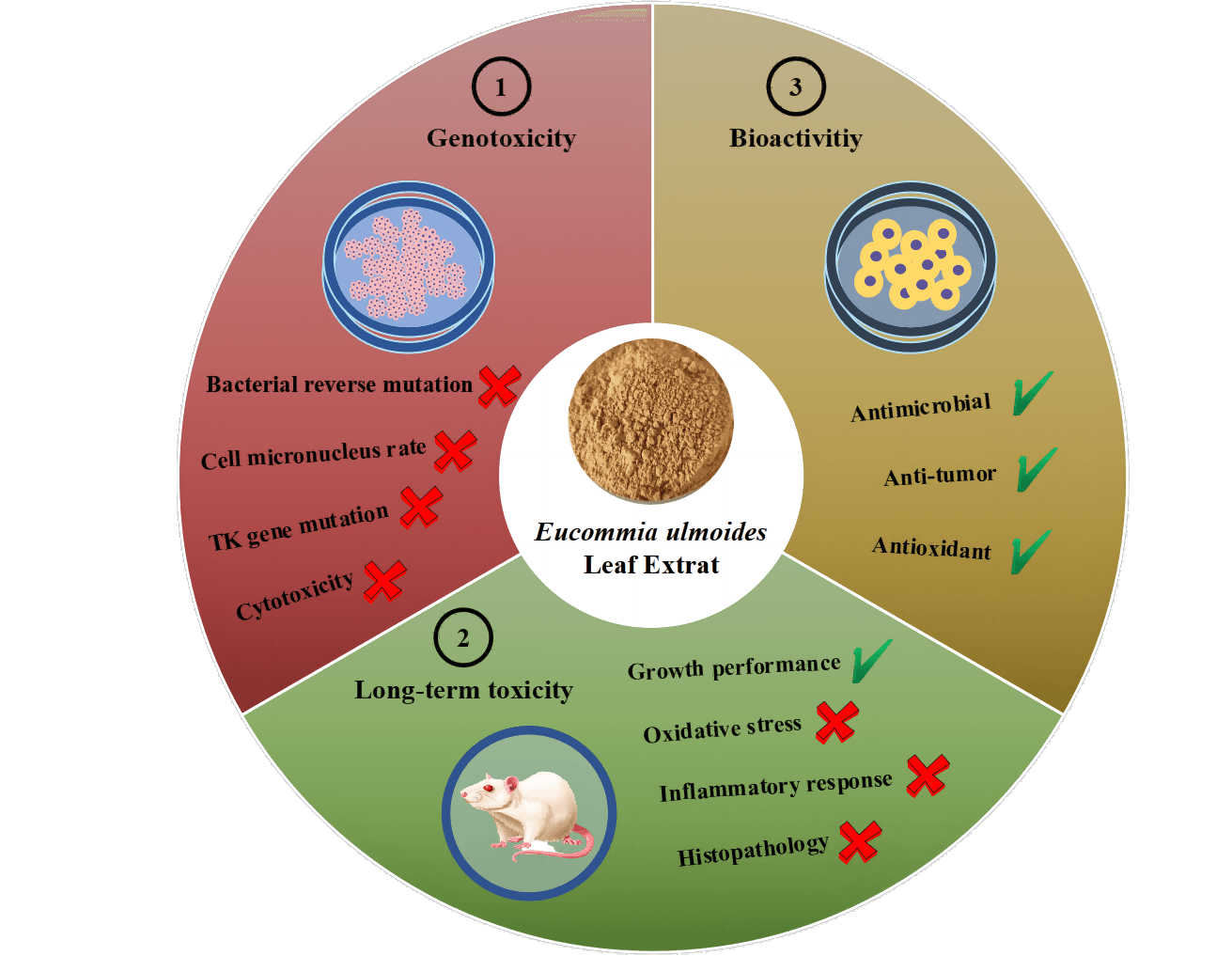
To ensure the export quality of Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (ELE) and facilitate E. ulmoides leaf inclusion in the directory of traditional Chinese health foods, an overall safety assessment of ELE was performed, including genotoxicity and long-term toxicity, according to the national food safety standards of China. No variations in the reverse mutation number of the nominal bacterial strains were observed under ELE treatment in comparison with the solvent control. Additionally, the micronucleus rates of in vivo mammalian erythrocytes and in vitro mammalian cells under ELE treatment were equivalent to or significantly lower than those of the solvent control. The fold change in the trifluorothymidine resistance mutation frequency of the thymidine kinase gene under ELE treatment was less than three times in comparison with the solvent control, suggesting that ELE did not cause genotoxicity. Moreover, animal experiments showed that the growth performance of rats under ELE treatment was enhanced because the body weights of rats increased. No oxidative injury or inflammatory responses were induced and no histopathological lesions of tissues were detected under ELE treatment. In addition, plasma triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels significantly decreased, and plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels significantly increased with ELE treatment, suggesting that ELE was health-promoting. Furthermore, moderate to excellent antimicrobial activities, a favorable anticancer capacity, and superior antioxidant abilities of ELE were found, implying ELE possesses good bioactivities. Therefore, we affirmed ELE is safe to consume as a traditional Chinese health food.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools