 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Low-Temperature Synthesis of Nano-AlN Based on Solid Nitrogen Source by Plasma-Assisted Ball Milling
1
Xiamen Ocean Vocational College, Xiamen, 361100, China
2
Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, Institute of Marine Engineering, Jimei University,
Xiamen, 361100, China
* Corresponding Author: Leyang Dai. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Carbon-Based Nanomaterials from Renewable Materials: Synthesis, Properties and Applications)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(6), 2941-2951. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.025723
Received 27 July 2022; Accepted 30 September 2022; Issue published 27 April 2023
Abstract
Plasma-assisted ball milling was carried out on the Al+C3H6N6 system and Al+C4H4N4 system, respectively. The phase structure, functional groups and synthesis mechanism were analyzed by XRD and FT-IR, and the differences in the synthesis process of nano-AlN with different solid nitrogen sources were discussed. The results show that C3H6N6 has a stable triazine ring structure, and its chemical bond is firm and difficult to break, so AlN cannot be synthesized directly by solid-solid reaction at room temperature. However, there are a large number of nitrile groups (-CN) and amino groups (-NH2) in C4H4N4 molecules. Under the combined action of plasma bombardment and mechanical energy activation, C4H4N4 molecules undergo polycondensation and deamination, so that the ball milling tank is filled with a large number of active nitrogen-containing groups such as N=, ≡N, etc. These groups and ball milling activated Al can synthesize nano-AlN at room temperature, with a conversion rate of 92%. SEM, DSC/TG analysis showed that the powder obtained by ball milling was formed by soft agglomeration of many fine primary particles about 50–80 nm. The surface morphology of the powder was loose and porous, and it had strong activity. After annealing at 800°C, the conversion rate of the Al+C4H4N4 system reached 99%.Keywords
Nomenclature
| CRN | Carbothermal reduction nitridation method |
| C3H6N6 | Melamine |
| C4H4N4 | Diaminomaleonitrile |
| DTA/DSC | Differential thermal analysis/Differential scanning calorimeter |
| TG | Thermal gravimetric analyzer |
| -NH2 | Amino |
| N-H | Hydrogen bonds |
Aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramics have a hexagonal wurtzite crystal structure, high thermal conductivity [1–3], high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, reliable insulation and thermal expansion coefficient similar to silicon [4–8], and its comprehensive properties are better than SiC and BeO ceramics [9]. It can be used as substrate materials for high-power devices, protection tubes for thermocouples and sensors [10–13], etc. Such as: the AlN ceramic materials can be used as copper-clad substrate materials, high-power device packaging materials, optical electronic device materials, coatings and functional enhancement materials, etc. [14–16].
At present, AlN products on the market are mainly prepared by direct nitridation or carbothermal reduction [17,18]. Both methods use gaseous nitrogen-containing substance nitrogen (N2) as a nitrogen source to synthesize AlN through a solid-gas reaction. These reaction modes require a separate gas supply system, and the flow rate, air pressure and gas purity of the gas supply have an impact on the synthesis results. Secondly, when the powder comes into contact with a gaseous nitrogen source, AlN preferentially synthesized on the surface will hinder the diffusion of gas into the powder, which makes the synthesis temperature and time of the reaction high. It is found that the powder activated by high-energy ball milling can significantly reduce the synthesis temperature of AlN [19,20]. Dai et al. [21] activated Al2O3 powder by plasma-assisted ball milling, which reduced the synthesis temperature of carbothermal reduction by 450°C. Xu et al. [22] used Al2O3 and carbon black as raw materials to synthesize ultrafine AlN powders by carbothermal reduction nitridation method (CRN) under 1.5 h soaking time, 1650°C and 300 Pa N2 pressure. The Al6C3N2 intermediate is mainly obtained by ball milling, the reaction temperature is lowered and the soaking time is shortened through the reaction of Al6C3N2 + 2N2(g) → 6AlN + 3C. Fu et al. [23] used Al(OH)3, carbon black and Y2O3 as raw materials to synthesize aluminum nitride powder by the carbothermal reduction-nitridation method. Using Y2O3 as the promoting additive, and the intermediate product YAlO3 is generated, and the temperature for synthesizing AlN powder is reduced to 1350°C–1400°C in a flowing nitrogen atmosphere.
The above research can reduce the reaction temperature to a certain extent, but the defects of the gaseous nitrogen source itself cannot be avoided [24]. Since the solid nitrogen source with the same volume contains more nitrogen than the gaseous nitrogen source [19], the solid nitrogen source and aluminum powder are in solid-solid contact during ball milling. As shown in Fig. 1, the uniform dielectric barrier discharge is formed around the electrode. Under the synergistic effect of mechanical force and plasma discharge, the grain size becomes smaller. The diffusion and movement of atoms on the surface and inside of the powder are stimulated, which makes the contact between powder more sufficient and the reactivity of mixed powders in the system is enhanced, promoting the chemical reaction of the powder across the reaction barrier. Therefore, the solid-solid reaction mode to synthesize AlN is expected to overcome the shortcomings of solid-gas reaction, simplify the device, reduce the synthesis temperature and realize the synthesis of AlN at room temperature. In this study, the synthesis mechanism of AlN in the solid-solid reaction mode and the differences between different solid nitrogen sources in the synthesis of AlN were discussed.

Figure 1: Dielectric barrier discharge situation in ball mill (a) stationary state; (b) vibrational state
2 Experimental Design and Methods
In this paper, metal aluminum (Al) is used as the aluminum source, and the preparation technology of aluminum powder is mature and the output is abundant. Melamine (chemical formula: C3H6N6, nitrogen content 66.7%) and diaminomaleonitrile (chemical formula: C4H4N4, nitrogen content 51.85%), which have high nitrogen content and low cost, are used as solid nitrogen sources. AlN was directly prepared at room temperature by plasma-assisted ball milling through solid-solid reaction mode. To investigate whether high purity and fine grain AlN can be synthesized more quickly and efficiently by using melamine (C3H6N6) with higher nitrogen content under plasma-assisted ball milling. The phase structure, thermodynamic changes and microstructure of the mixed powder in this mode were analyzed. The differences between different solid nitrogen sources in the synthesis of AlN were discussed.
The experimental raw materials include: Al powder is a Shanghai national medicine chemical reagent (purity > 99.9%); C3H6N6 is a Shanghai national medicine chemical reagent (purity > 99%); C4H4N4 is McCassie reagent Co., Chengdu, China (purity & gt; 98%). The Al powder and C3H6N6 are mixed in a molar ratio of 6: 1 and put into a ball milling tank, and the Al powder and C4H4N4 are put into a ball milling tank in a molar ratio of 4:1, and the ball-to-material ratio is 65:1. The Al+C3H6N6 system and Al+C4H4N4 system were balls milled on a self-made plasma-assisted ball milling device [25] (shown in Fig. 2). In order to reduce the pollution of steel balls and the inner wall in the ball milling tank, Al powder was ball milled for 6 h by ordinary ball milling process before the test.

Figure 2: schematic diagram of plasma-assisted ball milling equipment 1. Motor 2. Coupling 3. Vial 4. Steel ball 5. Vibration exciter 6. Electrode rod 7. High voltage cable 8. AC Power 9. Gas cylinder 10. Gas check 11. Flow controller 12. Airway 13. Air inlet and outlet valve
Samples were taken in a glove box with nitrogen as protective gas to prevent oxygen in the air from interfering with the experimental results. Since heat release of C3H6N6 is instantaneous, if the ball milling time is too long in a closed container, the powder has high degree of refinement and strong activity, which may cause an explosion. Therefore, the plasma-assisted ball milling time should not be too long, and the sampling time of the two systems is 4, 8, 10, 14 h. Bruker D8 X-ray diffractometer was used to analyze the phase composition and changes of the samples. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to analyze the microscopic morphology of the samples; TGA/SDTA851 differential thermal analyzer and ZT-50-20 vacuum carbon tube furnace were used to analyze and anneal the samples milled by plasma-assisted ball milling for 8 h.
3.1 Phase Change of Plasma-Assisted Ball Milling
Fig. 3 is the XRD pattern of the Al+C3H6N6 system and the Al+C4H4N4 system respectively milled at different times. It can be seen from the figure that with the increase of plasma-assisted ball milling time, the diffraction peaks of Al in the two systems gradually dwarf and broaden, which is due to the increase of crystal structure defects and lattice distortion of the powder in the two systems under the synergistic effect of mechanical force and plasma bombardment. With the progress of ball milling, there is no AlN formation in the Al+C3H6N6 system with high nitrogen content. However, when the Al+C4H4N4 system is ball milled for 10 h, a small number of AlN peaks appear, and with the increase of ball milling time, the diffraction peaks of AlN gradually increase and strengthen.
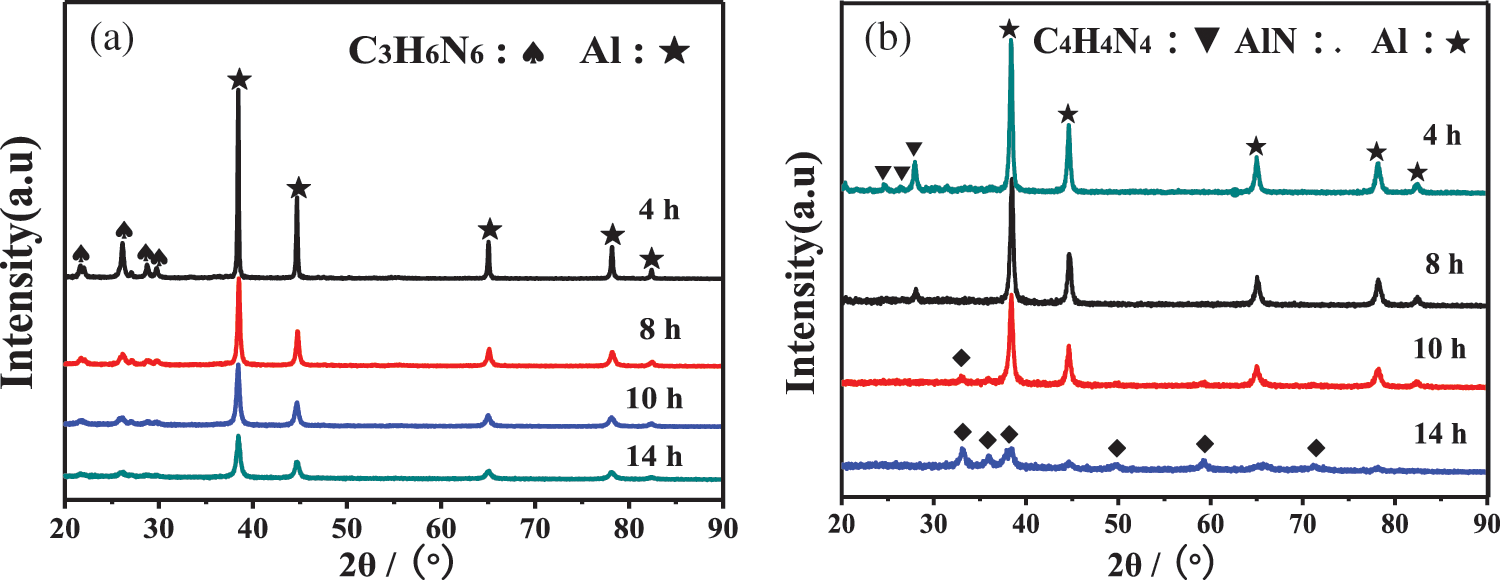
Figure 3: XRD spectra of plasma-assisted ball milling at different times (a) Al+C3H6N6; (b) Al+C4H4N4
Fig. 4 shows AlN conversion curves generated by plasma-assisted ball milling at different times obtained by the RIR (Ratio of Intensity Reference) reference intensity comparison method. It can be seen from the figure that although the nitrogen content of C3H6N6 in the Al+C3H6N6 system is high with the progress of ball milling, AlN is never formed, and the conversion rate is 0%. However, in the Al+C4H4N4 system, a small amount of AlN began to form after 8 h of plasma-assisted ball milling, and its conversion rate gradually increased with the progress of ball milling, and the conversion rate of AlN reached 92% after 14 h of ball milling.

Figure 4: AlN conversion at different times of plasma-assisted ball milling Al+C3H6N6; Al+C4H4N4
3.2 Crystallite Size and Lattice Distortion of Plasma-Assisted Ball Milling
Fig. 5 shows the grain size and lattice distortion of the two systems at different times of plasma-assisted ball milling by using the Voigt method and Scherrer [26,27] formula. As can be seen from Fig. 5a, the crystallite size of Al in the Al+C3H6N6 system is continuously refined with the progress of ball milling, and the grain refinement degree starts to slow down and gradually tends to be stable after 8 h of ball milling. However, in the Al+C4H4N4 system, the crystallite size still decreases obviously after 8 h of ball milling, which is due to the gradual reaction between Al and C4H4N4 after 8 h of ball milling, the Al phase in the mixed powder gradually transforms into AlN phase, while nitrogen has the effect of refining the grain [28]. As can be seen from Fig. 5b, the crystal defects and lattice distortion of the Al phase in the two systems also gradually increase with the increase of ball milling time, but after 8 h of ball milling, compared with the Al+C3H6N6 system, the upward trend of lattice distortion of the Al+C4H4N4 system is significantly enhanced. This is because the powder in the Al+C4H4N4 system is not only affected by mechanical force and high-frequency plasma pulse generated by dielectric barrier discharge after ball milling for 8 h, The nitridation reaction of Al also occurs, which is a strongly exothermic reaction, causing local “micro-explosion” when the temperature in the ball milling tank rises, and the crystal is subjected to stronger micro-zone stress, thus promoting more crystal defects and lattice distortion. These changes make the powder in an unstable state and contribute to the progress of the nitriding reaction.

Figure 5: Crystallite size and lattice distortion of Al phase at different times of plasma-assisted ball milling (a) Al+C3H6N6; (b) Al+C4H4N4
3.3 Differential Thermal Analysis of the System
Fig. 6 shows DSC-TG test results of plasma-assisted ball milling for 8 h in two systems. As can be seen from Fig. 6a, in the Al+C3H6N6 system, the mixed powder gradually loses weight between 96°C and 550°C, with a weight loss rate of 29.57%, and begins to stabilize after 550°C. This is due to water evaporation and thermal decomposition of C3H6N6 (theoretical decomposition temperature is 354°C) with the increase in temperature, and the corresponding DSC curve has small endothermic peaks at 100°C and 345°C. As plasma-assisted ball milling enhances the activity of mixed powder of the Al+C3H6N6 system, the decomposition temperature of C3H6N6 decreases slightly, and its endothermic peaks shift accordingly. Fig. 6b shows that in the Al+C4H4N4 system, the mixed powder gradually loses weight between 100°C and 653°C, with a weight loss rate of 19.35%, which is due to evaporation of water carried in the powder and polycondensation and deamination of C4H4N4 with the increase of temperature. Moreover, because the polycondensation reaction of C4H4N4 is exothermic [28] and is a gradual change process, the DSC curve as a whole shows a gradual upward trend, and an exothermic peak appears at the reaction temperature of C4H4N4 molecular polycondensation reaction of about 452°C. At the same time, after 653°C, the TG curve of the Al+C4H4N4 system gradually increased, which was due to the deamination and polycondensation of C4H4N4 molecules to produce a large number of N-containing groups, which were integrated into Al activated by plasma-assisted ball milling to produce AlN.
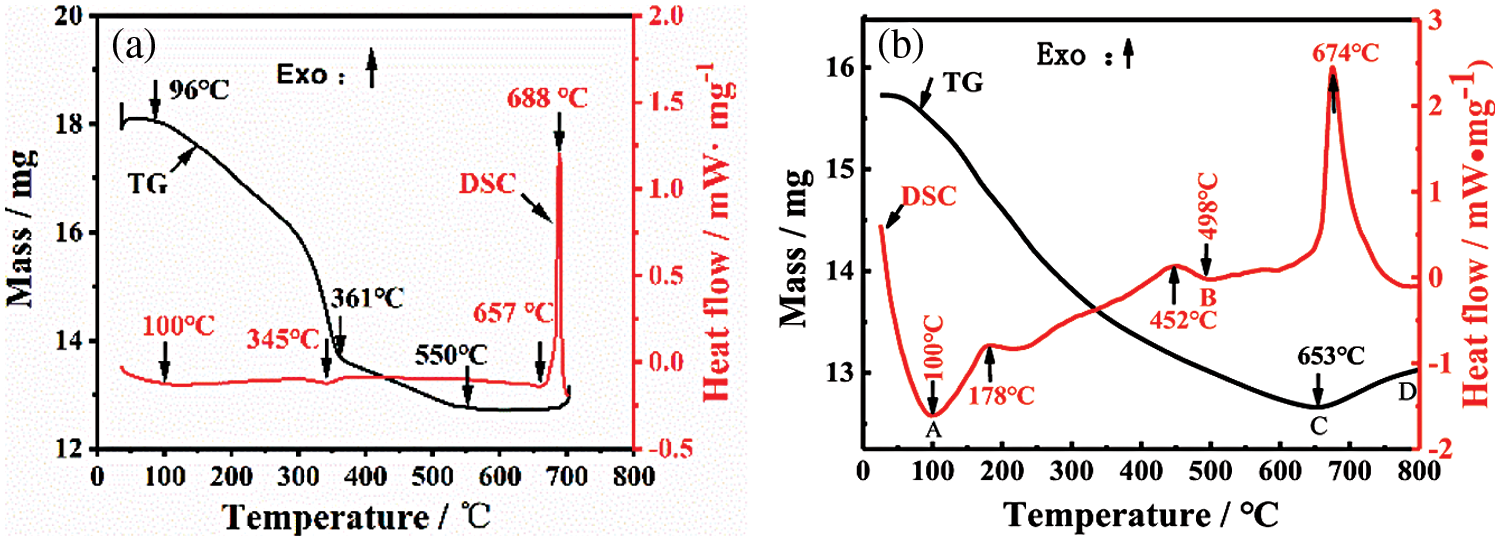
Figure 6: DSC-TG curves of the mixture after 8 h of plasma-assisted ball milling (a) Al+C3H6N6; (b) Al+C4H4N4
3.4 Microscopic Morphology Analysis of the System
Fig. 7 is the microscopic morphology of the mixed powder after 14 h of plasma-assisted ball milling. As shown in Fig. 7a, since the Al+C3H6N6 system does not undergo nitridation reaction during the ball milling process, the main component of the mixed powder in the system is flaky Al powder with a size of about 100–180 nm; Irregular granular C3H6N6 powder with a particle size of about 30–70 nm (see arrow in the figure). The powder is subjected to mechanical energy such as steel ball impact, shearing and extrusion, and the physical action of high-energy and high-speed plasma bombardment generated by dielectric barrier discharge. Due to the good plasticity and toughness of Al powder, it is sheared and extruded into flakes under the synergistic effect of the above comprehensive energy. As shown in Fig. 7b, The main component of the Al+C4H4N4 system is AlN when plasma-assisted ball milling for 14 h, Due to the exothermic reactions such as polycondensation, deamination and nitridation of C4H4N4 in the system, the temperature in the ball milling tank increases along with the reaction, and thermal explosion, splashing and cold welding occur in local micro-areas of the powder. Many fine primary particles with a size of about 50–80 nm (as shown by arrows in the figure) are agglomerated into larger particles with a particle size of about 550 nm. A large number of fine primary particles attached to these surfaces enhance the activity of the powder [29], and form agglomerates of a nano-scale composite structure composed of primary particles.

Figure 7: SEM image of plasma-assisted ball milling 14 h mixed powder (×50 K) (a) Al+C3H6N6; (b) Al+C4H4N4
3.5 Analysis of Heat Treatment of System
Fig. 8 shows the XRD pattern of the mixed powder milled by plasma for 8 h after annealing at 800°C in a vacuum carbon tube furnace. It can be seen from the figure that a small amount of AlN is formed in the Al+C3H6N6 system after heat treatment, and the conversion rate is about 17% through RIR semi-quantitative calculation. However, AlN was almost completely synthesized in the Al+C4H4N4 system, and the conversion rate reached 99%. It can be seen that the mixed powder activated by plasma-assisted ball milling is helpful to transform Al into AlN after proper heat treatment.
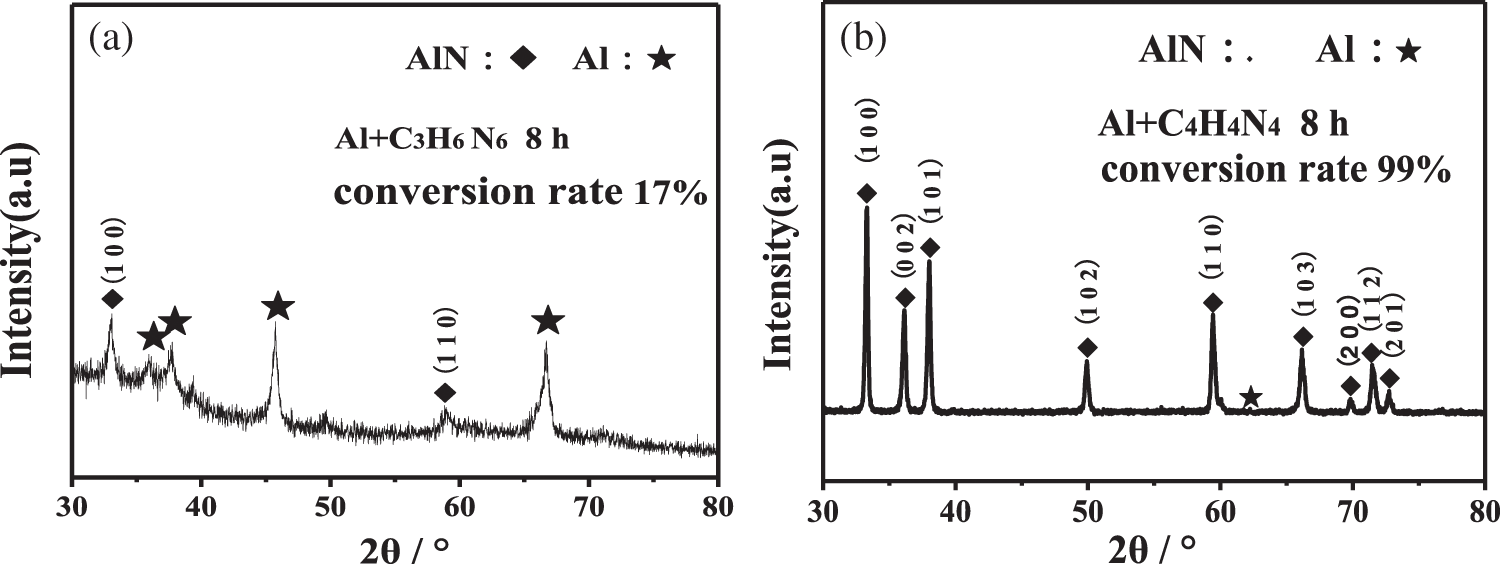
Figure 8: XRD patterns of production by Plasma assisted ball milled 8 h after annealing at 800°C (a) Al+C3H6N6; (b) Al+C4H4N4
Fig. 9 shows the microscopic morphology of the mixed powder after annealing heat treatment after plasma-assisted ball milling for 8 h. Fig. 9a shows a small amount of irregular light and dark stripes locally, which is due to the synthesis of a small amount of AlN in the heat-treated Al+C3H6N6 system, while AlN powder has large insulation resistance and “charging effect” to make the image show light and dark stripes (shown by arrows in the figure). During the heat treatment, the mixed powder agglomerates form aggregates with a size of about 1

Figure 9: SEM image of the mixed powder after annealing heat treatment (×20 K) (a) Al+C3H6N6; (b) Al+C4H4N4
3.6 Mechanism Analysis of AlN Synthesis
From the molecular structure analysis, it is because the C3H6N6 molecule has a stable and symmetrical triazine ring structure [30] (as shown in Fig. 10). Its structure is similar to a benzene ring, and the internal structure of the molecule is relatively stable, and the chemical bond is not easy to be destroyed, so it is not easy to react with Al to synthesize AlN. However, there is no triazine ring structure in the C4H4N4 molecule, but there are C≡N bonds and =NH2 bonds. Polycondensation and deamination easily occur in plasma-assisted ball milling, which makes the system full of free nitrogen-containing groups. These groups react with Al to synthesize AlN under the synergistic effect of mechanical energy and plasma. In terms of crystal structure, with the progress of plasma-assisted ball milling, the crystal defects of the powder increase, the grain size decreases, and the chemical bond breaks to produce a large number of free nitrogen-containing groups, which makes the powder in the tank in an unstable active state and promotes the nitridation reaction between Al and C4H4N4 molecules. The conversion rate of AlN reaches 92% after 14 h of ball milling. Therefore, the selection of a nitrogen source should not only consider its nitrogen content, but also comprehensively consider factors such as material cost, molecular structure, physical and chemical properties, etc.

Figure 10: Molecular structure diagram (a) C3H6N6; (b) C4H4N4
Fig. 11 shows the infrared spectra of that Al+C4H4N4 system after different times of plasma-assisted ball milling. As can be seen from Fig. 11, with the increase of plasma-assisted ball milling time, the C4H4N4 molecule first undergoes deamination, which is due to the weakest bond energy of -NH2 (amino) in the C4H4N4 molecule (about 276 kJ/mol [25]). Because the state of the C4H4N4 molecule after deamination is extremely unstable, the characteristic peak of the N-H bond (3200–3450 cm−1) gradually decreases and the shape gradually flattens with the progress of plasma-assisted ball milling. At the same time, the number of characteristic peaks of the C=C bond (1610–1690 cm−1) gradually decreases. After 8 h of ball milling, there are two types of groups: isolated vibrational C=C bond (1641 cm−1) and conjugated vibrational C=C bond (1617 cm−1). After 14 h of ball milling, only conjugated vibrational C=C bonds remain. This is due to the polycondensation reaction between C4H4N4 molecules with plasma-assisted ball milling. Different types of NH bonds and C=C bonds are condensed into one type, and hydrogen bonds (N–H bonds) are broken. The decrease in the number of hydrogen bonds leads to the gradual smoothness of the shape of the characteristic peak. With the progress of ball milling, the intensity of the characteristic peaks of the C-N bond (1240 cm−1–1370 cm−1) and the C≡N bond (2211 cm−1) became weaker and weaker, and basically disappeared after 14 h of plasma-assisted ball milling, while the characteristic peak of the Al≡N bond (723 cm−1) gradually increased, indicating that the C≡N bond and C–N bond in the C4H4N4 molecule broke during ball milling, and the reaction with Al under the combined action of plasma and mechanical force energy to synthesize AlN.
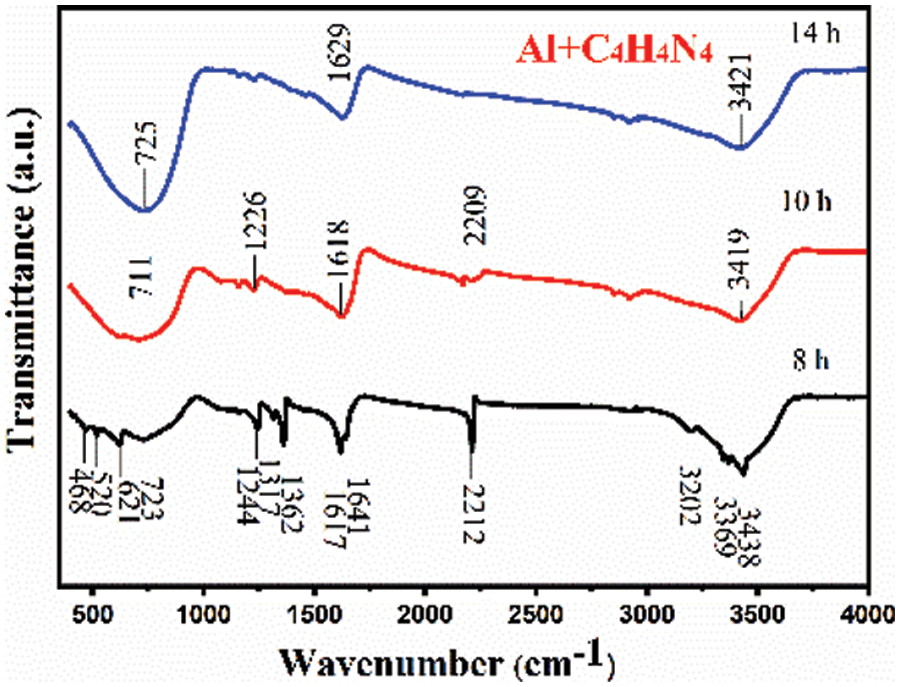
Figure 11: Infrared spectra of Al+C4H4N4 mixed powder at different times of plasma-assisted ball milling
(1) In the Al+C3H6N6 system, because the C3H6N6 molecule has a symmetrical triazine ring with a structure similar to the benzene ring, its chemical properties are stable and difficult to decompose, and its chemical bonds are difficult to break, AlN cannot be directly synthesized by plasma-assisted ball milling at room temperature. The nitridation reaction is not only related to nitrogen content, but also closely related to the molecular structure and chemical bonds of the solid nitrogen source.
(2) In the Al+C4H4N4 system, due to the existence of a large number of nitrile groups (-CN) and amino groups (-NH2) in the C4H4N4 molecular structure, C4H4N4 molecules undergo polycondensation and deamination during the plasma-assisted ball milling process, so that the ball milling tank is filled with free active nitrogen-containing groups such as N=, ≡N, etc. These nitrogen-containing groups react with plasma-activated Al powder to synthesize AlN at room temperature, and the conversion rate reaches 92% after ball milling for 14 h.
(3) Through the differential thermal analysis and annealing heat treatment of the mixed powder of the two systems milled for 8 h, it is found that only a small amount of AlN is formed in the Al+C3H6N6 system, and the conversion rate is 17%; Al+C4H4N4 system is almost completely converted to AlN, and the conversion rate is 99%. It shows that heat treatment can promote the nitridation reaction to a certain extent, but the molecular structure and chemical bond properties of the compound itself still play a decisive role in the nitridation reaction.
Funding Statement: The study was supported by the Education and Research Project for Young and Middle-Aged Teachers in Fujian Province (JAT201167).
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
References
1. Ji, P., Lu, X. F. (2022). Microstructure and thermal conductivity of nano-carbon/AlN composites. Diamond & Related Materials, 121, 108710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2021.108710 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
2. Duan, W. Y., Li, S., Wang, G., Dou, R., Wang, L. et al. (2020). Thermal conductivities and mechanical properties of AlN ceramics fabricated by three dimensional printing. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 40(10), 3535–3540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.04.004 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
3. Dai, S. T., Zhang, T., Mo, S. M., Cai, Y., Yuan, W. et al. (2019). Study on preparation, thermal conductivity, and electrical insulation properties of epoxy/AlN. IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 29(2), 1051–1057. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASC.2018.2890752 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
4. He, B. Y., Chen, X. M., Deng, P., Wang, W. J., Zhao, Z. Q. et al. (2022). Ab initio and experimental study on the mechanism of Al4C3 nitridation in vacuum to prepare AlN. Ceramics International, 48(5), 6977–6984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.11.255 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
5. Wei, Z. L., Li, K., Ge, B. Z., Guo, C. W., Xia, H. Y. et al. (2021). Synthesis of nearly spherical AlN parties by an in-situ nitriding combustion route. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 10(2), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-020-0440-3 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
6. Mao, X. X., Xu, Y. G., Mao, X. J., Zhang, H. L., Li, J. et al. (2019). Synthesis of fine AlN powders by foamed precursor-assisted carbothermal reduction-nitridation method. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 34(10), 1123–1127. [Google Scholar]
7. Chaurasia, H., Tripathi, S. K., Bilgaiyan, K., Pandey, A., Mukhopadhyay, K. et al. (2019). Preparation and properties of AlN (aluminum nitride) powder/thin films by single source precursor. New Journal of Chemistry, 43, 1900–1909. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ04594A [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
8. Lan, Y. P., Shi, Y. B., Qi, K. J., Ren, Z., Liu, H. H. (2018). Fabrication and characterization of single-phase a-axis AlN ceramic films. Ceramics International, 44(7), 8257–8262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.02.007 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
9. Wang, L. L., Ma, B. Y., Liu, C. M., Deng, C. J., Yu, J. K. et al. (2022). Research progress on sintering technology and performance optimization of AlN ceramics. Refractories, 56(2), 180–184 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
10. Huang, X. F., Tang, P., Yang, S., Fang, J. Y., Wan, Z. P. (2022). Investigation of AlN ceramic anisotropic deformation behavior during scratching. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 42(6), 2678–2690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2022.02.001 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
11. Wei, Z. L., Li, K., Ge, B. Z., Guo, C. W., Xia, H. Y. et al. (2021). Synthesis of nearly spherical AlN particles by an in-situ nitriding combustion route. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 10(2), 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40145-020-0440-3 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
12. Son, H. W., Kim, B. N., Suzuki, T. S., Suzuki, Y. (2018). Fabrication of translucent AlN ceramics with MgF2 additive by spark plasma sintering. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 101(10), 4430–4433. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.15726 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
13. Hironori, O., Yasuhiro, W., Tomohiko, S., Kohei, Y., Akira, U. et al. (2022). Impurity diffusion in ion implanted AlN layers on sapphire substrates by thermal annealing. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 61(2), 076802. [Google Scholar]
14. He, D. P., Huang, X. Y., Ren, G., Wang, Y., Yu, X. T. et al. (2022). Development on high thermal conductive and electric insulative AlN ceramics in aerospace devices. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 50(6), 1701–1714 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
15. Nie, G. L., Sheng, P. F., Li, Y. H., Bao, Y. W., Wu, S. H. et al. (2021). Preparation of a hydrolysis-resistant coating on AlN powder surface and Its effect on thermal conductivity of AlN ceramic. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 50(6), 1904–1909. [Google Scholar]
16. Ravichandran, M., Mohanavel, V., Sathish, T., Ganeshan, P., Suresh, K. S. et al. (2021). Mechanical properties of AlN and molybdenum disulfide reinforced aluminium alloy matrix composites. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2027(1), 1742–1750. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2027/1/012010 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
17. Chen, D., Chen, G. Q., Deng, M., Wang, H. M., Huang, Z. Y. et al. (2022). Fabrication and mechanical properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes doped AlN ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceramics International, 48(4), 4505–4511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.10.236 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
18. Jiang, Z. Q., Liu, Y. Z., Xue, L. Q., Liu, R. H., Liu, Y. H. et al. (2019). Research progress of aluminum nitride powder preparation technology. Semiconductor Technology, 44(8), 577–582+589 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
19. Yang, Z. L., Liao, H. F., Sun, D., Dai, L. Y., Liu, Z. J. et al. (2018). Mechanism of the effect of plasma-assisted ball milling on the synthesis of ultrafine AlN from Al+C4H4N4. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 28(8), 1587–1596 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
20. Zagorac, D., Zagorac, Z., Djukic, M. B., Jordanov, D., Matović, B. (2019). Theoretical study of AlN mechanical behavior under high pressure regime. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 103, 102289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102289 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
21. Dai, L. Y., Guo, X. P., Yan, J., Zhang, B. J., Liu, Z. J. et al. (2016). Mechanism for the effect on synthesis of AlN from Al2O3+C activated by plasma assisted ball milling during solid-state reaction. Functional Materials, 47(3), 3109–3114 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
22. Xu, Y. L., Zhou, Z. Q., Chen, X. M., Han, C. C., Yang, B. et al. (2021). Ultrafine AlN synthesis by alumina carbothermal reduction under vacuum: Mechanism and experimental study. Powder Technology, 377, 843–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.09.066 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
23. Fu, L., Qiao, L., Zheng, J. W., Ying, Y., Li, W. C. et al. (2018). Phase, microstructure and sintering of aluminum nitride powder by the carbothermal reduction-nitridation process with Y2O3 addition. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 38(4), 1170–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.10.029 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
24. Li, C. C., Cui, C. X., Wang, X., Zhao, L. C., Liu, S. Q. et al. (2019). Enhanced grain refinement of in-situ AlN-TiN/Al composite inoculant on aluminum assisted by ultrasonic treatment. Materials Letters, 255(8), 259–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126592 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
25. Liu, Z. J., Wang, W. C., Yang, D. Z., Wang, S., Dai, L. Y. et al. (2016). In situ synthesis of AlN nanoparticles by solid state reaction from plasma assisted ball milling Al and diaminomaleonitrile mixture. Ceramics International, 42(2), 3411–3417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.10.136 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
26. Simons, W. W. (1978). The sadtler handbook of infrared spectra. Sadtler Research Laboratories. [Google Scholar]
27. Sirotinkin, V. P., Shamray, V. F., Samokhin, A. V., Sinaiskiy, M. A. (2017). Use of double voigt method in X-RAY diffraction study of the microstructure of the titanium carbide nanopowders produced by plasma-chemical synthesis. Industrial Laboratory-Diagnostics of Materials, 83(12), 34–37. https://doi.org/10.26896/1028-6861-2017-83-12-34-37 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
28. Xue, R. R., Song, Z. G., Zheng, W. J., Du, Z. Z., Ren, J. B. (2013). Effect of nitrogen on grain size and mechanical properties of 316l. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 25(10), 36–42 (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
29. Liu, Z. J. (2016). Characteristics of large area discharge plasma and mechanism study of AlN nano powders prepared by it assisting high energy ball milling. Dalian University of Technology, China (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
30. Rounaghi, S. A., Eshghi, H., Kiani, A. R., Khaki, J. V., Khoshkhoo, M. S. et al. (2013). Synthesis of nanostructured AlN by solid state reaction of Al and diaminomaleonitrile. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 198, 542–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2012.11.018 [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools