 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Hydrolysable Chestnut Tannin Extract Chemical Complexity in Its Reactions for Non-Isocyanate Polyurethanes (NIPU) Foams
1 LERMAB, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Lorraine, Vandoeuvre les Nancy, 54506, France
2 LERMAB, University of Lorraine, Epinal, 88051, France
* Corresponding Authors: Antonio Pizzi. Email: ; Christine Gerardin-Charbonnier. Email:
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(6), 2823-2848. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.027651
Received 08 November 2022; Accepted 15 November 2022; Issue published 27 April 2023
Abstract
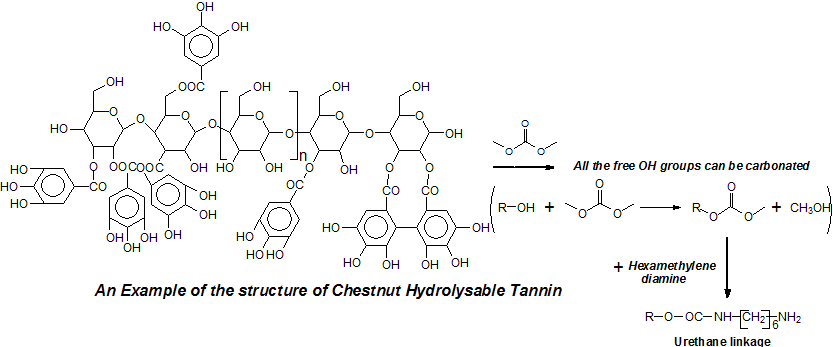
Non-isocyanate polyurethane (NIPU) foams from a commercial hydrolysable tannin extract, chestnut wood tannin extract, have been prepared to determine what chemical species and products are taking part in the reactions involved. This method is based on two main steps: the reaction with dimethyl carbonate and the formation of urethane bonds by further reaction of the carbonated tannin with a diamine-like hexamethylene diamine. The hydroxyl groups on the tannin polyphenols and on the carbohydrates intimately linked with it and part of a hydrolysable tannin are the groups involved in these reactions. The carbohydrate skeleton of the hydrolysable tannin is also able to participate through its hydroxyl groups to the same two reactions rendering the whole molecular complex able to react to form NIPUs. The analysis by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (13C NMR) to further investigate the reaction mechanisms involved revealed the unsuspected complexity of chestnut hydrolysable tannin, with different fragments reacting in different manners forming a hardened network of considerable complexity. As the morphology and performance of these types of foams changes slightly with the change in the amount of glutaraldehyde and hexamine hardeners, the best performing foam formulation previously determined was scanned by SEM and analysed chemically for the structures formed.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools