 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Preparation and Performance of Pueraria lobata Root Powder/Polylactic Acid Composite Films
1
Key Laboratory of Hunan Forest Products and Chemical Industry Engineering, Jishou University, Zhangjiajie, 427000, China
2
Central South Inventory and Planning Institute of National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Changsha, 410000, China
3
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Jishou University, Zhangjiajie, 427000, China
4
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Jishou University, Jishou, 416000, China
* Corresponding Author: Xianwu Zhou. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Polylactide Based Biopolymeric Systems)
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(6), 2531-2553. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.026066
Received 13 August 2022; Accepted 26 October 2022; Issue published 27 April 2023
Abstract
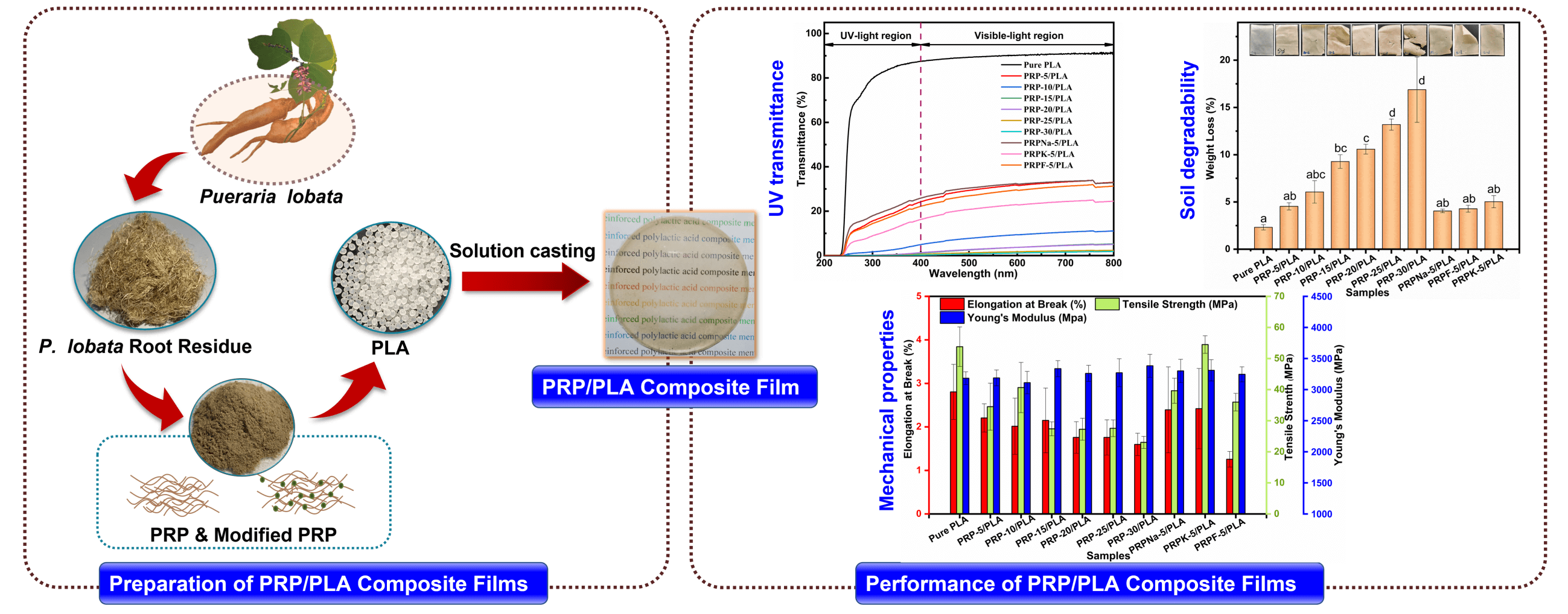
Petroleum-based materials, such as plastic, are characterized by adverse environmental pollution; as a result, researchers have sought alternative degradable plastics that are environmentally friendly, such as polylactic acid (PLA). PLA has shown great potential to replace petroleum-based plastics. In this study, seven different samples of unmodified Pueraria lobata root powder (PRP) with different contents (i.e., 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 wt%) and three different modified PRPs (i.e., treated with NaOH, NaOH-KH-550, and Formic) were used to reinforce polylactic acid (PLA) via solution casting process. These prepared PRP/PLA composite films were characterized using SEM, FTIR, UV-visible spectra analysis, TG, DSC, weight loss measurement (wt%), and mechanical measurements. The results showed that the PRP modified with KH-550 (PRPK) intensified the interaction in the interface region between the PRP and the PLA matrix, thus increasing the tensile strength (54.5 MPa), elongation at break (2.8%), and Young’s modulus (3310 MPa) of the PRPK/PLA biofilms. Contact angle measurement showed that the PRP treatments contributed to the hydrophobicity of films. The transparency of PRP-10/PLA film at λ800 was 11.09%, and its UVA and UVB transmittance were 3.28 and 1.16, respectively. After blending PLA with PRP, the PRP/PLA composite films exhibited excellent biodegradability. In summary, PRPK improved the mechanical properties of PLA and prevented the films from ultraviolet light, suggesting that PRPK-5/PLA film could be used as packaging materials.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools