 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
The Study on Bamboo Microfibers Isolated by Steam Explosion and Their Comprehensive Properties
1
Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory of Wood Adhesives and Glued Products, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, 650224,
China
2
International Joint Research Center for Biomass Materials, Ministry of Science and Technology, Southwest Forestry University,
Kunming, 650224, China
3
Key Laboratory for Forestry Resources Conversion and Utilization in the Southwest Mountains of China, Ministry of Education,
Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, 650224, China
4
Center for Renewable Carbon, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996, USA
* Corresponding Authors: Kaimeng Xu. Email: ; Lianpeng Zhang. Email:
# Qiushi Li and Ronggang Luo contributed equally to this work
Journal of Renewable Materials 2023, 11(6), 2809-2822. https://doi.org/10.32604/jrm.2023.026184
Received 22 August 2022; Accepted 11 October 2022; Issue published 27 April 2023
Abstract
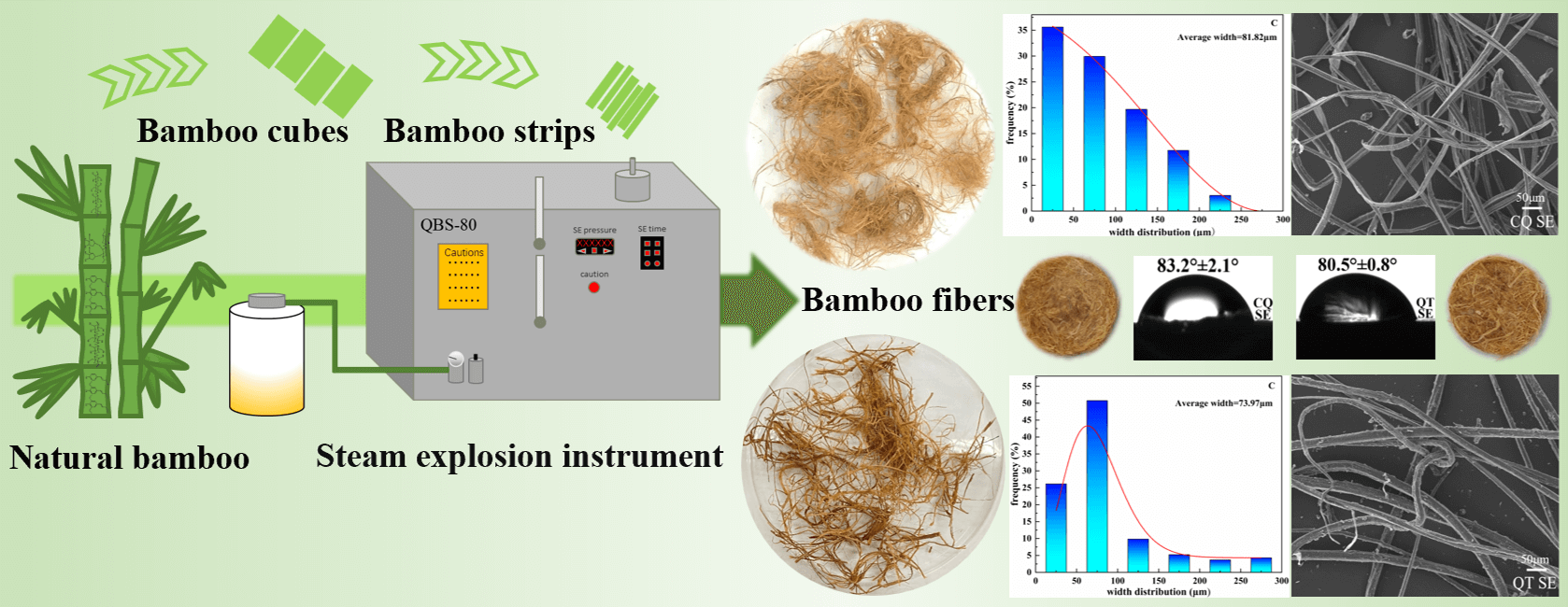
To overcome the shortage of wood resources as well as to develop novel natural fibers materials, the Chimonobambusa quadrangularis (CQ) and Qiongzhuea tumidinoda (QT) planted in Southwest China were effectively isolated by the steam explosion (SE). The fine and uniform bamboo microfibers derived from CQ and QT were obtained, and their smallest average widths were 12.62 μm and 16.05 μm, respectively. The effects of steam explosion on the micro-morphology, chemical composition, thermal stability, crystallinity, surface wettability, and mechanical properties of bamboo microfibers were comprehensively investigated. The results showed that the relative content of cellulose in bamboo microfibers increased but the hemicellulose and lignin contents decreased after SE. The degrees of crystallinity for CQ and QT increased from 40.49% and 39.46% to 68.90% and 55.78%, respectively. The thermal stability and surface hydrophilicity were also improved. The CQ microfibers had a maximum decomposition temperature of 2.79°C, a tensile strength of 58.54 MPa, an elongation at break of 0.6%, and a water contact angle of 2.7° higher than those of the QT microfibers.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools